Abstract
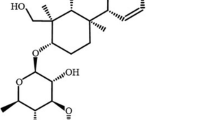
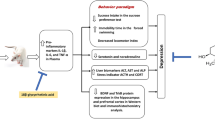
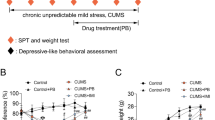
Chronic mild unpredictable stress (CUMS) causes neurogenesis damage in the hippocampus and depressive-like behaviors such as cognitive impairment. Radix Scutellariae from the dry root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, with the common name Baikal skullcap. In this study, we demonstrated that Radix Scutellariae (RS 500, 1000 mg/kg) notably improved the behavior of the rat, such as shortened escape latency in morris maze test, reduced immobility time in tail suspension test and in forced swimming test, as well as increased sucrose consumption in sucrose preference test. In addition, RS alleviated the damage CUMS-induced neurogenesis and the reduced levels of BrdU; DCX and NeuN, the neurons hallmark of hippocampus neurogenesis. Moreover, associated proteins in cAMP/PKA pathway were up-regulated after RS treatment. By HPLC analysis, we found that RS decoction contains four main components, including baicalin, baicalein, wogonoside and wogonin, respectively. In conclusion, RS could exert a natural antidepressant with improving depressive-like behavior via regulation of cAMP/PKA neurogenesis pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AOD:
-
Average optical density
- BCA:
-
Bicinchoninic acid
- BDNF:
-
Brain derived neurotrophic factor
- BrdU:
-
5-Bromo-2-deoxyUridine
- CUMS:
-
Chronic unpredictable mild stress
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic Adenosine monophosphate
- CREB:
-
cAMP-response element binding protein
- DCX:
-
Doublecortin
- DG:
-
Dentate gyrus
- Flu:
-
Fluoxetine
- FST:
-
Forced swimming test
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- NeuN:
-
Neuron specific nuclear protein
- NSCs:
-
Neural stem cells
- OFT:
-
Open field test
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- PVDF:
-
Polycinylidene difluoride
- RS:
-
Radix Scutellariae
- SD:
-
Spargue-Dawley
- SPT:
-
Sucrose preference test
References
Zhang C, Lueptow LM, Zhang HT et al (2017) The role of phosphodiesterase-2 in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Adv Neurobiol 17:307–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58811-7_12
Ali SS, Khan SA, Khosa F et al (2017) Noninvasive assessment of subclinical atherosclerosis in persons with symptoms of depression. Atherosclerosis 264:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.07.010
Rose EJ, Ebmeier KP (2006) Pattern of impaired working memory during major depression. J Affect Disord 90(2–3):149–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2005.11.003
Alexander LF, Oliver A, Burdine LK et al (2017) Reported maladaptive decision-making in unipolar and bipolar depression and its change with treatment. Psychiatry Res 257:386–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2017.08.004
Sun LN, Sun QS, Qi JS (2017) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis: an important target associated with antidepressant effects of exercise. Rev Neurosci 28(7):693–703. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2016-0076
Wang JH, Han B, Geng Y et al (2017) Chronic stress contributes to cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal metabolic abnormalities in APP/PS1 mice. Cell Physiol Biochem 41(5):1766–1776. https://doi.org/10.1159/000471869
Drew MR, Huckleberry KA (2017) Modulation of aversive memory by adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Neurotherapeutics 14(3):646–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-017-0528-9
Warner-Schmidt JL, Duman RS (2006) Hippocampal neurogenesis: opposing effects of stress and antidepressant treatment. Hippocampus 16(3):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20156
Morales-Garcia JA, Alonso-Gil S, Santos A et al (2017) Phosphodiesterase7 inhibition activates adult neurogenesis in hippocampus and subventricular zone in vitro and in vivo. Stem cells 35(2):458–472. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.2480
Gargantini E, Lazzari L, Settanni F et al (2016) Obestatin promotes proliferation and survival of adult hippocampal progenitors and reduces amyloid-β-induced toxicity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 422:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2015.11.008
Chiu FL, Qu HL, Chuang CY et al (2015) Elucidating the role of the A 2A adenosine receptor in neurodegeneration using neurons derived from Huntington’s disease iPSCs. Hum Mol Genet 24(21):6066–6079. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddv318
Zhao SS, Zhao M, Qu H et al (2014) Forced limb-use enhances brain plasticity through the cAMP/PKA/CREB signal transduction pathway after stroke in adult rats. Restor Neurol Neurosci 32(5):597–609. https://doi.org/10.3233/RNN-130374
Ko YH, Kwon SH, Jang CG (2017) Liquiritigenin ameliorates memory and cognitive impairment through cholinergic and BDNF pathways in the mouse hippocampus. Arch Pharm Res 40(10):1209–1217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0954-6
Zhu DY, Lau L, Liu SH et al (2004) Activation of cAMP-response-element-binding protein (CREB) after focal cerebral ischemia stimulates neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(25):9453–9457. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0401063101
Waterhouse EG, Xu B (2009) New insights into the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in synaptic plasticity. Mol Cell Neurosci 42(2):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2009.06.009
Acheson A, Conover JC, Fandl JP (1995) A BDNF autocrine loop in adult sensory neurons prevents cell death. Nature 374(6521):450–453. https://doi.org/10.1038/374450a0
Ren L, Chen G (2017) Rapid antidepressant effects of Yueju: a new look at the function and mechanism of an old herbal medicine. J Ethnopharmacol 203:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.03.042
Willner P (2016) The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: history, evaluation and usage. Neurobiol Stress 6:78–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ynstr.2016.08.002
Hill MN, Weinberg J, Verma P et al (2012) Neurobiology of chronic mild stress: parallels to major depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(9):2085–2117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.07.001
Ito N, Oikawa T, Hirose E et al (2017) Kososan, a Kampo medicine, prevents asocial avoidance behavior and attenuates neuroinflammation in socially defeated mice. J Neuroinflammation 14(1):98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0876-8
Guo YJ, Zhang ZJ, Wang SH et al (2009) Notch 1 signaling, hippocampal neurogenesis and behavioral responses to chronic unpredicted mild stress in adult ischemic rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33(4):688–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.03.022
Yan L, Mak MS, Lou J et al (2016) A Chinese herbal decoction, reformulated from Kai-Xin-San relieves the depression-like symptoms in stressed rats and induces neurogenesis in cultured neurons. Sci Rep 6:30014. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30014
Amini-Khoeiab H, Mohammadi-Asl A, Amiri S et al (2017) Oxytocin mitigated the depressive-like behaviors of maternal separation stress through modulating mitochondrial function and neuroinflammation. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 76:169–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.02.022
Shetty RA, Sadananda M (2017) Brief Social isolation in the adolescent Wistar-Kyoto rat model of endogenous depression alters corticosterone and regional monoamine concentrations. Neurochem Res 42(5):1470–1477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2203-2
Sun XX, Li SS, Xu LX et al (2017) Paeoniflorin ameliorates cognitive dysfunction via regulating SOCS2/IRS-1 pathway in diabetic rats. Physiol Behav 174:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.03.020
Appel JR, Ye s, Tang F et al (2018) Increased microglial activity, impaired adult hippocampal neurogenesis, and depressive-like behavior in microglial VPS35-depleted mice. J Neurosci 38(6):5949–5968. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3621-17.2018
Singh S, Mishra A, Bharti S et al (2018) Glycogen synthase kinase-3β regulates equilibrium between neurogenesis and gliogenesis in rat model of Parkinson’s disease: a crosstalk with Wnt and notch signaling. Mol Neurobiol 55(8):6500–6517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0860-4
Ritov G, Boltyansky B, Richter-Levin G (2016) A novel approach to PTSD modeling in rats reveals alternating patterns of limbic activity in different types of stress reaction. Mol Psychiatry 21(5):630–641. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.169
Yu HY, Yin ZJ, Yang SJ et al (2014) Baicalin reverse AMPA receptor expression and neuron apoptosis in chronic unpredictable mild stress rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 451(4):467–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.041
Deng XY, Xue JS, Li HY et al (2015) Geraniol produces antidepressant-like effects in a chronic unpredictable mild stress mice model. Physiol Behav 152(Pt-A):264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.10.008
Qiao H, Li MX, Xu C et al (2016) Dendritic spines in depression: what we learned from animal models. Neural Plast 2016:26. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8056370
Hu CL, Luo Y, Wang H et al (2017) Re-evaluation of the interrelationships among the behavioral tests in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. PLoS ONE 12(9):e0185129. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185129
Krza AM, Cao JJL, Agius M, Hoschl C (2017) Dose neurogenesis relate to depression and do antidepressants affect neurogenesis? Psychiatr Danub 29(4):241–246
Joshi SH, Pirnia T, Leaver A et al (2016) Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depressin. Biol Psychiatry 79(4):282–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.02.029
Schoenfeld TJ, Morris HD, Padmanaban V et al (2017) Stress and loss of adult neurogenesis differentially reduce hippocampal volume. Biol Psychiatry 82(12):914–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.05.013
MacQueen G, Frodl T (2011) The hippocampus in major depression: evidence for the convergence of the bench and bedside in psychiatric research? Mol Psychiatry 16(3):252–264. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2010.80
Wehbi VL, Taskén K (2016) Molecular mechanisms for cAMP-mediated immune-regulation in T cells—role of anchored protein kinase A signaling units. Front immunol 7:222. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00222
Yang HH, Yang LH (2016) Targeting cAMP/PKA pathway for glycemic control and type 2 diabetes therapy. J Mol Endocrinol 57(2):R93–R108. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-15-0316
Yu T, Yang G, Wu C et al (2017) Cytoplasmic GPER translocation in cancer-associated fibroblasts mediates cAMP/PKA/CREB/glycolytic axis to confer tumor cells with multidrug resistance. Oncogene 36(15):2131–2145. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.370
Jay TM (2003) Dopamine: a potential substrate for synaptic plasticity and memory mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 69(6):375–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-0082(03)00085-6
Landeira BS, Santana TTDS, Araújo JAM et al (2018) Activity-independent effects of CREB on neuronal survival and differentiation during mouse cerebral cortex development. Cereb Cortex 28(2):538–548. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw387
Hsiao YH, Hung HC, Chen SH et al (2014) Interaction rescues memory deficit in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease by increasing BDNF-dependent hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurosci 34(49):16207–16219. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0747-14.2014
Zhang K, Pan X, Wang F et al (2016) Baicalin promotes hippocampal neurogenesis via SGK1- and FKBP5-mediated glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in a neuroendocrine mouse model of anxiety/depression. Sci Rep 6:30951. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30951
Zhuang PW, Cui GZ, Zhang YJ et al (2013) Baicalin regulates neuronal fate decision in neural stem/progenitor cells and stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis in adult rats. CNS Neurosci Ther 19(3):154–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12050
Gao L, Li C, Lian WW et al (2015) Ameliorative effects of baicalein in MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: a microarray study. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 133:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2015.04.004
Li Y, Zhao J, Holscher C (2017) Therapeutic potential of baicalein in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. CNS Drugs 31(8):639–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-017-0451-y
Funding
This study was supported by The Natural Science Foundation of China (8157140641).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Guo, L., Ji, Z. et al. Radix Scutellariae Attenuates CUMS-Induced Depressive-Like Behavior by Promoting Neurogenesis via cAMP/PKA Pathway. Neurochem Res 43, 2111–2120 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2635-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2635-3