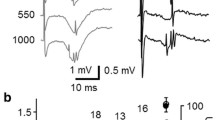
We investigated the effects of muscimol on generation of spike-wave discharges (SWDs) and shortterm plasticity alterations in the somatosensory cortex of WAG/Rij rats. The rats were implanted with a twisted tripolar electrode into the somatosensory cortex and with an intraventricular cannula into the right cerebral ventricle. EEG recordings were made before and after muscimol and saline injections. Paired-pulse stimulations (200 μsec, 100-1000 μA, 0.1 sec–1) were applied to the somatosensory cortex at 50-, 100-, 400-, and 500-msec-long intervals for 50 min. Pharmacological amplification of GABAergic transmission in the somatosensory cortex exerted an inhibitory effect on the thalamo-cortical circuit underlying the generation of spike-wave discharges (SWDs). Ten minutes post-injection of muscimol, paired-pulse facilitation was significantly reduced at 50- and 100-msec-long interpulse intervals (P < 0.05). The data obtained suggest that muscimol suppresses generation of SWDs and changes short-term plasticity via imitation of the effects of GABA in inhibitory synapses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. C. Snead, “Basic mechanisms of generalized absence seizures,” Ann. Neurol., 37, No. 2, 146-157 (1995).
G. D’Arcangelo, M. D’Antuono, G. Biagini, et al., “Thalamocortical oscillations in a genetic model of absence seizures,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 16, No. 12, 2383-2393 (2002).
E. van Luijtelaar and A. Coenen, “Two types of electrocortical paroxysms in an inbred strain of rats,” Neurosci. Lett., 70, No. 3, 393-397 (1986).
G. van Luijtelaar and E. Sitnikova, “Global and focal aspects of absence epilepsy: the contribution of genetic models,” Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 30, No. 7, 983-1003 (2006).
A. Lüttjohann, S. Zhang, R. de Peijper, and G. van Luijtelaar, “Electrical stimulation of the epileptic focus in absence epileptic WAG/Rij rats: assessment of local and network excitability,” Neuroscience, 188, 125-134 (2011).
A. M. L. Coenen and E. van Luijtelaar, “The WAG/Rij rat model for absence epilepsy: age and sex factors,” Epilepsy Res., 1, No. 5, 297-301 (1987).
L. Parsaei, M. Rangchiyan, S. Ahmadi, and M. R. Zarrindast, “GABAA receptors in the dorsal hippocampus are involved in sate-dependent learning induced by lithium in mice,” Iran J. Pharm. Res., 10, No. 1, 127 (2011).
M. Tian and R. L. Macdonald, “The intronic GABRG2 mutation, IVS6+ 2T→ G, associated with childhood absence epilepsy altered subunit mRNA intron splicing, activated nonsense-mediated decay, and produced a stable truncated γ2 subunit,” J. Neurosci., 32, No. 17, 5937-5952 (2012).
C. A. Reid and D. M. Kullmann, “GABA A receptor mutations in epilepsy (Commentary on Lachance, Touchette, et al.),” Eur. J. Neurosci., 34, No. 2, 235, (2011).
H. P. Goodkin, C. Sun, J. L. Yeh, et al., “GABA A receptor internalization during seizures,” Epilepsia, 48, s5, 109-113 (2007).
D. Debanne, N. C. Guerineau, B. Gähwiler, and S. M. Thompson, “Paired-pulse facilitation and depression at unitary synapses in rat hippocampus: quantal fluctuation affects subsequent release,” J. Physiol., 491, No. 1, 163-176 (1996).
C. F. Stevens and Y. Wang, “Facilitation and depression at single central synapses,” Neuron, 14, No. 4, 795-802 (1995).
M. A. Castro-Alamancos and B. W. Connors, “Cellular mechanisms of the augmenting response: short-term plasti-city in a thalamocortical pathway,” J. Neurosci., 16, No. 23, 7742-7756 (1996).
Z. Ataie, S. Babri, M. G. Golzar, et al., “GABA B receptor blockade prevents antiepileptic action of ghrelin in the rat hippocampus,” Adv. Pharm. Bull., 3, No. 2, 353 (2013).
G. Paxinos and C. Watson, The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition, Acad. Press (2006).
T. Baum and F. Becker, “Hypotensive and postural effects of the [gamma]-aminobutyric acid agonist muscimol and of clonidine,” J. Cardiovascul. Pharmacol., 4, No. 2, 165-159 (1982).
Y. Ma and D. A. Prince, “Functional alterations in GABAergic fast-spiking interneurons in chronically injured epileptogenic neocortex,” Neurobiol. Dis., 47, No. 1, 102-113 (2012).
A. Depaulis, M. Vergnes, C. Marescaux, et al., “Evidence that activation of GABA receptors in the substantia nigra suppresses spontaneous spike-and-wave discharges in the rat,” Brain Res., 448, No. 1, 20-29 (1988).
J. C. Mulley, I. E. Scheffer, S. Petrou, and S. F. Berkovic, “Channelopathies as a genetic cause of epilepsy,” Current Opin. Neurol., 16, No. 2, 171-176 (2003).
H. K. Meeren, J. G. Veening, T. A. Möderscheim, et al., “Thalamic lesions in a genetic rat model of absence epilepsy: dissociation between spike-wave discharges and sleep spindles,” Exp. Neurol., 217, No. 1, 25-37(2009).
D. Merlo, C. Mollinari, Y. Inaba, et al., “Reduced GABA B receptor subunit expression and paired-pulse depression in a genetic model of absence seizures,” Neurobiol. Dis., 25, No. 3, 631-641 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nejad, G.G., Vastyanov, R.S., Shahabi, P. et al. Abnormalities in the GABAergic Inhibitory System Leading to the Development of Spike-Wave Discharges in the Somatosensory Cortex of Wag/Rij Rats. Neurophysiology 47, 454–458 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-016-9555-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-016-9555-0