Abstract
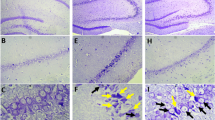
Exercise has been regarded as an effective rehabilitation strategy to facilitate motor and cognitive functional recovery after stroke, even though the complex effects associated with exercise-induced repair of cerebral ischemic injury are not fully elucidated. The enhancement of angiogenesis and neurogenesis, and the improvement of synaptic plasticity following moderate exercise are conducive to functional recovery after ischemic damage. Our previous studies have confirmed the angiogenesis and neurogenesis through the caveolin-1/VEGF pathway in MCAO rats. As an essential neurotrophic factor, BDNF has multiple effects on ischemic injury. In this study, we attempted to determine an additional mechanism of treadmill exercise-mediated motor and cognitive functional recovery through the caveolin-1/VEGF pathway associated with BDNF in the ischemic penumbra of MCAO mice. We found that mice exposed to treadmill exercise after the MCAO operation showed a significant up-regulation in expression of caveolin-1, VEGF, BDNF, synapsin I and CYFIP1 proteins, numbers of cells positive for BrdU/CD34, BDNF, BrdU/NeuN, BrdU/Synapsin I and CYFIP1 expression were increased, which support the reduction in neurological deficit and infarction volume, as well as improved synaptic morphology and spatial learning abilities, compared with the non-exercise mice. However, the caveolin-1 inhibitor, daidzein, resulted in increase in neurological deficit and infarction volume. The selective VEGFR2 inhibitor, PD173074, significantly induced larger infarction volume and neurological injury, and decreased the expression of BDNF in the ischemic penumbra. These findings indicate that exercise improves angiogenesis, neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity to ameliorate motor and cognitive impairment after stroke partially through the caveolin-1/VEGF pathway, which is associated with the coregulator factor, BDNF.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Krishnamurthi R, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA (2010) Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 383(9913):245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61953-4
Pendlebury ST, Rothwell PM (2009) Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 8:1006–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(09)70236-4
Lee M, Saver JL, Hong KS, Wu YL, Liu HC, Rao NM, Ovbiagele B (2014) Cognitive impairment and risk of future stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ 186:E536–E546. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.140147
Bazan NG, Marcheselli VL, Cole-Edwards K (2005) Brain response to injury and neurodegeneration: endogenous neuroprotective signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1053:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1344.011
Damodaran T, Hassan Z, Navaratnam V, Muzaimi M, Ng G, Muller CP, Liao P, Dringenberg HC (2014) Time course of motor and cognitive functions after chronic cerebral ischemia in rats. Behav Brain Res 275:252–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.09.014
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C (2010) The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 67:181–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.07.002
Gao Y, Zhao Y, Pan J, Yang L, Huang T, Feng X, Li C, Liang S, Zhou D, Liu C, Tu F, Tao C, Chen X (2014) Treadmill exercise promotes angiogenesis in the ischemic penumbra of rat brains through caveolin-1/VEGF signaling pathways. Brain Res 1585:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.08.032
Zhao Y, Pang Q, Liu M, Pan J, Xiang B, Huang T, Tu F, Liu C, Chen X (2017) Treadmill exercise promotes neurogenesis in ischemic rat brains via caveolin-1/VEGF signaling pathways. Neurochem Res 42:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2081-z
Pang Q, Zhang H, Chen Z, Wu Y, Bai M, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Tu F, Liu C, Chen X (2017) Role of caveolin-1/vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in basic fibroblast growth factor-induced angiogenesis and neurogenesis after treadmill training following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1663:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.03.012
Meis S, Endres T, Munsch T, Lessmann V (2017) The relation between long-term synaptic plasticity at glutamatergic synapses in the amygdala and fear learning in adult heterozygous BDNF-knockout mice. Cereb Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhx032
Usui T, Naruo A, Okada M, Hayabe Y, Yamawaki H (2014) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes angiogenic tube formation through generation of oxidative stress in human vascular endothelial cells. Acta Physiol 211:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12249
Park H, Poo MM (2013) Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:7–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3379
Leal G, Afonso PM, Salazar IL, Duarte CB (2015) Regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity by BDNF. Brain Res 1621:82–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.019
An JJ, Gharami K, Liao GY, Woo NH, Lau AG, Vanevski F, Torre ER, Jones KR, Feng Y, Lu B, Xu B (2008) Distinct role of long 3′ UTR BDNF mRNA in spine morphology and synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Cell 134:175–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.045
Roslavtceva VV, Salmina AB, Prokopenko SV, Pozhilenkova EA, Kobanenko IV, Rezvitskaya GG (2016) The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the regulation of development and functioning of the brain: new target molecules for pharmacotherapy. Biomed Khim 62:124–133. https://doi.org/10.18097/pbmc20166202124
Mackenzie F, Ruhrberg C (2012) Diverse roles for VEGF-A in the nervous system. Development 139:1371–1380. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.072348
Zechariah A, ElAli A, Doeppner TR, Jin F, Hasan MR, Helfrich I, Mies G, Hermann DM (2013) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes pericyte coverage of brain capillaries, improves cerebral blood flow during subsequent focal cerebral ischemia, and preserves the metabolic penumbra. Stroke 44:1690–1697. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000240
Yang J, Yao Y, Chen T, Zhang T (2014) VEGF ameliorates cognitive impairment in in vivo and in vitro ischemia via improving neuronal viability and function. Neuromol Med 16:376–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8284-4
Nakahashi T, Fujimura H, Altar CA, Li J, Kambayashi J, Tandon NN, Sun B (2000) Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett 470:113–117
Grasman JM, Kaplan DL (2017) Human endothelial cells secrete neurotropic factors to direct axonal growth of peripheral nerves. Sci Rep 7:4092. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04460-8
Deng G, Qiu Z, Li D, Fang Y, Zhang S (2017) Delayed administration of guanosine improves longterm functional recovery and enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis in a mouse model of photothrombotic stroke. Mol Med Rep 15:3999–4004. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6521
Zhou L, Lin Q, Wang P, Yao L, Leong K, Tan Z, Huang Z (2017) Enhanced neuroprotective efficacy of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells co-overexpressing BDNF and VEGF in a rat model of cardiac arrest-induced global cerebral ischemia. Cell Death Dis 8:e2774. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.184
Chen J, Zhang C, Jiang H, Li Y, Zhang L, Robin A, Katakowski M, Lu M, Chopp M (2005) Atorvastatin induction of VEGF and BDNF promotes brain plasticity after stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:281–290. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600034
Louissaint A Jr, Rao S, Leventhal C, Goldman SA (2002) Coordinated interaction of neurogenesis and angiogenesis in the adult songbird brain. Neuron 34:945–960
Xu L, Guo R, Xie Y, Ma M, Ye R, Liu X (2015) Caveolae: molecular insights and therapeutic targets for stroke. Expert Opin Ther Targets 19:633–650. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2015.1009446
Chidlow JH Jr, Sessa WC (2010) Caveolae, caveolins, and cavins: complex control of cellular signalling and inflammation. Cardiovasc Res 86:219–225. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvq075
Liu Y, Liang Z, Liu J, Zou W, Li X, Wang Y, An L (2013) Downregulation of caveolin-1 contributes to the synaptic plasticity deficit in the hippocampus of aged rats. Neural Regen Res 8:2725–2733. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.29.004
Gaudreault SB, Blain JF, Gratton JP, Poirier J (2005) A role for caveolin-1 in post-injury reactive neuronal plasticity. J Neurochem 92:831–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02917.x
Gioiosa L, Raggi C, Ricceri L, Jasmin JF, Frank PG, Capozza F, Lisanti MP, Alleva E, Sargiacomo M, Laviola G (2008) Altered emotionality, spatial memory and cholinergic function in caveolin-1 knock-out mice. Behav Brain Res 188:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2007.11.002
Enomoto S, Shimizu K, Nibuya M, Toda H, Yoshino A, Suzuki E, Kondo T, Fukuda H (2016) Increased expression of endocytosis-related proteins in rat hippocampus following 10-day electroconvulsive seizure treatment. Neurosci Lett 624:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.05.015
Head BP, Hu Y, Finley JC, Saldana MD, Bonds JA, Miyanohara A, Niesman IR, Ali SS, Murray F, Insel PA, Roth DM, Patel HH, Patel PM (2011) Neuron-targeted caveolin-1 protein enhances signaling and promotes arborization of primary neurons. J Biol Chem 286:33310–33321. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.255976
Hibbert AP, Kramer BM, Miller FD, Kaplan DR (2006) The localization, trafficking and retrograde transport of BDNF bound to p75NTR in sympathetic neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 32:387–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2006.06.001
Takamatsu Y, Ishida A, Hamakawa M, Tamakoshi K, Jung CG, Ishida K (2010) Treadmill running improves motor function and alters dendritic morphology in the striatum after collagenase-induced intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Brain Res 1355:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.07.070
Wang X, Zhang M, Feng R, Li WB, Ren SQ, Zhang J, Zhang F (2014) Physical exercise training and neurovascular unit in ischemic stroke. Neuroscience 271:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.04.030
MacManus JP, Koch CJ, Jian M, Walker T, Zurakowski B (1999) Decreased brain infarct following focal ischemia in mice lacking the transcription factor E2F1. Neuroreport 10:2711–2714
Ago T (2016) The neurovascular unit in health and ischemic stroke. Nihon Rinsho 74:583–588
Cai W, Zhang K, Li P, Zhu L, Xu J, Yang B, Hu X, Lu Z, Chen J (2017) Dysfunction of the neurovascular unit in ischemic stroke and neurodegenerative diseases: an aging effect. Ageing Res Rev 34:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.09.006
Zhao Y, Xu P, Hu S, Du L, Xu Z, Zhang H, Cui W, Mak S, Xu D, Shen J, Han Y, Liu Y, Xue M (2015) Tanshinone II A, a multiple target neuroprotectant, promotes caveolae-dependent neuronal differentiation. Eur J Pharmacol 765:437–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.09.006
Prakash YS, Thompson MA, Vaa B, Matabdin I, Peterson TE, He T, Pabelick CM (2007) Caveolins and intracellular calcium regulation in human airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293:L1118–L1126. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00136.2007
Vohra PK, Thompson MA, Sathish V, Kiel A, Jerde C, Pabelick CM, Singh BB, Prakash YS (2013) TRPC3 regulates release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor from human airway smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:2953–2960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.07.019
Alomari MA, Khabour OF, Alzoubi KH, Alzubi MA (2013) Forced and voluntary exercises equally improve spatial learning and memory and hippocampal BDNF levels. Behav Brain Res 247:34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.03.007
Ploughman M, Attwood Z, White N, Dore JJ, Corbett D (2007) Endurance exercise facilitates relearning of forelimb motor skill after focal ischemia. Eur J Neurosci 25:3453–3460. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05591.x
Zong X, Wu S, Li F, Lv L, Han D, Zhao N, Yan X, Hu S, Xu T (2017) Transplantation of VEGF-mediated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes functional improvement in a rat acute cerebral infarction model. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.08.006
Kermani P, Hempstead B (2007) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a newly described mediator of angiogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc Med 17:140–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2007.03.002
Myriam C, Sandrine C, Fanny M, Marilyn G, Karen A, Amandine Z, Pascale D (2013) Netrin 1 contributes to vascular remodeling in the subventricular zone and promotes progenitor emigration after demyelination. Development 140: 3107–3117. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.092999
Scharfman H, Goodman J, Macleod A, Phani S, Antonelli C, Croll S (2005) Increased neurogenesis and the ectopic granule cells after intrahippocampal BDNF infusion in adult rats. Exp Neurol 192:348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.11.016
Benraiss A, Chmielnicki E, Lerner K, Roh D, Goldman SA (2001) Adenoviral brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces both neostriatal and olfactory neuronal recruitment from endogenous progenitor cells in the adult forebrain. J Neurosci 21:6718–6731
Jones KR, Farinas I, Backus C, Reichardt LF (1994) Targeted disruption of the BDNF gene perturbs brain and sensory neuron development but not motor neuron development. Cell 76:989–999
Hori N, Carpenter DO (1994) Functional and morphological changes induced by transient in vivo ischemia. Exp Neurol 129:279–289. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1994.1170
Choi JH, Kim TS, Park JK, Sim YJ, Kim K, Lee SJ (2013) Short-term treadmill exercise preserves sensory-motor function through inhibiting apoptosis in the hippocampus of hypoxic ischemia injury rat pups. J Exerc Rehabil 9:457–462. https://doi.org/10.12965/jer.130055
Yeh T, Wu C, Hsieh Y et al (2017) Synergistic effects of aerobic exercise and cognitive training on cognition, physiological markers, daily function, and quality of life in stroke survivors with cognitive decline: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 18(1):405. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-017-2153-7
Bogen IL, Haug KH, Roberg B, Fonnum F, Walaas SI (2009) The importance of synapsin I and II for neurotransmitter levels and vesicular storage in cholinergic, glutamatergic and GABAergic nerve terminals. Neurochem Int 55:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2009.02.006
Marte A, Messa M, Benfenati F, Onofri F (2017) Synapsins are downstream players of the BDNF-mediated axonal growth. Mol Neurobiol 54:484–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9659-3
Pathania M, Davenport EC, Muir J, Sheehan DF, López-Doménech G, Kittler JT (2014) The autism and schizophrenia associated gene CYFIP1 is critical for the maintenance of dendritic complexity and the stabilization of mature spines. Transl Psychiatry 4:e374. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2014.16
Panja D, Bramham CR (2014) BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: a synthesis and breakdown. Neuropharmacology 76 Pt C:664–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.024
Genheden M, Kenney JW, Johnston HE, Manousopoulou A, Garbis SD, Proud CG (2015) BDNF stimulation of protein synthesis in cortical neurons requires the MAP kinase-interacting kinase MNK1. J Neurosci 35:972–984. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2641-14.2015
Namekata K, Harada C, Taya C, Guo X, Kimura H, Parada LF, Harada T (2010) Dock3 induces axonal outgrowth by stimulating membrane recruitment of the WAVE complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:7586–7591. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914514107
Xu C, Fu X, Zhu S, Liu JJ (2016) Retrolinkin recruits the WAVE1 protein complex to facilitate BDNF-induced TrkB endocytosis and dendrite outgrowth. Mol Biol Cell 27:3342–3356. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E16-05-0326
Nishijima T, Torres-Aleman I, Soya H (2016) Exercise and cerebrovascular plasticity. Prog Brain Res 225:243–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pbr.2016.03.010
Leal G, Comprido D, Duarte CB (2014) BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology 76 Pt C: 639–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.005
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. Y12H170002) and Wenzhou Muni cipal Science and Technology Bureau (No. Y20170070). Moreover, we would like to express immense gratitude to the technical assistance of the Laboratory Animal Centre of Wenzhou Medical University and the Laboratory Centre of the Second Affiliated Hospital & Yuying Children’s Hospital of Wenzhou.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
We declare that all authors have no financial or other conflict of interests in connection with the submitted article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Hu, Q., Xie, Q. et al. Effects of Treadmill Exercise on Motor and Cognitive Function Recovery of MCAO Mice Through the Caveolin-1/VEGF Signaling Pathway in Ischemic Penumbra. Neurochem Res 44, 930–946 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02728-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02728-1