Abstract
Purpose
The phenomenon of radiation therapy (RT) causing regression of targeted lesions as well as lesions outside of the radiation field is known as the abscopal effect and is thought to be mediated by immunologic causes. This phenomena has been described following whole brain radiation (WBRT) and stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) of brain metastasis (BM) in advanced melanoma and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We systematically reviewed the available literature to identify which radiation modality and immunotherapy (IT) combination may elicit the abscopal effect, the optimal timing of RT and IT, and potential adverse effects inherent to the combination of RT and IT.
Methods
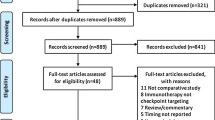
Using PRISMA guidelines, a search of PubMed, Medline, and Web of Science was conducted to identify studies demonstrating the abscopal effect during treatment of NSCLC or melanoma with BM.
Results
598 cases of irradiated BM of melanoma or NSCLC in 18 studies met inclusion criteria. The most commonly administered ITs included PD-1 or CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI), with RT most commonly administered within 3 months of ICI. Synergy between ICI and RT was described in 16 studies including evidence of higher tumor response within and outside of the irradiated field. In the 12 papers (n = 232 patients) that reported objective response rate (ORR) in patients with BM treated with RT and concurrent systemic IT, the non-weighted mean ORR was 49.4%; in the 5 papers (n = 110 patients) that reported ORR for treatment with RT or IT alone, the non-weighted mean ORR was 27.8%. No studies found evidence of significantly increased toxicity in patients receiving RT and ICI.
Conclusion
The combination of RT and ICIs may enhance ICI efficacy and induce more durable responses via the abscopal effect in patients with brain metastases of melanoma or NSCLC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janopaul-Naylor JR, Shen Y, Qian DC, Buchwald ZS (2021) The Abscopal Effect: a review of pre-clinical and clinical advances. Int J Mol Sci https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011061
Abuodeh Y, Venkat P, Kim S (2016) Systematic review of case reports on the abscopal effect. Curr Probl Cancer 40:25–37
D’Andrea MA, Reddy GK (2019) Extracranial abscopal effects induced by brain radiation in advanced lung cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 42:951–957
Aboudaram A, Modesto A, Chaltiel L et al (2017) Concurrent radiotherapy for patients with metastatic melanoma and receiving anti-programmed-death 1 therapy: a safe and effective combination. Melanoma Res 27:485–491
Bassanelli M, Ricciuti B, Giannarelli D et al (2022) Systemic effect of radiotherapy before or after nivolumab in lung cancer: an observational, retrospective, multicenter study. Tumori 108:250–257
Chandra RA, Wilhite TJ, Balboni TA et al (2015) A systematic evaluation of abscopal responses following radiotherapy in patients with metastatic melanoma treated with ipilimumab. Oncoimmunology 4:e1046028
Funck-Brentano E, Baghad B, Fort M et al (2020) Efficacy of late concurrent hypofractionated radiotherapy in advanced melanoma patients failing anti-PD-1 monotherapy. Int J Cancer 147:1707–1714
Galli G, Cavalieri S, Di Guardo L et al (2019) Combination of Immunotherapy and Brain Radiotherapy in metastatic melanoma: a retrospective analysis. Oncol Res Treat 42:186–194
Grimaldi AM, Simeone E, Giannarelli D et al (2014) Abscopal effects of radiotherapy on advanced melanoma patients who progressed after ipilimumab immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 3:e28780
Koller KM, Mackley HB, Liu J et al (2017) Improved survival and complete response rates in patients with advanced melanoma treated with concurrent ipilimumab and radiotherapy versus ipilimumab alone. Cancer Biol Ther 18:36–42
Roger A, Finet A, Boru B et al (2018) Efficacy of combined hypo-fractionated radiotherapy and anti-PD-1 monotherapy in difficult-to-treat advanced melanoma patients. Oncoimmunology 7:e1442166
Saiag P, Molinier R, Roger A et al (2022) Efficacy of large use of combined Hypofractionated Radiotherapy in a cohort of Anti-PD-1 monotherapy-treated Melanoma patients. Cancers 14(17):4069. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174069
Samuel E, Lie G, Balasubramanian A et al (2021) Impact of Radiotherapy on the efficacy and toxicity of anti-PD-1 inhibitors in metastatic NSCLC. Clin Lung Cancer 22:e425–e430
Schoenfeld JD, Mahadevan A, Floyd SR et al (2015) Ipilmumab and cranial radiation in metastatic melanoma patients: a case series and review. J Immunother Cancer 3:50
Singh SA, McDermott DM, Mattes MD (2020) Impact of systemic therapy type and timing on intracranial Tumor Control in patients with Brain Metastasis from Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. World Neurosurg 144:e813–e823
Sumodhee S, Guo L, Bouhlel L et al (2022) Impact of radiotherapy schedule on survival of patients treated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors for advanced melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Radiother 26:1045–1053
Trommer M, Yeo SY, Persigehl T et al (2019) Abscopal effects in Radio-Immunotherapy-Response analysis of metastatic Cancer patients with Progressive Disease under Anti-PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibition. Front Pharmacol 10:511
Umeda Y, Yoshikawa S, Kiniwa Y et al (2021) Real-world efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibody or combined anti-PD-1 plus anti-CTLA-4 antibodies, with or without radiotherapy, in advanced mucosal melanoma patients: a retrospective, multicenter study. Eur J Cancer 157:361–372
Wang P, Yin T, Zhao K et al (2022) Efficacy of single-site radiotherapy plus PD-1 inhibitors vs PD-1 inhibitors for oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148:1253–1261
Formenti SC, Rudqvist N-P, Golden E et al (2018) Radiotherapy induces responses of lung cancer to CTLA-4 blockade. Nat Med 24:1845–1851
Takayama Y, Yano J, Seike R et al (2022) Efficacy of Chemoimmunotherapy in NSCLC Patients with Brain Metastasis with or without prior brain Radiotherapy. Anticancer Res 42:4805–4812
Craig DJ, Nanavaty NS, Devanaboyina M et al (2021) The abscopal effect of radiation therapy. Future Oncol 17:1683–1694
Sharpe AH, Pauken KE (2018) The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat Rev Immunol 18:153–167
Garelli E, Rittmeyer A, Putora PM et al (2019) Abscopal effect in lung cancer: three case reports and a concise review. Immunotherapy 11:1445–1461
Page S, Milner-Watts C, Perna M et al (2020) Systemic treatment of brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer 132:187–198
Colaco RJ, Martin P, Kluger HM et al (2016) Does immunotherapy increase the rate of radiation necrosis after radiosurgical treatment of brain metastases? J Neurosurg 125:17–23
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W et al (2018) PRISMA Extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann Intern Med 169:467–473
Moola S, Munn Z, Tufanaru C et al (2020) Chap. 7: systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In: JBI Manual for evidence synthesis. JBI
Wegner RE, Abel S, D’Amico RS et al (2021) Time from stereotactic radiosurgery to immunotherapy in patients with melanoma brain metastases and impact on outcome. J Neurooncol 152:79–87
De Martino M, Padilla O, Daviaud C et al (2021) Exploiting Radiation Therapy to restore Immune Reactivity of Glioblastoma. Front Oncol 11:671044
Pangal DJ, Yarovinsky B, Cardinal T et al (2022) The abscopal effect: systematic review in patients with brain and spine metastases. Neurooncol Adv 4:vdac132
D’Andrea MA, Reddy GK (2021) Systemic Effects of Radiation Therapy-Induced Abscopal responses in patients with Advanced Lung Cancer. Oncology 99:1–14
Carvalho H, de Villar A RC (2018) Radiotherapy and immune response: the systemic effects of a local treatment. Clinics 73:e557s
Hamilton AJ, Seid J, Verdecchia K, Chuba P (2018) Abscopal Effect after Radiosurgery for Solitary Brain Metastasis from Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Cureus 10:e3777
Galkin MV, Golanov AV, Vetlova E et al (2018) Advanced survival in patients with multiple irradiations for brain melanoma metastases and associated abscopal effect. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.2034
Ishikawa Y, Umezawa R, Yamamoto T et al (2022) Differential abscopal effect in extracranial and intracranial lesions after radiotherapy alone for vertebral bone metastasis of unknown primary: a case report. J Med Case Rep 16:1–12
Parry RV, Chemnitz JM, Frauwirth KA et al (2005) CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 25:9543–9553
Tarhini A, Lo E, Minor DR (2010) Releasing the brake on the immune system: ipilimumab in melanoma and other tumors. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 25:601–613
Ai L, Chen J, Yan H et al (2020) Research Status and Outlook of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:3625–3649
Silk AW, Bassetti MF, West BT et al (2013) Ipilimumab and radiation therapy for melanoma brain metastases. Cancer Med 2:899–906
Shepard MJ, Xu Z, Donahue J et al (2019) Stereotactic radiosurgery with and without checkpoint inhibition for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer to the brain: a matched cohort study. J Neurosurg 26:1–8
Chen L, Douglass J, Kleinberg L et al (2018) Concurrent Immune checkpoint inhibitors and stereotactic radiosurgery for Brain Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Melanoma, and renal cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100:916–925
Shen CJ, Kummerlowe MN, Redmond KJ et al (2016) Stereotactic radiosurgery: treatment of Brain Metastasis without interruption of systemic therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95:735–742
Kim JM, Miller JA, Kotecha R et al (2017) The risk of radiation necrosis following stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent systemic therapies. J Neurooncol 133:357–368
Doyen J, Picard A, Naghavi AO et al (2017) Clinical outcomes of metastatic melanoma treated with checkpoint inhibitors and Multisite Radiotherapy. JAMA Dermatol 153:1056–1059
Luke JJ, Lemons JM, Karrison TG et al (2018) Safety and clinical activity of Pembrolizumab and Multisite Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. J Clin Oncol 36:1611–1618
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R et al (2015) Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 372:2018–2028
Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA et al (2019) Five-year overall survival for patients with Advanced non–small-cell lung Cancer treated with Pembrolizumab: results from the phase I KEYNOTE-001 study. J Clin Oncol 37:2518–2527
Leighl NB, Hellmann MD, Hui R et al (2019) Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-001): 3-year results from an open-label, phase 1 study. Lancet Respir Med 7:347–357
Helis CA, Hughes RT, Glenn CW et al (2020) Predictors of adverse Radiation Effect in Brain Metastasis Patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery and Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 108:295–303
Martin AM, Cagney DN, Catalano PJ et al (2018) Immunotherapy and Symptomatic Radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases treated with Stereotactic Radiation. JAMA Oncol 4:1123–1124
Lehrer EJ, Peterson J, Brown PD et al (2019) Treatment of brain metastases with stereotactic radiosurgery and immune checkpoint inhibitors: an international meta-analysis of individual patient data. Radiother Oncol 130:104–112
Kohutek ZA, Yamada Y, Chan TA et al (2015) Long-term risk of radionecrosis and imaging changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 125:149–156
Badrigilan S, Meola A, Chang SD et al (2022) Stereotactic radiosurgery with immune checkpoint inhibitors for brain metastases: a meta-analysis study. Br J Neurosurg 4:1–11
Yang L, Liu L, Wu X et al (2020) Hypofractionated radiation therapy with versus without immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with brain metastases: a meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol 80:106148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: all authors. Acquisition of data: all authors. Drafting the article: T, D, N. Critically revising the article: all authors. Reviewed submitted version of manuscript: all authors. Approved the final version of the manuscript on behalf of all authors: DA. Study supervision: DA.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tracz, J.A., Donnelly, B.M., Ngu, S. et al. The abscopal effect: inducing immunogenicity in the treatment of brain metastases secondary to lung cancer and melanoma. J Neurooncol 163, 1–14 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04312-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04312-8