Abstract
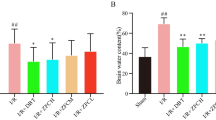
Ginseng (Panax ginseng), an herbal medicine, has been used to prevent neurodegenerative disorders. Ginsenosides (e.g., Re, Rb1, or Rg1) were obtained from Korean mountain cultivated ginseng. The anticonvulsant activity of ginsenoside Re (20 mg/kg/day × 3) against trimethyltin (TMT) insult was the most pronounced out of ginsenosides (e.g., Re, Rb1, and Rg1). Re itself did not significantly alter tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interferon-ϒ (IFN-ϒ), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) expression, however, it significantly increases the interleukin-6 (IL-6) expression. In addition, Re attenuated the TMT-induced decreases in IL-6 protein level. Therefore, IL-6 knockout (−/−) mice were employed to investigate whether Re requires IL-6-dependent neuroprotective activity against TMT toxicity. Re significantly attenuated TMT-induced lipid peroxidation, protein peroxidation, and reactive oxygen species in the hippocampus. Re-mediated antioxidant effects were more pronounced in IL-6 (−/−) mice than in WT mice. Consistently, TMT-induced increase in c-Fos-immunoreactivity (c-Fos-IR), TUNEL-positive cells, and nuclear chromatin clumping in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus were significantly attenuated by Re. Furthermore, Re attenuated TMT-induced proapoptotic changes. Protective potentials by Re were comparable to those by recombinant IL-6 protein (rIL-6) against TMT-insult in IL-6 (−/−) mice. Moreover, treatment with a phosphoinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, LY294002 (1.6 µg, i.c.v) counteracted the protective potential mediated by Re or rIL-6 against TMT insult. The results suggest that ginsenoside Re requires IL-6-dependent PI3K/Akt signaling for its protective potential against TMT-induced neurotoxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gomez FD, Apodaca P, Holloway LN, Pannell KH, Whalen MM (2007) Effect of a series of triorganotins on the immune function of human natural killer cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 23:18–24
Shawky S, Emons H (1998) Distribution pattern of organotin compounds at different trophic levels of aquatic ecosystems. Chemosphere 36:523–535
Tang X, Wu X, Dubois AM, Sui G, Wu B, Lai G, Gong Z, Gao H, Liu S, Zhong Z, Lin Z, Olson J, Ren X (2013) Toxicity of trimethyltin and dimethyltin in rats and mice. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90:626–633
Geloso MC, Corvino V, Michetti F (2011) Trimethyltin-induced hippocampal degeneration as a tool to investigate neurodegenerative processes. Neurochem Int 58:729–738
Shin EJ, Jeong JH, Chung YH, Kim WK, Ko KH, Bach JH, Hong JS, Yoneda Y, Kim HC (2011) Role of oxidative stress in epileptic seizures. Neurochem Int 59:122–137
Ishida N, Akaike M, Tsutsumi S, Kanai H, Masui A, Sadamatsu M, Kuroda Y, Watanabe Y, McEwen BS, Kato N (1997) Trimethyltin syndrome as a hippocampal degeneration model: temporal changes and neurochemical features of seizure susceptibility and learning impairment. Neuroscience 81:1183–1191
Fortemps E, Amand G, Bomboir A, Lauwerys R, Laterre EC (1978) Trimethyltin poisoning. Report of two cases. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 41:1–6
Ikeda K, Iwasaki Y, Shiojima T, Kinoshita M (1996) Neuroprotective effect of various cytokines on developing spinal motoneurons following axotomy. J Neurol Sci 135:109–113
Kushima Y, Hatanaka H (1992) Interleukin-6 and leukemia inhibitory factor promote the survival of acetylcholinesterase-positive neurons in culture from embryonic rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 143:110–114
Vezzani A, Balosso S, Ravizza T (2008) The role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of epilepsy. Brain Behav Immun 22:797–803
Vezzani A, Conti M, De Luigi A, Ravizza T, Moneta D, Marchesi F, De Simoni MG (1999) Interleukin-1beta immunoreactivity and microglia are enhanced in the rat hippocampus by focal kainate application: functional evidence for enhancement of electrographic seizures. J Neurosci 19:5054–5065
Li G, Bauer S, Nowak M, Norwood B, Tackenberg B, Rosenow F, Knake S, Oertel WH, Hamer HM (2011) Cytokines and epilepsy. Seizure 20:249–256
Tran HY, Shin EJ, Saito K, Nguyen XK, Chung YH, Jeong JH, Bach JH, Park DH, Yamada K, Nabeshima T, Yoneda Y, Kim HC (2012) Protective potential of IL-6 against trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in vivo. Free Radic Biol Med 52:1159–1174
Penkowa M, Molinero A, Carrasco J, Hidalgo J (2001) Interleukin-6 deficiency reduces the brain inflammatory response and increases oxidative stress and neurodegeneration after kainic acid-induced seizures. Neuroscience 102:805–818
Penkowa M, Moos T, Carrasco J, Hadberg H, Molinero A, Bluethmann H, Hidalgo J (1999) Strongly compromised inflammatory response to brain injury in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Glia 25:343–357
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, Gonzalez-Baron M (2004) PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 30:193–204
Chung TD, Yu JJ, Kong TA, Spiotto MT, Lin JM (2000) Interleukin-6 activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, which inhibits apoptosis in human prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate 42:1–7
Kim DH (2012) Chemical diversity of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquifolium, and Panax notoginseng. J Ginseng Res 36:1–15
Liu D LY, Xu H, Sun SQ, Wang ZT (2008) Differentiation of the root of Cultivated Ginseng, Mountain Cultivated Ginseng and Mountain Wild Ginseng using FT-IR and two-dimensional correlation IR spectroscopy. J Mol Struct 883–884:228–235
Choi YE, Kim YS, Yi MJ, Park WG, Yi JS, Chun SR, Han SS, Lee SJ (2007) Physiological and chemical characteristics of field- and mountain-cultivated ginseng roots. J Plant Biol 50:198–205
Ma L, Liu H, Xie Z, Yang S, Xu W, Hou J, Yu B (2014) Ginsenoside Rb3 protects cardiomyocytes against ischemia-reperfusion injury via the inhibition of JNK-mediated NF-kappaB pathway: a mouse cardiomyocyte model. PLoS ONE 9:e103628
Paul S, Shin HS, Kang SC (2012) Inhibition of inflammations and macrophage activation by ginsenoside-Re isolated from Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer). Food Chem Toxicol 50:1354–1361
Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan CS (1999) Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol 58:1685–1693
Zhang JK, Gao R, Dou DQ, Kang TG (2013) The ginsenosides and carbohydrate profiles of ginseng cultivated under mountainous forest. Pharmacogn Mag 9:S38–43
Lopez MV, Cuadrado MP, Ruiz-Poveda OM, Del Fresno AM, Accame ME (2007) Neuroprotective effect of individual ginsenosides on astrocytes primary culture. Biochim Biophys Acta 1770:1308–1316
Lee YS, Chung IS, Lee IR, Kim KH, Hong WS, Yun YS (1997) Activation of multiple effector pathways of immune system by the antineoplastic immunostimulator acidic polysaccharide ginsan isolated from Panax ginseng. Anticancer Res 17:323–331
Zhang X, Shi M, Bjoras M, Wang W, Zhang G, Han J, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wang B, Chen J, Zhu Y, Xiong L, Zhao G (2013) Ginsenoside Rd promotes glutamate clearance by up-regulating glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 via PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 pathways. Front Pharmacol 4:152
Chen LM, Zhou XM, Cao YL, Hu WX (2008) Neuroprotection of ginsenoside Re in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Asian Nat Prod Res 10:439–445
Shin EJ, Shin SW, Nguyen TT, Park DH, Wie MB, Jang CG, Nah SY, Yang BW, Ko SK, Nabeshima T, Kim HC (2014) Ginsenoside Re rescues methamphetamine-induced oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, microglial activation, and dopaminergic degeneration by inhibiting the protein kinase Cdelta gene. Mol Neurobiol 49:1400–1421
Shin EJ, Nam Y, Tu TH, Lim YK, Wie MB, Kim DJ, Jeong JH, Kim HC (2016) Protein kinase Cdelta mediates trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in mice in vivo via inhibition of glutathione defense mechanism. Arch Toxicol 90:937–953
Tran TH, Mai HN, Shin EJ, Nam Y, Nguyen BT, Lee YJ, Jeong JH, Tran HY, Cho EH, Nah SY, Lei XG, Nabeshima T, Kim NH, Kim HC (2016) Repeated exposure to far infrared ray attenuates acute restraint stress in mice via inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway by induction of glutathione peroxidase-1. Neurochem Int 94:9–22
Oliver CN, Levine RL, Stadtman ER (1987) A role of mixed-function oxidation reactions in the accumulation of altered enzyme forms during aging. J Am Geriatr Soc 35:947–956
Shin EJ, Duong CX, Nguyen XK, Li Z, Bing G, Bach JH, Park DH, Nakayama K, Ali SF, Kanthasamy AG, Cadet JL, Nabeshima T, Kim HC (2012) Role of oxidative stress in methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic toxicity mediated by protein kinase Cdelta. Behav Brain Res 232:98–113
Kim J, Yang M, Son Y, Jang H, Kim D, Kim JC, Kim SH, Kang MJ, Im HI, Shin T, Moon C (2014) Glial activation with concurrent up-regulation of inflammatory mediators in trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in mice. Acta Histochem 116:1490–1500
Kim BK, Tran HY, Shin EJ, Lee C, Chung YH, Jeong JH, Bach JH, Kim WK, Park DH, Saito K, Nabeshima T, Kim HC (2013) IL-6 attenuates trimethyltin-induced cognitive dysfunction via activation of JAK2/STAT3, M1 mAChR and ERK signaling network. Cell Signal 25:1348–1360
Shin EJ, Suh SK, Lim YK, Jhoo WK, Hjelle OP, Ottersen OP, Shin CY, Ko KH, Kim WK, Kim DS, Chun W, Ali S, Kim HC (2005) Ascorbate attenuates trimethyltin-induced oxidative burden and neuronal degeneration in the rat hippocampus by maintaining glutathione homeostasis. Neuroscience 133:715–727
Yamada M, Hatanaka H (1994) Interleukin-6 protects cultured rat hippocampal neurons against glutamate-induced cell death. Brain Res 643:173–180
Dyer RS, Walsh TJ, Wonderlin WF, Bercegeay M (1982) The trimethyltin syndrome in rats. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 4:127–133
Shin EJ, Ko KH, Kim WK, Chae JS, Yen TP, Kim HJ, Wie MB, Kim HC (2008) Role of glutathione peroxidase in the ontogeny of hippocampal oxidative stress and kainate seizure sensitivity in the genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Neurochem Int 52:1134–1147
Shin EJ, Koh YH, Kim AY, Nah SY, Jeong JH, Chae JS, Kim SC, Yen TP, Yoon HJ, Kim WK, Ko KH, Kim HC (2009) Ginsenosides attenuate kainic acid-induced synaptosomal oxidative stress via stimulation of adenosine A(2A) receptors in rat hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 197:239–245
Dragunow M, Robertson HA (1987) Kindling stimulation induces c-fos protein(s) in granule cells of the rat dentate gyrus. Nature 329:441–442
Shin EJ, Jeong JH, Kim AY, Koh YH, Nah SY, Kim WK, Ko KH, Kim HJ, Wie MB, Kwon YS, Yoneda Y, Kim HC (2009) Protection against kainate neurotoxicity by ginsenosides: attenuation of convulsive behavior, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress. J Neurosci Res 87:710–722
Tilg H, Trehu E, Atkins MB, Dinarello CA, Mier JW (1994) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) as an anti-inflammatory cytokine: induction of circulating IL-1 receptor antagonist and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor p55. Blood 83:113–118
Aderka D, Le JM, Vilcek J (1989) IL-6 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in cultured human monocytes, U937 cells, and in mice. J Immunol 143:3517–3523
Zhong J, Dietzel ID, Wahle P, Kopf M, Heumann R (1999) Sensory impairments and delayed regeneration of sensory axons in interleukin-6-deficient mice. J Neurosci 19:4305–4313
Funk JA, Gohlke J, Kraft AD, McPherson CA, Collins JB, Jean Harry G (2011) Voluntary exercise protects hippocampal neurons from trimethyltin injury: possible role of interleukin-6 to modulate tumor necrosis factor receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Brain Behav Immun 25:1063–1077
Penkowa M, Giralt M, Lago N, Camats J, Carrasco J, Hernandez J, Molinero A, Campbell IL, Hidalgo J (2003) Astrocyte-targeted expression of IL-6 protects the CNS against a focal brain injury. Exp Neurol 181:130–148
Casalbore P, Barone I, Felsani A, D’Agnano I, Michetti F, Maira G, Cenciarelli C (2010) Neural stem cells modified to express BDNF antagonize trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity through PI3K/Akt and MAP kinase pathways. J Cell Physiol 224:710–721
Xu X, Cao Z, Cao B, Li J, Guo L, Que L, Ha T, Chen Q, Li C, Li Y (2009) Carbamylated erythropoietin protects the myocardium from acute ischemia/reperfusion injury through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Surgery 146:506–514
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Noshita N, Lewen A, Sugawara T, Chan PH (2002) Akt phosphorylation and neuronal survival after traumatic brain injury in mice. Neurobiol Dis 9:294–304
Noshita N, Lewen A, Sugawara T, Chan PH (2001) Evidence of phosphorylation of Akt and neuronal survival after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:1442–1450
Kalimuthu S, Se-Kwon K (2013) Cell survival and apoptosis signaling as therapeutic target for cancer: marine bioactive compounds. Int J Mol Sci 14:2334–2354
Wang CM, Liu MY, Wang F, Wei MJ, Wang S, Wu CF, Yang JY (2013) Anti-amnesic effect of pseudoginsenoside-F11 in two mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 106:57–67
Tran TV, Shin EJ, Ko SK, Nam Y, Chung YH, Jeong JH, Jang CG, Nah SY, Yamada K, Nabeshima T, Byun JK, Kim HC (2016) Mountain-cultivated ginseng attenuates phencyclidine-induced abnormal behaviors in mice by positive modulation of glutathione in the prefrontal cortex of mice. J Med Food 19:961–969
Kim YC, Kim SR, Markelonis GJ, Oh TH (1998) Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg3 protect cultured rat cortical cells from glutamate-induced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci Res 53:426–432
He B, Chen P, Yang J, Yun Y, Zhang X, Yang R, Shen Z (2012) Neuroprotective effect of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg(3) against transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 526:106–111
Hu S, Han R, Mak S, Han Y (2011) Protection against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+)-induced apoptosis by water extract of ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) in SH-SY5Y cells. J Ethnopharmacol 135:34–42
Liu XY, Zhou XY, Hou JC, Zhu H, Wang Z, Liu JX, Zheng YQ (2015) Ginsenoside Rd promotes neurogenesis in rat brain after transient focal cerebral ischemia via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36:421–428
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant (Project No. S111415L020100) of the ‘‘Forestry Technology Projects’’ provided by the Korea Forest Service, and by the Basic Science Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (#NRF-2013R1A1A2060894 and #NRF-2016R1A1A1A050055201), Republic of Korea. Thu-Hien Thi Tu, Naveen Sharma, and Hai-Quyen Tran were supported by the BK21 PLUS program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Additional information
Thu-Hien Thi Tu and Naveen Sharma have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, TH.T., Sharma, N., Shin, EJ. et al. Ginsenoside Re Protects Trimethyltin-Induced Neurotoxicity via Activation of IL-6-Mediated Phosphoinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Signaling in Mice. Neurochem Res 42, 3125–3139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2349-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2349-y