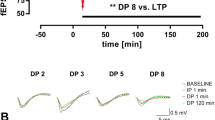
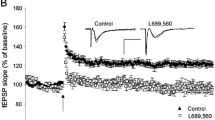
Abstract
Aging, as the major risk factor of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), may increase susceptibility to neurodegenerative diseases through many gradual molecular and biochemical changes. Extracellular glutamate homeostasis and extrasynaptic glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) are among early synaptic targets of oligomeric amyloid β (Aβo), one of the AD related synaptotoxic protein species. In this study, we asked for the effects of Aβo on long-term depression (LTD), a form of synaptic plasticity dependent on extrasynaptic NMDAR activation, and on a tonic current (TC) resulting from the activation of extrasynaptic NMDAR by ambient glutamate in hippocampal slices from young (3–6-month-old) and aged (24–28-month-old) Sprague–Dawley rats. Aβo significantly enhanced the magnitude of LTD and the amplitude of TC in aged slices compared to young ones. TBOA, a glutamate transporter inhibitor, also significantly increased LTD magnitude and TC amplitude in slices from aged rats, suggesting either an age-related weakness of the glutamate clearance system and/or a facilitated extrasynaptic NMDAR activation. From our present data, we hypothesize that senescence-related impairment of the extrasynaptic environment may be a vector of vulnerability of the aged hippocampus to neurodegenerative promotors such as Aβo.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes CA (1979) Memory deficits associated with senescence: a neurophysiological and behavioral study in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol 93:74–104
Barnes CA, McNaughton BL (1985) An age comparison of the rates of acquisition and forgetting of spatial information in relation to long-term enhancement of hippocampal synapses. Behav Neurosci 99:1040–1048
Burke SN, Barnes CA (2006) Neural plasticity in the ageing brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:30–40
Rosenzweig ES, Barnes CA (2003) Impact of aging on hippocampal function: plasticity, network dynamics, and cognition. Prog Neurobiol 69:143–179
Collingridge GL, Peineau S, Howland JG, Wang YT (2010) Long-term depression in the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:459–473
Foster TC (2012) Dissecting the age-related decline on spatial learning and memory tasks in rodent models: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and voltage-dependent Ca2 + channels in senescent synaptic plasticity. Prog Neurobiol 96:283–303
Billard JM, Rouaud E (2007) Deficit of NMDA receptor activation in CA1 hippocampal area of aged rats is rescued by D-cycloserine. Eur J Neurosci 25:2260–2268
Kollen M, Stephan A, Faivre-Bauman A, Loudes C, Sinet PM, Alliot J, Billard JM, Epelbaum J, Dutar P, Jouvenceau A (2010) Preserved memory capacities in aged Lou/C/Jall rats. Neurobiol Aging 31:129–142
Lee HK, Min SS, Gallagher M, Kirkwood A (2005) NMDA receptor-independent long-term depression correlates with successful aging in rats. Nat Neurosci 8:1657–1659
Massey PV, Johnson BE, Moult PR, Auberson YP, Brown MW, Molnar E, Collingridge GL, Bashir ZI (2004) Differential roles of NR2A and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in cortical long-term potentiation and long-term depression. J Neurosci 24:7821–7828
Liu DD, Yang Q, Li ST (2013) Activation of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors induces LTD in rat hippocampal CA1 neurons. Brain Res Bull 93:10–16
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Tzingounis AV, Wadiche JI (2007) Glutamate transporters: confining runaway excitation by shaping synaptic transmission. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:935–947
Cotrina ML, Nedergaard M (2002) Astrocytes in the aging brain. J Neurosci Res 67:1–10
Jiang T, Cadenas E (2014) Astrocytic metabolic and inflammatory changes as a function of age. Aging Cell 13:1059–1067
Najlerahim A, Francis PT, Bowen DM (1990) Age-related alteration in excitatory amino acid neurotransmission in rat brain. Neurobiol Aging 11:155–158
Saransaari P, Oja SS (1995) Age-related changes in the uptake and release of glutamate and aspartate in the mouse brain. Mech Ageing Dev 81:61–71
Vatassery GT, Lai JC, Smith WE, Quach HT (1998) Aging is associated with a decrease in synaptosomal glutamate uptake and an increase in the susceptibility of synaptosomal vitamin E to oxidative stress. Neurochem Res 23:121–125
Wheeler DD, Ondo JG (1986) Time course of the aging of the high affinity L-glutamate transporter in rat cortical synaptosomes. Exp Gerontol 21:159–168
Nickell J, Salvatore MF, Pomerleau F, Apparsundaram S, Gerhardt GA (2007) Reduced plasma membrane surface expression of GLAST mediates decreased glutamate regulation in the aged striatum. Neurobiol Aging 28:1737–1748
Potier B, Billard JM, Riviere S, Sinet PM, Denis I, Champeil-Potokar G, Grintal B, Jouvenceau A, Kollen M, Dutar P (2010) Reduction in glutamate uptake is associated with extrasynaptic NMDA and metabotropic glutamate receptor activation at the hippocampal CA1 synapse of aged rats. Aging Cell 9:722–735
Latour A, Grintal B, Champeil-Potokar G, Hennebelle M, Lavialle M, Dutar P, Potier B, Billard JM, Vancassel S, Denis I (2013) Omega-3 fatty acids deficiency aggravates glutamatergic synapse and astroglial aging in the rat hippocampal CA1. Aging Cell 12:76–84
Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N, DeTeresa R, Hill R, Hansen LA, Katzman R (1991) Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 30:572–580
McLean CA, Cherny RA, Fraser FW, Fuller SJ, Smith MJ, Beyreuther K, Bush AI, Masters CL (1999) Soluble pool of Abeta amyloid as a determinant of severity of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 46:860–866
Selkoe DJ (2002) Deciphering the genesis and fate of amyloid beta-protein yields novel therapies for Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest 110:1375–1381
Hsia AY, Masliah E, McConlogue L, Yu GQ, Tatsuno G, Hu K, Kholodenko D, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA, Mucke L (1999) Plaque-independent disruption of neural circuits in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:3228–3233
Mucke L, Masliah E, Yu GQ, Mallory M, Rockenstein EM, Tatsuno G, Hu K, Kholodenko D, Johnson-Wood K, McConlogue L (2000) High-level neuronal expression of abeta 1–42 in wild-type human amyloid protein precursor transgenic mice: synaptotoxicity without plaque formation. J Neurosci 20:4050–4058
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Brett FM, Farrell MA, Rowan MJ, Lemere CA, Regan CM, Walsh DM, Sabatini BL, Selkoe DJ (2008) Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer’s brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med 14:837–842
Kim JH, Anwyl R, Suh YH, Djamgoz MB, Rowan MJ (2001) Use-dependent effects of amyloidogenic fragments of (beta)-amyloid precursor protein on synaptic plasticity in rat hippocampus in vivo. J Neurosci 21:1327–1333
Li S, Hong S, Shepardson NE, Walsh DM, Shankar GM, Selkoe D (2009) Soluble oligomers of amyloid beta protein facilitate hippocampal long-term depression by disrupting neuronal glutamate uptake. Neuron 62:788–801
Huang S, Tong H, Lei M, Zhou M, Guo W, Li G, Tang X, Li Z, Mo M, Zhang X, Chen X, Cen L, Wei L, Xiao Y, Li K, Huang Q, Yang X, Liu W, Zhang L, Qu S, Li S, Xu P (2018) Astrocytic glutamatergic transporters are involved in Aβ-induced synaptic dysfunction. Brain Res 1678:129–137
Kervern M, Angeli A, Nicole O, Leveille F, Parent B, Villette V, Buisson A, Dutar P (2012) Selective impairment of some forms of synaptic plasticity by oligomeric amyloid-beta peptide in the mouse hippocampus: implication of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors. J Alzheimers Dis 32:183–196
Minogue AM, Lynch AM, Loane DJ, Herron CE, Lynch MA (2007) Modulation of amyloid-beta-induced and age-associated changes in rat hippocampus by eicosapentaenoic acid. J Neurochem 103:914–926
Le Meur K, Galante M, Angulo MC, Audinat E (2007) Tonic activation of NMDA receptors by ambient glutamate of non-synaptic origin in the rat hippocampus. J Physiol 580:373–383
Audrain M, Fol R, Dutar P, Potier B, Billard JM, Flament J, Alves S, Burlot MA, Dufayet-Chaffaud G, Bemelmans AP, Valette J, Hantraye P, Deglon N, Cartier N, Braudeau J (2016) Alzheimer’s disease-like APP processing in wild-type mice identifies synaptic defects as initial steps of disease progression. Mol Neurodegener 11:016–0070
Anderson WW, Collingridge GL (2007) Capabilities of the WinLTP data acquisition program extending beyond basic LTP experimental functions. J Neurosci Methods 162:346–356
Klein WL (2002) Aβ toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease: globular oligomers (ADDLs) as new vaccine and drug targets. Neurochem Int 41:345–352
Puzzo D, Privitera L, Palmeri A (2012) Hormetic effect of amyloid-beta peptide in synaptic plasticity and memory. Neurobiol Aging 33:1484.e1415-1484.e1424
Spires-Jones TL, Hyman BT (2014) The intersection of amyloid beta and tau at synapses in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 82:756–771
Takamura Y, Ono K, Matsumoto J, Yamada M, Nishijo H (2014) Effects of the neurotrophic agent T-817MA on oligomeric amyloid-beta-induced deficits in long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 subfield. Neurobiol Aging 35:532–536
Hsieh H, Boehm J, Sato C, Iwatsubo T, Tomita T, Sisodia S, Malinow R (2006) AMPAR removal underlies Abeta-induced synaptic depression and dendritic spine loss. Neuron 52:831–843
Talantova M, Sanz-Blasco S, Zhang X, Xia P, Akhtar MW, Okamoto S, Dziewczapolski G, Nakamura T, Cao G, Pratt AE, Kang YJ, Tu S, Molokanova E, McKercher SR, Hires SA, Sason H, Stouffer DG, Buczynski MW, Solomon JP, Michael S, Powers ET, Kelly JW, Roberts A, Tong G, Fang-Newmeyer T, Parker J, Holland EA, Zhang D, Nakanishi N, Chen HS, Wolosker H, Wang Y, Parsons LH, Ambasudhan R, Masliah E, Heinemann SF, Pina-Crespo JC, Lipton SA (2013) Abeta induces astrocytic glutamate release, extrasynaptic NMDA receptor activation, and synaptic loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:17
Villette V, Dutar P (2017) GABAergic microcircuits in Alzheimer’s disease models. Curr Alzheimer Res 14:30–39
Zhao LN, Long H, Mu Y, Chew LY (2012) the toxicity of amyloid β oligomers. Int J Mol Sci 13:7303–7327
Ondrejcak T, Klyubin I, Hu N-W, Barry AE, Cullen WK, Rowan MJ (2010) Alzheimer’s disease amyloid β-protein and synaptic function. NeuroMol Med 12:13–26
Povysheva NV, Johnson JW (2012) tonic NMDA receptor-mediated current in prefrontal cortical pyramidal cells and fast-spiking interneurons. J Neurophysiol 107:2232–2243
Rozovsky I, Finch CE, Morgan TE (1998) Age-related activation of microglia and astrocytes: in vitro studies show persistent phenotypes of aging, increased proliferation, and resistance to down-regulation. Neurobiol Aging 19:97–103
Schipper HM (1996) Astrocytes, brain aging, and neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Aging 17:467–480
Sykova E, Mazel T, Hasenohrl RU, Harvey AR, Simonova Z, Mulders WH, Huston JP (2002) Learning deficits in aged rats related to decrease in extracellular volume and loss of diffusion anisotropy in hippocampus. Hippocampus 12:269–279
Sykova E, Vorisek I, Mazel T, Antonova T, Schachner M (2005) Reduced extracellular space in the brain of tenascin-R- and HNK-1-sulphotransferase deficient mice. Eur J Neurosci 22:1873–1880
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by INSERM. The authors are grateful to the animal caretakers of the CPN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Special issue: In honor of Graham Collingridge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutar, P., Potier, B. Susceptibility to Aβo and TBOA of LTD and Extrasynaptic NMDAR-Dependent Tonic Current in the Aged Rat Hippocampus. Neurochem Res 44, 692–702 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2677-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2677-6