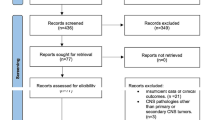
Abstract
Purpose
Both laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) and bevacizumab have been used successfully to treat radiation necrosis (RN) after radiation for brain metastases. Our purpose is to compare pre-treatment patient characteristics and outcomes between the two treatment options.
Methods
Single-institution retrospective chart review identified brain metastasis patients who developed RN between 2011 and 2018. Pre-treatment factors and treatment responses were compared between those treated with LITT versus bevacizumab.
Results
Twenty-five patients underwent LITT and 13 patients were treated with bevacizumab. The LITT cohort had a longer overall survival (median 24.8 vs. 15.2 months for bevacizumab, p = 0.003) and trended to have a longer time to local recurrence (median 12.1 months vs. 2.0 for bevacizumab), although the latter failed to achieve statistical significance (p = 0.091). LITT resulted in an initial increase in lesional volume compared to bevacizumab (p < 0.001). However, this trend reversed in the long term follow-up, with LITT resulting in a median volume decrease at 1 year post-treatment of − 64.7% (range − 96.0% to + > 100%), while bevacizumab patients saw a median volume increase of + > 100% (range − 63.0% to + > 100%), p = 0.010.
Conclusions
Our study suggests that patients undergoing LITT for RN have longer overall survival and better long-term lesional volume reduction than those treated with bevacizumab. However, it remains unclear whether our findings are due only to a difference in efficacy of the treatments or the implications of selection bias.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- KPS:
-
Karnofsky performance score
- LITT:
-
Laser interstitial thermal therapy
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- RN:
-
Radiation necrosis
- SRS:
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery
- WBRT:
-
Whole brain radiation therapy
References
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Rotman M, Mehta MP, Curran WJ Jr (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet (London, England) 363(9422):1665–1672. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(04)16250-8
Glantz MJ, Burger PC, Friedman AH, Radtke RA, Massey EW, Schold SC Jr (1994) Treatment of radiation-induced nervous system injury with heparin and warfarin. Neurology 44(11):2020–2027. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.44.11.2020
Miyatake S, Nonoguchi N, Furuse M, Yoritsune E, Miyata T, Kawabata S, Kuroiwa T (2015) Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of radiation necrosis in the brain. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 55(1):50–59. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.ra.2014-0188
Sneed PK, Mendez J, Vemer-van den Hoek JG, Seymour ZA, Ma L, Molinaro AM, Fogh SE, Nakamura JL, McDermott MW (2015) Adverse radiation effect after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: incidence, time course, and risk factors. J Neurosurg 123(2):373–386. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.Jns141610
Levin VA, Bidaut L, Hou P, Kumar AJ, Wefel JS, Bekele BN, Grewal J, Prabhu S, Loghin M, Gilbert MR, Jackson EF (2011) Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of bevacizumab therapy for radiation necrosis of the central nervous system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79(5):1487–1495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.12.061
Sloan AE, Ahluwalia MS, Valerio-Pascua J, Manjila S, Torchia MG, Jones SE, Sunshine JL, Phillips M, Griswold MA, Clampitt M, Brewer C, Jochum J, McGraw MV, Diorio D, Ditz G, Barnett GH (2013) Results of the NeuroBlate System first-in-humans Phase I clinical trial for recurrent glioblastoma: clinical article. J Neurosurg 118(6):1202–1219. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.1.Jns1291
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0. (2017) National Cancer Institute. https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf. 2020
Lin NU, Lee EQ, Aoyama H, Barani IJ, Barboriak DP, Baumert BG, Bendszus M, Brown PD, Camidge DR, Chang SM, Dancey J, de Vries EG, Gaspar LE, Harris GJ, Hodi FS, Kalkanis SN, Linskey ME, Macdonald DR, Margolin K, Mehta MP, Schiff D, Soffietti R, Suh JH, van den Bent MJ, Vogelbaum MA, Wen PY (2015) Response assessment criteria for brain metastases: proposal from the RANO group. Lancet Oncol 16(6):e270–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70057-4
Furuse M, Nonoguchi N, Kawabata S, Miyatake S, Kuroiwa T (2015) Delayed brain radiation necrosis: pathological review and new molecular targets for treatment. Med Mol Morphol 48(4):183–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-015-0123-2
Carpentier A, McNichols RJ, Stafford RJ, Itzcovitz J, Guichard JP, Reizine D, Delaloge S, Vicaut E, Payen D, Gowda A, George B (2008) Real-time magnetic resonance-guided laser thermal therapy for focal metastatic brain tumors. J Neurosurg: https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000335007.07381
Torres-Reveron J, Tomasiewicz HC, Shetty A, Amankulor NM, Chiang VL (2013) Stereotactic laser induced thermotherapy (LITT): a novel treatment for brain lesions regrowing after radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 113(3):495–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1142-2
Ahluwalia M, Barnett GH, Deng D, Tatter SB, Laxton AW, Mohammadi AM, Leuthardt E, Chamoun R, Judy K, Asher A, Essig M, Dietrich J, Chiang VL (2018) Laser ablation after stereotactic radiosurgery: a multicenter prospective study in patients with metastatic brain tumors and radiation necrosis. J Neurosurg 130(3):804–811. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.11.Jns171273
Chaunzwa TL, Deng D, Leuthardt EC, Tatter SB, Mohammadi AM, Barnett GH, Chiang VL (2018) Laser thermal ablation for metastases failing radiosurgery: a multicentered retrospective study. Neurosurgery 82(1):56–63. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyx142
Rao MS, Hargreaves EL, Khan AJ, Haffty BG, Danish SF (2014) Magnetic resonance-guided laser ablation improves local control for postradiosurgery recurrence and/or radiation necrosis. J Neurosurg: https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000000332
Hong CS, Deng D, Vera A, Chiang VL (2019) Laser-interstitial thermal therapy compared to craniotomy for treatment of radiation necrosis or recurrent tumor in brain metastases failing radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 142(2):309–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03097-z
Kim JH, Chung YG, Kim CY, Kim HK, Lee HK (2004) Upregulation of VEGF and FGF2 in normal rat brain after experimental intraoperative radiation therapy. J Korean Med Sci 19(6):879–886. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.6.879
Nonoguchi N, Miyatake S, Fukumoto M, Furuse M, Hiramatsu R, Kawabata S, Kuroiwa T, Tsuji M, Fukumoto M, Ono K (2011) The distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor-producing cells in clinical radiation necrosis of the brain: pathological consideration of their potential roles. J Neurooncol 105(2):423–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0610-9
Francisco S, Genentech CA (2018) US Food and Drug Administration website. J Neurooncol. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.11111
Boothe D, Young R, Yamada Y, Prager A, Chan T, Beal K (2013) Bevacizumab as a treatment for radiation necrosis of brain metastases post stereotactic radiosurgery. Neuro-oncology 15(9):1257–1263. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not085
Carpentier A, McNichols RJ, Stafford RJ, Guichard JP, Reizine D, Delaloge S, Vicaut E, Payen D, Gowda A, George B (2011) Laser thermal therapy: real-time MRI-guided and computer-controlled procedures for metastatic brain tumors. Lasers Surg Med 43(10):943–950. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.21138
Torcuator R, Zuniga R, Mohan YS, Rock J, Doyle T, Anderson J, Gutierrez J, Ryu S, Jain R, Rosenblum M, Mikkelsen T (2009) Initial experience with bevacizumab treatment for biopsy confirmed cerebral radiation necrosis. J Neurooncol 94(1):63–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9801-z
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Nanthiya Sujijantarat, MD, Christopher S. Hong, MD, Kent A. Owusu, PharmD, BCCCP, BCPS, Aladine A. Elsamadicy, MD, Joseph P. Antonios, MD, PhD, and Andrew B. Koo, MD. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Nanthiya Sujijantarat, MD, and edited by Veronica L. Chiang, MD and Joachim Baehring, MD. All authors commented on subsequent versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The senior author of this paper (VC) is a consultant for Monteris Medical Inc. (Minnesota, USA) and Clearpoint Neuro (California, USA). No other authors have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sujijantarat, N., Hong, C.S., Owusu, K.A. et al. Laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) vs. bevacizumab for radiation necrosis in previously irradiated brain metastases. J Neurooncol 148, 641–649 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03570-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03570-0