Abstract
Background
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) to the surgical bed of resected brain metastases is now considered the standard of care due to its advantages over whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT). Despite the upward trend in SRS adoption since the 2000s, disparities have been reported suggesting that socio-economic factors can influence SRS utilization.
Objective
To analyze recent trends in SRS use and identify factors that influence treatment.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study with the Optum Commercial Claims and Encounters Database and included all patients from 2004 to 2021 who received SRS or WBRT within 60 days after resection of tumors metastatic to the brain.
Results
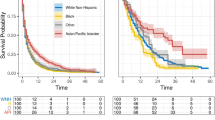
A total of 3495 patients met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. There were 1998 patients in the SRS group and 1497 patients in the WBRT group. SRS use now supersedes WBRT by a wide margin. Lung, breast and colon were the most common sites of primary tumor. Although we found no significant differences based on race among the treatment groups, patients with annual household income greater than $75,000 and those with some college or higher education are significantly more likely to receive SRS (OR 1.44 and 1.30; 95% CI 1.18–1.76 and 1.08–1.56; P = 0.001 and 0.005, respective). Patients with Elixhauser Comorbidity Index of three or more were significantly more likely to receive SRS treatment.
Conclusion
The use of post-surgical SRS for brain metastasis has increased significantly over time, however education and income were associated with differential SRS utilization.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPT:
-
Current procedural terminology
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- SRS:
-
Stereo-tactic radiosurgery
- WBRT:
-
Whole brain radiotherapy
- QoL:
-
Quality of life
References
Chin AL, Li G, Gephart MH et al (2020) Stereotactic radiosurgery after resection of brain metastases: changing patterns of care in the United States. World Neurosurg 144:e797–e806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.09.085
Trifiletti DM, Sheehan JP, Grover S et al (2017) National trends in radiotherapy for brain metastases at time of diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Neurosci 45:48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2017.08.028
Soliman H, Das S, Larson DA, Sahgal A (2016) Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in the modern management of patients with brain metastases. Oncotarget 7(11):12318–12330. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7131
Sheehan JP, Grills I, Chiang VL et al (2018) Quality of life outcomes for brain metastasis patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery: pre-procedural predictive factors from a prospective national registry. J Neurosurg 131(6):1848–1854. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.8.Jns181599
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR et al (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10(11):1037–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(09)70263-3
Niranjan A, Monaco E, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD (2019) Guidelines for multiple brain metastases radiosurgery. Prog Neurol Surg 34:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493055
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29(2):134–141. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2010.30.1655
Bunevicius A, Lavezzo K, Shabo L, McClure J, Sheehan JP (2020) Quality-of-life trajectories after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Neurosurg 134(6):1791–1799. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.4.Jns20788
Minniti G, Soltys SG, Halasz LM et al (2018) Stereotactic radiosurgery for resected brain metastases: new evidence supports a practice shift, but questions remain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100(3):535–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.08.024
Shi S, Sandhu N, Jin MC et al (2020) Stereotactic radiosurgery for resected brain metastases: single-institutional experience of over 500 cavities. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 106(4):764–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.11.022
Soltys SG, Adler JR, Lipani JD et al (2008) Stereotactic radiosurgery of the postoperative resection cavity for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70(1):187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.06.068
Brown PD, Jaeckle K, Ballman KV et al (2016) Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 316(4):401–409. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.9839
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295(21):2483–2491. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.295.21.2483
Warsi NM, Karmur BS, Brar K et al (2020) The role of stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of brain metastases from a health-economic perspective: a systematic review. Neurosurgery 87(3):484–497. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyaa075
Kann BH, Park HS, Johnson SB, Chiang VL, Yu JB (2017) Radiosurgery for brain metastases: changing practice patterns and disparities in the United States. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 15(12):1494–1502. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2017.7003
De la Garza RR, Benton JA, Gelfand Y et al (2020) Racial disparities in clinical presentation, type of intervention, and in-hospital outcomes of patients with metastatic spine disease: an analysis of 145,809 admissions in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol 68:101792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2020.101792
Hung B, Pennington Z, Hersh AM et al (2021) Impact of race on nonroutine discharge, length of stay, and postoperative complications after surgery for spinal metastases. J Neurosurg Spine 5:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.7.Spine21287
Poorman GW, Moon JY, Wang C et al (2018) Rates of mortality in lumbar spine surgery and factors associated with its occurrence over a 10-year period: a study of 803,949 patients in the nationwide inpatient sample. Int J Spine Surg 12(5):617–623. https://doi.org/10.14444/5076
Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH et al (2017) Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC.3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(8):1049–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30441-2
Mahajan A, Ahmed S, McAleer MF et al (2017) Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery versus observation for completely resected brain metastases: a single-centre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(8):1040–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30414-X
Lester-Coll NH, Dosoretz AP, Magnuson WJ, Laurans MS, Chiang VL, Yu JB (2016) Cost-effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery versus whole-brain radiation therapy for up to 10 brain metastases. J Neurosurg 125(Suppl 1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.7.GKS161499
Ascha MS, Funk K, Sloan AE, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2020) Disparities in the use of stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of lung cancer brain metastases: a SEER-Medicare study. Clin Exp Metastasis 37(1):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-019-10005-2
Modh A, Doshi A, Burmeister C, Elshaikh MA, Lee I, Shah M (2019) Disparities in the use of single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Cureus 11(2):e4031. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.4031
Halasz LM, Weeks JC, Neville BA, Taback N, Punglia RS (2013) Use of stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer in the United States. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85(2):e109–e116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.08.007
Haque W, Verma V, Butler EB, Teh BS (2018) Utilization of stereotactic radiosurgery for renal cell carcinoma brain metastases. Clin Genitourin Cancer 16(4):e935–e943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2018.03.015
Lippitz B, Lindquist C, Paddick I, Peterson D, O’Neill K, Beaney R (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of brain metastases: the current evidence. Cancer Treat Rev 40(1):48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.05.002
Kim E, McClelland S 3rd, Jaboin JJ, Attia A (2021) Disparities in patterns of conventional versus stereotactic body radiotherapy in the treatment of spine metastasis in the United States. J Palliat Care 36(2):130–134. https://doi.org/10.1177/0825859720982204
Mazor MB, Li L, Morillo J, Allen OS, Wisnivesky JP, Smith CB (2022) Disparities in supportive care needs over time between racial and ethnic minority and non-minority patients with advanced lung cancer. J Pain Symptom Manage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2021.12.007
Mainwaring W, Bowers J, Pham N et al (2019) Stereotactic radiosurgery versus whole brain radiation therapy: a propensity score analysis and predictors of care for patients with brain metastases from breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 19(2):e343–e351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clbc.2018.11.001
McClelland S 3rd, Page BR, Jaboin JJ, Chapman CH, Deville C Jr, Thomas CR Jr (2017) The pervasive crisis of diminishing radiation therapy access for vulnerable populations in the United States, part 1: African-American patients. Adv Radiat Oncol 2(4):523–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2017.07.002
Beydoun HA, Huang S, Beydoun MA, Eid SM, Zonderman AB (2022) Interrupted time-series analysis of stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases before and after the affordable care act. Cureus 14(1):e21338. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.21338
McClelland S 3rd, Degnin C, Chen Y, Watson GA, Jaboin JJ (2019) Impact of the American tax payer relief act on stereotactic radiosurgery utilization in the united States. J Neurooncol 145(1):159–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03283-z
Funding
Anand Veeravagu, MD receives support from the Arkadi Khulman Fund. David Dadey, MD, PhD receives support from the Stanford Neurosurgery Equity Seed Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DD: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, project administration. AR: methodology, formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft. GH: writing—methodology, original draft. EP: writing—review & editing JA: conceptualization, writing—review & editing. AV: conceptualization, writing—review & editing, supervision, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
John Adler, MD is an employee of Zap Surgical Systems Inc. Erqi L. Pollom, MD, MS is on the advocacy board for Vysioneer and receives research funding from Genentech.
Ethical approval
This observational study was not considered human subject research and received exemption from Institutional Review Board approval at our institution.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dadey, D.Y.A., Rodrigues, A., Haider, G. et al. Impact of socio-economic factors on radiation treatment after resection of metastatic brain tumors: trends from a private insurance database. J Neurooncol 158, 445–451 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04031-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04031-6