Abstract
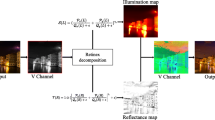
Retinex decomposition is a prevalent solution to low-light image enhancement. It is usually considered as a constrained optimization problem. To improve enhancement performance, the Retinex model is incorporated with various prior constraints, which make the optimization process complicated and difficult. In this paper, a method of low-light enhancement with regularized Gaussian Fields (RGF) model is proposed to address this issue. Firstly, we construct an RGF-based optimization model to formulate simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation as an unconstrained optimization problem. Therefore, Retinex decomposition in RGF model can be solved by gradient descent techniques and has superiority on computational convenience. Then, to suppress noise and preserve detail in the estimated reflectance, the detail-preserving model based on Gaussian total variation (GTV) is established. The qualitative and quantitative comparisons on several public datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method over several state-of-the-arts in terms of enhancement efficiency and quality.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao B, Chen C, Xiao X, Xia S (2022) Towards a category-extended object detector with limited data. Patt Recognit 132:108943
Chen Q, Fu K, Liu Z, Chen G, Du H, Qiu B, Shao L (2021) Ef-net: a novel enhancement and fusion network for RGB-D saliency detection. Patt Recognit 112:107740
Sultana M, Mahmood A, Jung SK (2022) Unsupervised moving object segmentation using background subtraction and optimal adversarial noise sample search. Patt Recognit 129:108719
Li C, Anwar S, Porikli F (2020) Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement. Patt Recognit 98:107038
Jiang Q, Zhang Y, Bao F, Zhao X, Zhang C, Liu P (2022) Two-step domain adaptation for underwater image enhancement. Patt Recognit 122:108324
Sazak Ç, Nelson CJ, Obara B (2019) The multiscale bowler-hat transform for blood vessel enhancement in retinal images. Patt Recognit 88:739–750
Sharma A, Mishra PK (2022) Covid-manet: multi-task attention network for explainable diagnosis and severity assessment of covid-19 from CXR images. Patt Recognit 131:108826
Li M, Liu J, Yang W, Sun X, Guo Z (2018) Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust Retinex model. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(6):2828–2841
Li H, Wu X-J (2018) Densefuse: a fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(5):2614–2623
Land EH (1977) The Retinex theory of color vision. Sci Am 237(6):108–129
Fu X, Zeng D, Huang Y, Zhang X-P, Ding X (2016) A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2782–2790
Ren X, Yang W, Cheng W-H, Liu J (2020) Lr3m: robust low-light enhancement via low-rank regularized Retinex model. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:5862–5876
Hao S, Han X, Guo Y, Xu X, Wang M (2020) Low-light image enhancement with semi-decoupled decomposition. IEEE Trans Multimed 22(12):3025–3038
Cheng H-D, Shi X (2004) A simple and effective histogram equalization approach to image enhancement. Digit Sign Process 14(2):158–170
Abdullah-Al-Wadud M, Kabir MH, Dewan MAA, Chae O (2007) A dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 53(2):593–600
Pizer SM (1990) Contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization: speed and effectiveness stephen m. pizer, r. eugene johnston, james p. ericksen, bonnie c. yankaskas, keith e. muller medical image display research group. In: Proceedings of the first conference on visualization in biomedical computing, Atlanta, Georgia, vol. 337, p 1
Celik T, Tjahjadi T (2011) Contextual and variational contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(12):3431–3441
Lee C, Lee C, Kim C-S (2013) Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation of 2d histograms. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):5372–5384
Jobson DJ, Rahman Z-U, Woodell GA (1997) Properties and performance of a center/surround Retinex. IEEE Trans Image Process 6(3):451–462
Wang S, Luo G (2017) Naturalness preserved image enhancement using a priori multi-layer lightness statistics. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(2):938–948
Jobson DJ, Rahman Z-U, Woodell GA (1997) A multiscale Retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans Image process 6(7):965–976
Ma W, Morel J-M, Osher S, Chien A (2011) An l 1-based variational model for Retinex theory and its application to medical images. In: CVPR 2011, IEEE, pp 153–160
Ng MK, Wang W (2011) A total variation model for Retinex. SIAM J Imag Sci 4(1):345–365
Ma W, Osher S (2012) A tv Bregman iterative model of Retinex theory. Inverse Probl Imag 6(4):697–708
Wang W, Ng MK (2014) A nonlocal total variation model for image decomposition: illumination and reflectance. Numer Math: Theory Methods Appl 7(3):334–355
Guo X, Li Y, Ling H (2016) Lime: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(2):982–993
Jha M, Bhandari AK (2022) Camera response based nighttime image enhancement using concurrent reflectance. IEEE Trans Instrum Measurement 71:1–11
Yang J, Jiang X, Pan C, Liu C-L (2016) Enhancement of low light level images with coupled dictionary learning. In: 2016 23rd international conference on pattern recognition (ICPR), IEEE, pp 751–756
Lore KG, Akintayo A, Sarkar S (2017) Llnet: a deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Patt Recognit 61:650–662
Yang W, Wang S, Fang Y, Wang Y, Liu J (2020) From fidelity to perceptual quality: a semi-supervised approach for low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3063–3072
Zhao Z, Xiong B, Wang L, Ou Q, Yu L, Kuang F (2021) Retinexdip: a unified deep framework for low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 32(3):1076–1088
Zhang H, Yang J, Xie J, Qian J, Zhang B (2017) Weighted sparse coding regularized nonconvex matrix regression for robust face recognition. Inf Sci 394:1–17
Zhang H, Qian F, Zhang B, Du W, Qian J, Yang J (2022) Incorporating linear regression problems into an adaptive framework with feasible optimizations. IEEE Trans Multimed
Min C, Gu Y, Li Y, Yang F (2020) Non-rigid infrared and visible image registration by enhanced affine transformation. Patt Recognit 106:107377
Loke MH, Barker RD (1996) Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-newton method1. Geophys Prospect 44(1):131–152
Marques TP, Branzan Albu A (2020) L2uwe: a framework for the efficient enhancement of low-light underwater images using local contrast and multi-scale fusion. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW), pp 2286–2295. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW50498.2020.00277
Wei C, Wang W, Yang W, Liu J (2018) Deep Retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement
Dabov K, Foi A, Katkovnik V, Egiazarian K (2007) Image denoising by sparse 3-d transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(8):2080–2095
Bychkovsky V, Paris S, Chan E, Durand F (2011) Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs. In: CVPR 2011, IEEE, pp 97–104
Ma J, Zhao J, Ma Y, Tian J (2015) Non-rigid visible and infrared face registration via regularized gaussian fields criterion. Patt Recognit 48(3):772–784
Wang S, Ma K, Yeganeh H, Wang Z, Lin W (2015) A patch-structure representation method for quality assessment of contrast changed images. IEEE Sign Process Lett 22(12):2387–2390
Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik AC (2012) Making a “completely blind’’ image quality analyzer. IEEE Sign Process Lett 20(3):209–212
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61901157).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, X., Min, C., Shao, M. et al. Low-Light Image Enhancement via Regularized Gaussian Fields Model. Neural Process Lett 55, 12017–12037 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-023-11407-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-023-11407-w