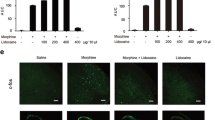
Abstract
AMD3100 is a specific C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) antagonist which blocks the interaction between CXCR4 and CXCL12. Multiple lines of evidence suggest that AMD3100 has analgesic effects on many pathological pain states, including peripheral neuropathic pain. However, little is known about the underlying mechanisms. In the current study, we investigated the effect of different doses of AMD3100 on neuropathic pain in rats after L5 spinal nerve ligation. We used naloxone methiodide (NLXM) to further determine whether AMD3100-mediated analgesic effect was opioid-dependent. Behavioral study showed that early repeated administration of AMD3100 (2 and 5 mg/kg, i.p.) dose-dependently alleviates peripheral neuropathic pain. Flow cytometry, immunofluorescence and NLXM experiments showed that AMD3100 alleviates neuropathic pain partially by augmenting leukocyte-derived endogenous opioid secretion. Furthermore, we found that pro-inflammatory cytokines were down-regulated by AMD3100 using Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay. Our data indicate that AMD3100 dose-dependently alleviates neuropathic pain partially by augmenting leukocyte-derived endogenous opioid secretion. This finding suggests that AMD3100 may be a viable pharmacotherapeutic strategy for the treatment of neuropathic pain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raja SN, Haythornthwaite JA (2005) Combination therapy for neuropathic pain–which drugs, which combination, which patients? N Engl J Med 352:1373–1375
Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2002) Can we conquer pain? Nat Neurosci 5(Suppl):1062–1067
Stein C, Schafer M, Machelska H (2003) Attacking pain at its source: new perspectives on opioids. Nat Med 9:1003–1008
Zuk A, Gershenovich M, Ivanova Y, MacFarland RT, Fricker SP, Ledbetter S (2014) CXCR(4)antagonism as a therapeutic approach to prevent acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 307:F783–F797
Jujo K, Ii M, Sekiguchi H, Klyachko E, Misener S, Tanaka T, Tongers J, Roncalli J, Renault MA, Thorne T, Ito A, Clarke T, Kamide C, Tsurumi Y, Hagiwara N, Qin G, Asahi M, Losordo DW (2013) CXC-chemokine receptor 4 antagonist AMD3100 promotes cardiac functional recovery after ischemia/reperfusion injury via endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent mechanism. Circulation 127:63–73
Drummond S, Ramachandran S, Torres E, Huang J, Hehre D, Suguihara C, Young KC (2015) CXCR4 blockade attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats. Neonatology 107:304–311
Watanabe K, Penfold ME, Matsuda A, Ohyanagi N, Kaneko K, Miyabe Y, Matsumoto K, Schall TJ, Miyasaka N, Nanki T (2010) Pathogenic role of CXCR7 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62:3211–3220
Scholten DJ, Canals M, Maussang D, Roumen L, Smit MJ, Wijtmans M, de Graaf C, Vischer HF, Leurs R (2012) Pharmacological modulation of chemokine receptor function. Br J Pharmacol 165:1617–1643
Hendrix CW, Flexner C, MacFarland RT, Giandomenico C, Fuchs EJ, Redpath E, Bridger G, Henson GW (2000) Pharmacokinetics and safety of AMD-3100, a novel antagonist of the CXCR-4 chemokine receptor, in human volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:1667–1673
Liles WC, Broxmeyer HE, Rodger E, Wood B, Hubel K, Cooper S, Hangoc G, Bridger GJ, Henson GW, Calandra G, Dale DC (2003) Mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells in healthy volunteers by AMD3100, a CXCR4 antagonist. Blood 102:2728–2730
Liu Q, Li Z, Gao JL, Wan W, Ganesan S, McDermott DH, Murphy PM (2015) CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 redistributes leukocytes from primary immune organs to secondary immune organs, lung, and blood in mice. Eur J Immunol 45:1855–1867
Dar A, Schajnovitz A, Lapid K, Kalinkovich A, Itkin T, Ludin A, Kao WM, Battista M, Tesio M, Kollet O, Cohen NN, Margalit R, Buss EC, Baleux F, Oishi S, Fujii N, Larochelle A, Dunbar CE, Broxmeyer HE, Frenette PS, Lapidot T (2011) Rapid mobilization of hematopoietic progenitors by AMD3100 and catecholamines is mediated by CXCR4-dependent SDF-1 release from bone marrow stromal cells. Leukemia 25:1286–1296
Hubel K, Liles WC, Broxmeyer HE, Rodger E, Wood B, Cooper S, Hangoc G, Macfarland R, Bridger GJ, Henson GW, Calandra G, Dale DC (2004) Leukocytosis and mobilization of CD34 + hematopoietic progenitor cells by AMD3100, a CXCR4 antagonist. Support Cancer Ther 1:165–172
Herbert KE, Demosthenous L, Wiesner G, Link E, Westerman DA, Came N, Ritchie DS, Harrison S, Seymour JF, Prince HM (2014) Plerixafor plus pegfilgrastim is a safe, effective mobilization regimen for poor or adequate mobilizers of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells: a phase I clinical trial. Bone Marrow Transpl 49:1056–1062
Wilson NM, Jung H, Ripsch MS, Miller RJ, White FA (2011) CXCR4 signaling mediates morphine-induced tactile hyperalgesia. Brain Behav Immun 25:565–573
Bhangoo SK, Ren D, Miller RJ, Chan DM, Ripsch MS, Weiss C, McGinnis C, White FA (2007) CXCR4 chemokine receptor signaling mediates pain hypersensitivity in association with antiretroviral toxic neuropathy. Brain Behav Immun 21:581–591
Bhangoo SK, Ripsch MS, Buchanan DJ, Miller RJ, White FA (2009) Increased chemokine signaling in a model of HIV1-associated peripheral neuropathy. Mol Pain 5:48
Huang W, Zheng W, Liu S, Zeng W, Levitt RC, Candiotti KA, Lubarsky DA, Hao S (2014) HSV-mediated p55TNFSR reduces neuropathic pain induced by HIV gp120 in rats through CXCR4 activity. Gene Ther 21:328–336
Huang W, Zheng W, Ouyang H, Yi H, Liu S, Zeng W, Levitt RC, Candiotti KA, Lubarsky DA, Hao S (2014) Mechanical allodynia induced by nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor is suppressed by p55TNFSR mediated by herpes simplex virus vector through the SDF1alpha/CXCR4 system in rats. Anesth Analg 118:671–680
Luo X, Tai WL, Sun L, Qiu Q, Xia Z, Chung SK, Cheung CW (2014) Central administration of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 antagonist alleviates the development and maintenance of peripheral neuropathic pain in mice. PLoS ONE 9:e104860
Menichella DM, Abdelhak B, Ren D, Shum A, Frietag C, Miller RJ (2014) CXCR4 chemokine receptor signaling mediates pain in diabetic neuropathy. Mol Pain 10:42
Shen W, Hu XM, Liu YN, Han Y, Chen LP, Wang CC, Song C (2014) CXCL12 in astrocytes contributes to bone cancer pain through CXCR4-mediated neuronal sensitization and glial activation in rat spinal cord. J Neuroinflammation 11:75
Hu XM, Liu YN, Zhang HL, Cao SB, Zhang T, Chen LP, Shen W (2015) CXCL12/CXCR4 chemokine signaling in spinal glia induces pain hypersensitivity through MAPKs-mediated neuroinflammation in bone cancer rats. J Neurochem 132:452–463
Kim KJ, Yoon YW, Chung JM (1997) Comparison of three rodent neuropathic pain models. Exp Brain Res 113:200–206
Labuz D, Schmidt Y, Schreiter A, Rittner HL, Mousa SA, Machelska H (2009) Immune cell-derived opioids protect against neuropathic pain in mice. J Clin Invest 119:278–286
Dixon WJ (1980) Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:441–462
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32:77–88
Martucci C, Trovato AE, Costa B, Borsani E, Franchi S, Magnaghi V, Panerai AE, Rodella LF, Valsecchi AE, Sacerdote P, Colleoni M (2008) The purinergic antagonist PPADS reduces pain related behaviours and interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, iNOS and nNOS overproduction in central and peripheral nervous system after peripheral neuropathy in mice. Pain 137:81–95
Xie F, Li X, Bao M, Guo R, Zhang C, Wu A, Yue Y, Guan Y, Wang Y (2015) Plerixafor may treat intractable post-herpetic neuralgia. Med Hypotheses 85:491–493
Dubovy P, Klusakova I, Svizenska I, Brazda V (2010) Spatio-temporal changes of SDF1 and its CXCR4 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia following unilateral sciatic nerve injury as a model of neuropathic pain. Histochem Cell Biol 133:323–337
Semerad CL, Liu F, Gregory AD, Stumpf K, Link DC (2002) G-CSF is an essential regulator of neutrophil trafficking from the bone marrow to the blood. Immunity 17:413–423
Chen G, Park CK, Xie RG, Ji RR (2015) Intrathecal bone marrow stromal cells inhibit neuropathic pain via TGF-beta secretion. J Clin Invest 125:3226–3240
Rittner HL, Brack A, Machelska H, Mousa SA, Bauer M, Schafer M, Stein C (2001) Opioid peptide-expressing leukocytes: identification, recruitment, and simultaneously increasing inhibition of inflammatory pain. Anesthesiology 95:500–508
Mousa SA, Machelska H, Schafer M, Stein C (2002) Immunohistochemical localization of endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2 in immune cells and spinal cord in a model of inflammatory pain. J Neuroimmunol 126:5–15
Machelska H, Heppenstall PA, Stein C (2003) Breaking the pain barrier. Nat Med 9:1353–1354
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Hasegawa A, Noguchi T (2008) Pre-Irradiation of blood by gallium aluminum arsenide (830 nm) low-level laser enhances peripheral endogenous opioid analgesia in rats. Anesth Analg 107:1058–1063
Binder W, Mousa SA, Sitte N, Kaiser M, Stein C, Schafer M (2004) Sympathetic activation triggers endogenous opioid release and analgesia within peripheral inflamed tissue. Eur J Neurosci 20:92–100
Mousa SA, Shakibaei M, Sitte N, Schafer M, Stein C (2004) Subcellular pathways of beta-endorphin synthesis, processing, and release from immunocytes in inflammatory pain. Endocrinology 145:1331–1341
Cabot PJ, Carter L, Gaiddon C, Zhang Q, Schafer M, Loeffler JP, Stein C (1997) Immune cell-derived beta-endorphin. Production, release, and control of inflammatory pain in rats. J Clin Invest 100:142–148
Cabot PJ, Carter L, Schafer M, Stein C (2001) Methionine-enkephalin-and Dynorphin A-release from immune cells and control of inflammatory pain. Pain 93:207–212
Wengner AM, Pitchford SC, Furze RC, Rankin SM (2008) The coordinated action of G-CSF and ELR + CXC chemokines in neutrophil mobilization during acute inflammation. Blood 111:42–49
Chao PK, Lu KT, Lee YL, Chen JC, Wang HL, Yang YL, Cheng MY, Liao MF, Ro LS (2012) Early systemic granulocyte-colony stimulating factor treatment attenuates neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. PLoS ONE 7:e43680
Chadzinska M, Starowicz K, Scislowska-Czarnecka A, Bilecki W, Pierzchala-Koziec K, Przewlocki R, Przewlocka B, Plytycz B (2005) Morphine-induced changes in the activity of proopiomelanocortin and prodynorphin systems in zymosan-induced peritonitis in mice. Immunol Lett 101:185–192
Endres-Becker J, Heppenstall PA, Mousa SA, Labuz D, Oksche A, Schafer M, Stein C, Zollner C (2007) Mu-opioid receptor activation modulates transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) currents in sensory neurons in a model of inflammatory pain. Mol Pharmacol 71:12–18
Schafer M, Mousa SA, Zhang Q, Carter L, Stein C (1996) Expression of corticotropin-releasing factor in inflamed tissue is required for intrinsic peripheral opioid analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:6096–6100
Czlonkowski A, Stein C, Herz A (1993) Peripheral mechanisms of opioid antinociception in inflammation: involvement of cytokines. Eur J Pharmacol 242:229–235
Kim KS, Song YS, Jin J, Joe JH, So BI, Park JY, Fang CH, Kim MJ, Cho YH, Hwang S, Ro YS, Kim H, Ahn YH, Sung HJ, Sung JJ, Park SH, Lipton SA (2015) Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor as a treatment for diabetic neuropathy in rat. Mol Cell Endocrinol 414:64–72
Franchi S, Valsecchi AE, Borsani E, Procacci P, Ferrari D, Zalfa C, Sartori P, Rodella LF, Vescovi A, Maione S, Rossi F, Sacerdote P, Colleoni M, Panerai AE (2012) Intravenous neural stem cells abolish nociceptive hypersensitivity and trigger nerve regeneration in experimental neuropathy. Pain 153:850–861
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81571065, 81428008), Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (7152056), the Excellent Program for Scientific Activity of Returned Oversea Scholar, Beijing, China (2013), and the Program for High Levels of Health Personnel in Beijing City, China (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, F., Wang, Y., Li, X. et al. Early Repeated Administration of CXCR4 Antagonist AMD3100 Dose-Dependently Improves Neuropathic Pain in Rats After L5 Spinal Nerve Ligation. Neurochem Res 41, 2289–2299 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1943-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1943-8