Abstract
Purpose
Life expectancy continues to increase for patients with brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). The present study sought to retrospectively analyze brain metastasis patients who have survived 2 years or more, and assess for what factors may predict for a final brain metastasis velocity (BMV) of zero.
Methods
This was a single-institution retrospective study of 300 patients treated with SRS from 2001 to 2019 for brain metastases who survived greater than 2 years after first SRS. Final BMV is calculated by summing all metastases through the observed time divided by the total time in years. A BMV of zero is defined as at least 2 years of imaging follow-up without distant brain failure (DBF).
Results
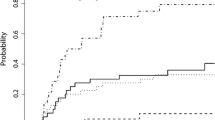
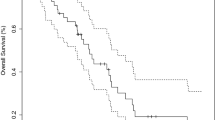
Median age at first SRS is 61 (IQR: 53, 70). Kaplan-Meier estimated median overall survival is 4.9 years and time to DBF is 1.5 years (95% CI 1.2, 2.0). Twenty-eight (9.3%) patients underwent subsequent WBRT. One hundred and one (33.7%) patients never had any further brain metastases (BMV = 0) at a median follow-up time of 3.3 years. Median BMV is 0.4 (IQR: 0, 1.4). Distant brain failures reach a plateau at 4 years where the cumulative incidence of DBF is 82%. 70% of first time DBFs have occurred by 2 years. Factors significantly associated with a BMV of zero include fewer brain metastases at first SRS (HR 1.1; p = 0.0004) and Caucasian race (HR 1.5; p = 0.03).
Conclusion
Approximately one third of brain metastasis patients who live beyond 2 years after initial SRS have a BMV of zero. DBFs appear to reach a plateau at 4 years. Factors significantly associated with a BMV of zero include Caucasian race and having had a single brain metastasis at first SRS.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Research data are stored in an institutional repository and will be shared upon request to the corresponding.
References
Devoid H-M, McTyre ER, Page BR et al (2016) Recent advances in radiosurgical management of brain metastases. Front Biosci 8:203–214
Lester SC, Taksler GB, Kuremsky JG et al (2014) Clinical and economic outcomes of patients with brain metastases based on symptoms: an argument for routine brain screening of those treated with upfront radiosurgery. Cancer 120:433–441
Lanier CM, Hughes R, Ahmed T et al (2019) Immunotherapy is associated with improved survival and decreased neurologic death after SRS for brain metastases from lung and melanoma primaries. Neurooncol Pract 6:402–409
Mu F, Lucas JT Jr, Watts JM et al (2015) Tumor resection with carmustine wafer placement as salvage therapy after local failure of radiosurgery for brain metastasis. J Clin Neurosci 22:561–565
Brown PD, Jaeckle K, Ballman KV et al (2016) Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 316:401–409
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR et al (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044
Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH et al (2017) Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC·3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1049–1060
Soike MH, Hughes RT, Farris M et al (2019) Does stereotactic radiosurgery have a role in the management of patients presenting with 4 or more brain metastases? Neurosurgery 84:558–566
Hughes RT, Masters AH, McTyre ER et al (2019) Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 104:1091–1098
Dohm A, Su J, McTyre ER et al (2019) Identification of CD37, cystatin A, and IL-23A gene expression in association with brain metastasis: analysis of a prospective trial. Int J Biol Mark 31:90–97
Ayala-Peacock DN, Peiffer AM, Lucas JT et al (2014) A nomogram for predicting distant brain failure in patients treated with gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery without whole brain radiotherapy. NeuroOncology 16:1283–1288
McTyre E, Ayala-Peacock D, Contessa J et al (2018) Multi-institutional competing risks analysis of distant brain failure and salvage patterns after upfront radiosurgery without whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastasis. Ann Oncol 29:497–503
Ayala-Peacock DN, Attia A, Braunstein SE et al (2017) Prediction of new brain metastases after radiosurgery: validation and analysis of performance of a multi-institutional nomogram. J Neurooncol 135:403–411
Gorovets D, Ayala-Peacock D, Tybor DJ et al (2017) Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 97:246–253
Farris M, McTyre ER, Cramer CK et al (2017) Brain metastasis velocity: a novel prognostic metric predictive of overall survival and freedom from whole-brain radiation therapy after distant brain failure following upfront radiosurgery alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 98:131–141
McTyre ER, Soike MH, Farris M et al (2020) Multi-institutional validation of brain metastasis velocity, a recently defined predictor of outcomes following stereotactic radiosurgery. Radiother Oncol 142:168–174
Yamamoto M, Aiyama H, Koiso T et al (2019) Validity of a recently proposed prognostic grading index, brain metastasis velocity, for patients with brain metastasis undergoing multiple radiosurgical procedures. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 103:631–637
Fritz C, Borsky K, Stark LS et al (2018) Repeated courses of radiosurgery for new brain metastases to defer whole brain radiotherapy: feasibility and outcome with validation of the new prognostic metric brain metastasis velocity. Front Oncol 8:551
Gogineni E, Vargo JA, Glaser SM et al (2018) Long-term survivorship following stereotactic radiosurgery alone for brain metastases: risk of intracranial failure and implications for surveillance and counseling. Neurosurgery 83:203–209
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90–05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Kotecha R, Vogel S, Suh JH et al (2016) A cure is possible: a study of 10-year survivors of brain metastases. J Neurooncol 129:545–555
Johnson AG, Ruiz J, Hughes R et al (2015) Impact of systemic targeted agents on the clinical outcomes of patients with brain metastases. Oncotarget 6:18945–18955
LeCompte MC, Hughes RT, Farris M et al (2020) Impact of brain metastasis velocity on neurologic death for brain metastasis patients experiencing distant brain failure after initial stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 146:285–292
Sawrie SM, Guthrie BL, Spencer SA et al (2008) Predictors of distant brain recurrence for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:181–186
Sundaresan N, Galicich JH (1985) Surgical treatment of single brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Invest 3:107–113
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15:387–395
Niemiec M, Głogowski M, Tyc-Szczepaniak D et al (2011) Characteristics of long-term survivors of brain metastases from lung cancer. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 16:49–53
Alphonse-Sullivan N, Taksler GB, Lycan T et al (2017) Sociodemographic predictors of patients with brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Oncotarget 8:101005–101011
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection was performed by CML, MD Material preparation was performed by CML, MD and MDC, MD Analysis was performed by SI, MS The first draft of the manuscript was written by MDC, MD and CML, MD All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
Financial interests: Adrian W. Laxton, M.D. has received a consulting fee from Monteris Medical. There are no other financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This is an observational study. The IRB Research Ethics Committee has confirmed that no ethical approval is required.
Consent to participate
Due to the retrospective and observational nature of this study, the IRB Research Ethics Committee has confirmed no consent to participate is required.
Consent to publish
Due to the retrospective and observational nature of this study, the IRB Research Ethics Committee has confirmed no consent to publish is required.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lanier, C.M., Pearce, J., Isom, S. et al. Long term survivors of stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: do distant brain failures reach a plateau and what factors are associated with a brain metastasis velocity of zero?. J Neurooncol 160, 643–648 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04183-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04183-5