Abstract
Background
Group 3 tumors account for approximately 25–30% of medulloblastomas and have the worst prognosis. UAB30 is a novel synthetic rexinoid shown to have limited toxicities in humans and significant efficacy in the pediatric neuroectodermal tumor, neuroblastoma. We hypothesized that treatment with UAB30 would decrease tumorigenicity in medulloblastoma patient-derived xenografts (PDXs).
Methods
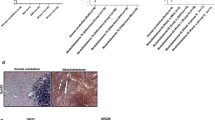
Three group 3 medulloblastoma PDXs (D341, D384 and D425) were utilized. Cell viability, proliferation, migration and invasion assays were performed after treatment with UAB30 or 13-cis-retinoic acid (RA). Cell cycle analysis was completed using flow cytometry. A flank model, a cerebellar model, and a model of leptomeningeal metastasis using human medulloblastoma PDX cells was used to assess the in vivo effects of UAB30 and RA.
Results
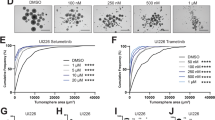
UAB30 treatment led to cell differentiation and decreased medulloblastoma PDX cell viability, proliferation, migration and invasion and G1 cell cycle arrest in all three PDXs similar to RA. UAB30 and RA treatment of mice bearing medulloblastoma PDX tumors resulted in a significant decrease in tumor growth and metastasis compared to vehicle treated animals.
Conclusions
UAB30 decreased viability, proliferation, and motility in group 3 medulloblastoma PDX cells and significantly decreased tumor growth in vivo in a fashion similar to RA, suggesting that further investigations into the potential therapeutic application of UAB30 for medulloblastoma are warranted.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T, Eberhart CG, Mack S, Bouffet E, Clifford SC, Hawkins CE, French P, Rutka JT, Pfister S, Taylor MD (2011) Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 29:1408–1414
Kool M, Korshunov A, Remke M, Jones DT, Schlanstein M, Northcott PA, Cho YJ, Koster J, Schouten-van Meeteren A, van Vuurden D, Clifford SC, Pietsch T, von Bueren AO, Rutkowski S, McCabe M, Collins VP, Bäcklund ML, Haberler C, Bourdeaut F, Delattre O, Doz F, Ellison DW, Gilbertson RJ, Pomeroy SL, Taylor MD, Lichter P, Pfister SM (2012) Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: an international meta-analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol 123:473–484
Cho YJ, Tsherniak A, Tamayo P, Santagata S, Ligon A, Greulich H, Berhoukim R, Amani V, Goumnerova L, Eberhart CG, Lau CC, Olson JM, Gilbertson RJ, Gajjar A, Delattre O, Kool M, Ligon K, Meyerson M, Mesirov JP, Pomeroy SL (2011) Integrative genomic analysis of medulloblastoma identifies a molecular subgroup that drives poor clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol 29:1424–1430
Eberhart CG (2012) Three down and one to go: modeling medulloblastoma subgroups. Cancer Cell 21:137–138
Palmer SL, Reddick WE, Gajjar A (2007) Understanding the cognitive impact on children who are treated for medulloblastoma. J Pediatr Psychol 2:1040–1049
Diller L, Chow EJ, Gurney JG, Hudson MM, Kadin-Lottick NS, Kawashima TI, Leisenring WM, Meacham LR, Mertens AC, Mulrooney DA, Oeffinger KC, Packer RJ, Robison LL, Sklar CA (2009) Chronic disease in the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study cohort: a review of published findings. J Clin Oncol 27:2339–2355
Ying M, Wang S, Sang Y, Sun P, Lal B, Goodwin CR, Guerrero-Cazares H, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Laterra J, Xia S (2011) Regulation of glioblastoma stem cells by retinoic acid: role for Notch pathway inhibition. Oncogene 30:3454–3467
Bai R, Siu IM, Tyler BM, Staedtke V, Gallia GL, Riggins GJ (2010) Evaluation of retinoic acid therapy for OTX2-positive medulloblastomas. Neuro Oncol 12:655–663
Di C, Liao S, Adamson DC, Parrett TJ, Broderick DK, Shi Q, Lengauer C, Cummins JM, Velculescu VE, Fults DW, McLendon RE, Bigner DD, Yan H (2005) Identification of OTX2 as a medulloblastoma oncogene whose product can be targeted by all-trans retinoic acid. Cancer Res 65:919–924
Karmakar S, Banik NL, Ray SK (2008) Combination of all-trans retinoic acid and paclitaxel-induced differentiation and apoptosis in human glioblastoma U87MG xenografts in nude mice. Cancer 112:596–607
Karmakar S, Banik NL, Patel SJ, Ray SK (2007) Combination of all-trans retinoic acid and taxol regressed glioblastoma T98G xenografts in nude mice. Apoptosis 12:2077–2087
Spiller SE, Ditzler SH, Pullar BJ, Olson JM (2008) Response of preclinical medulloblastoma models to combination therapy with 13-cis-retinoic acid and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA). J Neurooncol 87:133–141
David M, Hodak E. Lowe NJ (1988) Adverse effects of retinoids. Med Toxicol Advers Drug Exp 3:273–288
Muccio DD, Brouillette WJ, Breitman TR, Taimi M, Emanuel PD, Zhang X, Chen G, Sani BP, Venepally P, Reddy L, Alam M, Simpson-Herren L, Hill DL (1998) Conformationally defined retinoic acid analogues. 4. Potential new agents for acute promyelocytic and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemias. J Med Chem 41:1679–1687
Grubbs CJ, Hill DL, Bland KI, Beenken SW, Lin TH, Eto I, Atigadda VR, Vines KK, Brouillette WJ, Muccio DD (2003) 9cUAB30, an RXR specific retinoid, and/or tamoxifen in the prevention of methylnitrosourea-induced mammary cancers. Cancer Lett 201:17–24
Wu L, Chaudhary SC, Atigadda VR, Belyaeva OV, Harville SR, Elmets CA, Muccio DD, Athar M, Kedishvili NY (2016) Retinoid X receptor agonists upregulate genes responsible for the biosynthesis of all-trans-retinoic acid in human epidermis. PLoS ONE 11:e0153556
Vedell PT, Lu Y, Grubbs CJ, Yin Y, Jiang H, Bland KI, Muccio DD, Cvetkovic D, You M, Lubet R (2013) Effects on gene expression in rat liver after administration of RXR agonists: UAB30, 4-methyl-UAB30, and Targretin (Bexarotene). Mol Pharmacol 83:698–708
Kolesar JM, Hoel R, Pomplun M, Havighurst T, Stublaski J, Wollmer B, Krontiras H, Brouillette W, Muccio D, Kim K, Grubbs CJ, Bailey HE (2010) A pilot, first-in-human, pharmacokinetic study of 9cUAB30 in healthy volunteers. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 3:1565–1570
Waters AM, Stewart JE, Atigadda VR, Mroczek-Musulman E, Muccio DD, Grubbs CJ, Beierle EA (2015) Preclinical evaluation of a novel RXR agonist for the treatment of neuroblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther 14:1559–1569
Waters AM, Stewart JE, Atigadda VR, Mroczek-Musulman E, Muccio DD, Grubbs CJ, Beierle EA (2016) Preclinical evaluation of UAB30 in pediatric renal and hepatic malignancies. Mol Cancer Ther 15:911–921
Snuderl M, Batista A, Kirkpatrick ND, Ruiz de Almodovar C, Riedemann L, Walsh EC, Anolik R, Huang Y, Martin JD, Kamoun W, Knevels E, Schmidt T, Farrar CT, Vakoc BJ, Mohan N, Chung E, Roberge S, Peterson T, Bais C, Zhelyazkova BH, Yip S, Hasselblatt M, Rossig C, Niemeyer E, Ferrara N, Klagsbrun M, Duda DG, Fukumura D, Xu L, Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2013) Targeting placental growth factor/neuropilin 1 pathway inhibits growth and spread of medulloblastoma. Cell 152:1065–1076
Friedman GK, Moore BP, Nan L, Kelly VM, Etminan T, Langford CP, Xu H, Han X, Markert JM, Beierle EA, Gillespie GY (2016) Pediatric medulloblastoma xenografts including molecular subgroup 3 and CD133 + and CD15 + cells are sensitive to killing by oncolytic herpes simplex viruses. Neuro Oncol 18:227–235
He XM, Skapek SX, Wikstrand CJ, Friedman HS, Trojanowski JQ, Kemshead JT, Coakham HB, Bigner SH, Bigner DD (1989) Phenotypic analysis of four human medulloblastoma cell lines and transplantable xenografts. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 48:48–68
He XM, Wikstrand CJ, Friedman HS, Bigner SH, Pleasure S, Trojanowski JQ, Bigner DD (1991) Differentiation characteristics of newly established medulloblastoma cell lines (D384 Med, D425 Med, and D458 Med) and their transplantable xenografts. Lab Invest 64:833–843
Atigadda VR, Vines KK, Grubbs CJ, Hill DL, Beenken SL, Bland KI, Brouillette WJ, Muccio DD (2003) Conformationally defined retinoic acid analogues. 5. Large-scale synthesis and mammary cancer chemopreventive activity for (2E,4E,6Z,8E)-8-(3′,4′-dihydro-1′(2′H)-naphthalen-1′-ylidene)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6-octatrienoic acid (9cUAB30). J Med Chem 46:3766–3769
Shah N, Wang J, Selich-Anderson J, Graham G, Siddiqui H, Li X, Khan J, Toretsky J (2014) PBX1 is a favorable prognostic biomarker as it modulates 13-cis retinoic acid-mediated differentiation in neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 20:4400–4412
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Lindeblad M, Kapetanovic IM, Kabirov KK, Dinger N, Mankovskaya I, Morrisey R, Martín-Jiménez T, Lyubimov A (2011) Assessment of oral toxicity and safety of 9-cis-UAB30, a potential chemopreventive agent, in rat and dog studies. Drug Chem Toxicol 34:300–310
Walker K, Hjelmeland A (2014) Method for efficient transduction of cancer stem cells. J Cancer Stem Cell Res. https://doi.org/10.14343/JCSCR.2014.2e1008
Studebaker AW, Hutzen B, Pierson CR, Russell SJ, Galanis E, Raffel C (2012) Oncolytic measles virus prolongs survival in a murine model of cerebral spinal fluid-disseminated medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol 14:459–470
Gudas LJ, Wagner JA (2011) Retinoids regulate stem cell differentiation. J Cell Physiol 226:322–330
Robson JA, Sidell N (1985) Ultrastructural features of a human neuroblastoma cell line treated with retinoic acid. Neuroscience 14:1149–1162
Miloso M, Villa D, Crimi M, Galbiati S, Donzelli E, Nicolini G, Tredici G (2004) Retinoic acid-induced neuritogenesis of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells is ERK independent and PKC dependent. J Neurosci Res 75:241–252
Qiao J, Paul P, Lee S, Qiao L, Josifi E, Tiao JR, Chung DH (2012) PI3K/AKT and ERK regulate retinoic acid-induced neuroblastoma cellular differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 424:421–426
Annabi B, Rojas-Sutterlin S, Laflamme C, Lachambre MP, Rolland Y, Sartelet H, Béliveau R (2008) Tumor environment dictates medulloblastoma cancer stem cell expression and invasive phenotype. Mol Cancer Res 6:907–916
Di Martino D, Avignolo C, Marsano B, Di Vinci A, Cara A, Giaretti W, Tonini GP (1990) Neurite outgrowth and cell cycle kinetic changes induced by cis-diamminedichloroplatinum II and retinoic acid in a human neuroblastoma cell line. Cancer Lett 52:101–106
Chang Q, Chen Z, You J, McNutt MA, Zhang T, Han Z, Zhang X, Gong E, Gu J (2007) All-trans-retinoic acid induces cell growth arrest in a human medulloblastoma cell line. J Neurooncol 84:263–267
Clark O, Daga S, Stoker AW (2013) Tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors combined with retinoic acid can enhance differentiation of neuroblastoma cells and trigger ERK- and AKT-dependent, p53-independent senescence. Cancer Lett 328:44–54
Taylor RE, Bailey CC, Robinson KJ, Weston CL, Walker DA, Ellison D, Ironside J, Pizer BL, Lashford LS (2005) Outcome for patients with metastatic (M2-3) medulloblastoma treated with SIOP/UKCCSG PNET-3 chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer 41:727–734
Matthay KK, Reynolds CP, Seeger RC, Shimada H, Adkins ES, Haas-Kogan D, Gerbing RB, London WB, Villablanca JG (2009) Long-term results for children with high-risk neuroblastoma treated on a randomized trial of myeloablative therapy followed by 13-cis-retinoic acid: a children’s oncology group study. J Clin Oncol 27:1007–1013
Reynolds CP, Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Maurer BJ (2003) Retinoid therapy of high-risk neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett 197:185–192
Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Seeger RC, Stram DO, Harris RE, Ramsay NK, Swift P, Shimada H, Black CT, Brodeur GM, Gerbing RB, Reynolds CP (1999) Treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma with intensive chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous bone marrow transplantation, and 13-cis-retinoic acid. Children’s Cancer Group. N Engl J Med 341:1165–1173
Muccio DD, Atigadda VR, Brouillette WJ, Bland KI, Krontiras H, Grubbs CJ (2017) Translation of a tissue-selective rexinoid, UAB30, to the clinic for breast cancer prevention. Curr Top Med Chem 17:676–695
Chambon P (1994) The retinoid signaling pathway: molecular and genetic analyses. Semin Cell Biol 5:115–125
Allenby G, Bocquel MT, Saunders M, Kazmer S, Speck J, Rosenberger M, Lovey A, Kastner T, Grippo JF, Chambon P, Levin AA (1993) Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors: interactions with endogenous retinoic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:30–34
Gumireddy K, Sutton LN, Phillips PC, Reddy CD (2003) All-trans-retinoic acid-induced apoptosis in human medulloblastoma: activation of caspase-3/poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 pathway. Clin Cancer Res 9:4052–4059
Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Chandraratna RA, Ellenbogen RG, Geyer JR, Overland RP, Strand AD, Tapscott SJ, Olson JM (2003) BMP-2 mediates retinoid-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma cells through a paracrine effect. Nat Med 9:1033–1038
Fu YS, Wang Q, Ma JX, Yang XH, Wu ML, Zhang KL, Kong QY, Chen XY, Sun Y, Chen NN, Shu XH, Li H, Liu J (2012) CRABP-II methylation: a critical determinant of retinoic acid resistance of medulloblastoma cells. Mol Oncol 6:48–61
Celay J, Blanco I, Lazcoz P, Rotinen M, Castresana JS, Encio I (2013) Changes in gene expression profiling of apoptotic genes in neuroblastoma cell lines upon retinoic acid treatment. PLoS ONE 8:e62771
Imran M, Park TJ, Lim IK (2012) TIS21/BTG2/PC3 enhances downregulation of c-Myc during differentiation of HL-60 cells by activating Erk1/2 and inhibiting Akt in response to all-trans-retinoic acid. Eur J Cancer 48:2474–2485
Cheepala SB, Yin W, Syed Z, Gill JN, McMillian A, Kleiner HE, Lynch M, Loganantharaj R, Trutschl M, Cvek U, Clifford JL (2009) Identification of the B-Raf/Mek/Erk MAP kinase pathway as a target for all-trans retinoic acid during skin cancer promotion. Mol Cancer 8:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-8-27
Bassani B, Bartolini D, Pagani A, Principi E, Zollo M, Noonan DM, Albini A, Bruno A (2016) Fenretinide (4-HPR) targets caspase-9, ERK 1/2 and the Wnt3a/β-Catenin pathway in medulloblastoma cells and medulloblastoma cell spheroids. PLoS ONE 11(7):e0154111
Taylor MD, Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Remke M, Cho YJ, Clifford SC, Eberhart CG, Parsons DW, Rutkowski S, Gajjar A, Ellison DW, Lichter P, Gilbertson RJ, Pomeroy SL, Kool M, Pfister SM (2012) Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol 123:465–472
Northcott PA, Buchhalter I, Morrissy AS, Hovestadt V, Weischenfeldt J, Ehrenberger T, Gröbner S, Segura-Wang M, Zichner T, Rudneva VA, Warnatz HJ, Sidiropoulos N, Phillips AH, Schumacher S, Kleinheinz K, Waszak SM, Erkek S, Jones DTW, Worst BC, Kool M, Zapatka M, Jäger N, Chavez L, Hutter B, Bieg M, Paramasivam N, Heinold M, Gu Z, Ishaque N, Jäger-Schmidt C, Imbusch CD, Jugold A, Hübschmann D, Risch T, Amstislavskiy V, Gonzalez FGR, Weber UD, Wolf S, Robinson GW, Zhou X, Wu G, Finkelstein D, Liu Y, Cavalli FMG, Luu B, Ramaswamy V, Wu X, Koster J, Ryzhova M, Cho YJ, Pomeroy SL, Herold-Mende C, Schuhmann M, Ebinger M, Liau LM, Mora J, McLendon RE, Jabado N, Kumabe T, Chuah E, Ma Y, Moore RA, Mungall AJ, Mungall KL, Thiessen N, Tse K, Wong T, Jones SJM, Witt O, Milde T, Von Deimling A, Capper D, Korshunov A, Yaspo ML, Kriwacki R, Gajjar A, Zhang J, Beroukhim R, Fraenkel E, Korbel JO, Brors B, Schlesner M, Eils R, Marra MA, Pfister SM, Taylor MD, Lichter P (2017) The whole-genome landscape of medulloblastoma subtypes. Nature 547:311–317
Acknowledgements
Funding provided by the University of Alabama, Birmingham, Comprehensive Cancer Center to G.K.F. and E.A.B. National Institutes of Health (T32 CA091078 to E.F.G. and L.L.S.) (T32 CA183926 to A.P.W.) and (P30 AR048311 and P30 AI27667 to the University of Alabama Flow Cytometry Core).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the manuscript and have approved the final version. Details include: EFG experimental design, data acquisition, analysis and interpretation of the data, manuscript revision; LLS data acquisition, manuscript revision; APW data acquisition, manuscript revision; JMA data acquisition, manuscript revision; CG data analysis, manuscript revision; VRA experimental design and reagents, manuscript revision; BPM data acquisition, manuscript revision; NL data analysis, manuscript revision; JES data acquisition, data analysis, manuscript revision; ABH experimental design and reagents, manuscript revision; GFK experimental design, manuscript revision; EAB experimental design, data analysis and interpretation, writing manuscript, manuscript revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and /or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted. The University of Alabama, Birmingham Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all animal experiments (IACUC-09355, IACUC-10299). This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garner, E.F., Stafman, L.L., Williams, A.P. et al. UAB30, a novel RXR agonist, decreases tumorigenesis and leptomeningeal disease in group 3 medulloblastoma patient-derived xenografts. J Neurooncol 140, 209–224 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2950-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2950-1