Abstract
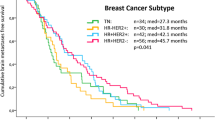
Breast cancer brain metastasis (BCBM) is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Patients with breast cancer risk factors associated with rapid development of BCBM could potentially benefit from early brain metastasis screening. We retrospectively reviewed all BCBM patients treated with brain radiotherapy at our institution from 1997 to 2015. Interval time to BCBM was defined as date of pathologic breast cancer diagnosis to date of radiographic evidence of brain metastasis. Patients were stratified by breast cancer molecular subtype and stage at diagnosis. Kaplan Meier analysis was conducted on time to development of BCBM. Breast cancer risk factors were correlated with time to BCBM on Cox proportion hazard analysis. The study cohort comprised 121 BCBM patients, with median interval time to BCBM of 46 months. Times to BCBM for Her2+/2HR+, Her2+, Her2−/HR+, and triple-negative (TNBC) subtypes were 70, 44, 42, and 28 months respectively (p = 0.002). Time to BCBM for stages I, II, III, and IV were 70, 54, 29, and 24 months, respectively (p = 0.000). BCBM patients were further stratified by both molecular subtype (TNBC vs. non-TNBC) and stage (I, II vs. III, IV). Median times to BCBM for non-TNBC/stage I–II, TNBC/stage I–II, non-TNBC stage III–IV, and TNBC/stage III–IV were 68, 47, 29, and 6 months respectively (p = 0.000). Subtype and stage were associated with shorter time to BCBM on multivariate analysis. Subtype and initial stage are independently correlated with decreased time to development of BCBM. Patients with advanced high stage and triple negative breast cancer develop brain metastases significantly earlier.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29. doi:10.3322/caac.20138
Eichler AF, Kuter I, Ryan P, Schapira L, Younger J, Henson JW (2008) Survival in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer: the importance of HER-2 status. Cancer 112:2359–2367. doi:10.1002/cncr.23468
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 30:419–425. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.38.0527
Subbiah IM, Lei X, Weinberg JS, Sulman EP, Chavez-MacGregor M, Tripathy D, Gupta R, Varma A, Chouhan J, Guevarra RP, Valero V, Gilbert MR, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2015) Validation and development of a modified breast graded prognostic assessment as a tool for survival in patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 33:2239–2245. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.58.8517
Hofer S, Pestalozzi BC (2013) Treatment of breast cancer brain metastases. Eur J Pharmacol 717:84–87. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.11.068
Freedman RA, Anders CK (2012) Treatment of breast cancer brain metastases. Curr Breast Cancer Rep 4: 1–9 doi:10.1007/s12609-011-0061-5
Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW, Lane WW (1983) Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Autopsy study. Cancer 52:2349–2354
Gori S, Rimondini S, De Angelis V, Colozza M, Bisagni G, Moretti G, Sidoni A, Basurto C, Aristei C, Anastasi P, Crino L (2007) Central nervous system metastases in HER-2 positive metastatic breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab: incidence, survival, and risk factors. Oncologist 12:766–773. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.12-7-766
Tomasello G, Bedard PL, de Azambuja E, Lossignol D, Devriendt D, Piccart-Gebhart MJ (2010) Brain metastases in HER2-positive breast cancer: the evolving role of lapatinib. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 75:110–121. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2009.11.003
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang MC, Voduc D, Speers CH, Nielsen TO, Gelmon K (2010) Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol 28:3271–3277. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.9820
Clayton AJ, Danson S, Jolly S, Ryder WD, Burt PA, Stewart AL, Wilkinson PM, Welch RS, Magee B, Wilson G, Howell A, Wardley AM (2004) Incidence of cerebral metastases in patients treated with trastuzumab for metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer 91:639–643. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601970
Niwinska A, Murawska M, Pogoda K (2010) Breast cancer brain metastases: differences in survival depending on biological subtype, RPA RTOG prognostic class and systemic treatment after whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT). Ann Oncol 21:942–948. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp407
Nam BH, Kim SY, Han HS, Kwon Y, Lee KS, Kim TH, Ro J (2008) Breast cancer subtypes and survival in patients with brain metastases. Breast Cancer Res 10:R20. doi:10.1186/bcr1870
Niikura N, Hayashi N, Masuda N, Takashima S, Nakamura R, Watanabe K, Kanbayashi C, Ishida M, Hozumi Y, Tsuneizumi M, Kondo N, Naito Y, Honda Y, Matsui A, Fujisawa T, Oshitanai R, Yasojima H, Tokuda Y, Saji S, Iwata H (2014) Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with brain metastases from breast cancer of each subtype: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 147:103–112. doi:10.1007/s10549-014-3090-8
Grubb CS, Jani A, Wu CC, Saad S, Qureshi YH, Nanda T, Yaeh A, Rozenblat T, Sisti MB, Bruce JN, McKhann GM 2nd, Sheth SA, Lesser J, Cheng SK, Isaacson SR, Lassman AB, Connolly EP, Wang TJ (2016) Breast cancer subtype as a predictor for outcomes and control in the setting of brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 127:103–110. doi:10.1007/s11060-015-2014-8
Bartsch R, Berghoff AS, Preusser M (2013) Optimal management of brain metastases from breast cancer. Issues and considerations. CNS Drugs 27:121–134. doi:10.1007/s40263-012-0024-z
Rojas MP, Telaro E, Russo A, Moschetti I, Coe L, Fossati R, Palli D, del Roselli TM, Liberati A (2005) Follow-up strategies for women treated for early breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001768.pub2
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Chao ST, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Suh J, Weil RJ, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2013) The effect of tumor subtype on the time from primary diagnosis to development of brain metastases and survival in patients with breast cancer. J Neurooncol 112:467–472. doi:10.1007/s11060-013-1083-9
Aversa C, Rossi V, Geuna E, Martinello R, Milani A, Redana S, Valabrega G, Aglietta M, Montemurro F (2014) Metastatic breast cancer subtypes and central nervous system metastases. Breast 23:623–628. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2014.06.009
Leone JP, Lee AV, Brufsky AM (2015) Prognostic factors and survival of patients with brain metastasis from breast cancer who underwent craniotomy. Cancer Med 4: 989–994. doi:10.1002/cam4.439
Niwinska A, Tacikowska M, Murawska M (2010) The effect of early detection of occult brain metastases in HER2-positive breast cancer patients on survival and cause of death. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:1134–1139. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.030
Miller KD, Weathers T, Haney LG, Timmerman R, Dickler M, Shen J, Sledge GW Jr (2003) Occult central nervous system involvement in patients with metastatic breast cancer: prevalence, predictive factors and impact on overall survival. Ann Oncol 14:1072–1077
Lobbezoo DJ, van Kampen RJ, Voogd AC, Dercksen MW, van den Berkmortel F, Smilde TJ, van de Wouw AJ, Peters FP, van Riel JM, Peters NA, de Boer M, Borm GF, Tjan-Heijnen VC (2013) Prognosis of metastatic breast cancer subtypes: the hormone receptor/HER2-positive subtype is associated with the most favorable outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat 141:507–514. doi:10.1007/s10549-013-2711-y
Zhu X, Verma S (2015) Targeted therapy in her2-positive metastatic breast cancer: a review of the literature. Curr Oncol 22:S19–S28. doi:10.3747/co.22.2363
Negi P, Kingsley PA, Jain K, Sachdeva J, Srivastava H, Marcus S, Pannu A (2016) Survival of triple negative versus triple positive breast cancers: comparison and contrast. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 17:3911–3916
Schott AF (2016) Adjuvant trastuzumab benefit in patients diagnosed with triple-positive breast cancer. JAMA Oncol 2:1047–1048. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.0446
Vici P, Pizzuti L, Sperduti I, Frassoldati A, Natoli C, Gamucci T, Tomao S, Michelotti A, Moscetti L, Gori S, Baldini E, Giotta F, Cassano A, Santini D, Giannarelli D, Di Lauro L, Corsi DC, Marchetti P, Sini V, Sergi D, Barba M, Maugeri-Sacca M, Russillo M, Mentuccia L, D’Onofrio L, Iezzi L, Scinto AF, Da Ros L, Bertolini I, Basile ML, Rossi V, De Maria R, Montemurro F (2016) “Triple positive” early breast cancer: an observational multicenter retrospective analysis of outcome. Oncotarget 7:17932–17944. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.7480
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2012) Effect of tumor subtype on survival and the graded prognostic assessment for patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:2111–2117. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.02.027
Tsao MN, Rades D, Wirth A, Lo SS, Danielson BL, Gaspar LE, Sperduto PW, Vogelbaum MA, Radawski JD, Wang JZ, Gillin MT, Mohideen N, Hahn CA, Chang EL (2012) Radiotherapeutic and surgical management for newly diagnosed brain metastasis(es): an American Society for radiation oncology evidence-based guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol 2:210–225. doi:10.1016/j.prro.2011.12.004
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, Kenjyo M, Oya N, Hirota S, Shioura H, Kunieda E, Inomata T, Hayakawa K, Katoh N, Kobashi G (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491. doi:10.1001/jama.295.21.2483
Tallet AV, Azria D, Barlesi F, Spano JP, Carpentier AF, Goncalves A, Metellus P (2012) Neurocognitive function impairment after whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases: actual assessment. Radiat Oncol 7:77. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-7-77
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Meyers CA (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70263-3
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Rotman M, Mehta MP, Curran WJ Jr (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16250-8
Kondziolka D, Patel A, Lunsford LD, Kassam A, Flickinger JC (1999) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for patients with multiple brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45:427–434
Davies C, Pan H, Godwin J, Gray R, Arriagada R, Raina V, Abraham M, Medeiros Alencar VH, Badran A, Bonfill X, Bradbury J, Clarke M, Collins R, Davis SR, Delmestri A, Forbes JF, Haddad P, Hou MF, Inbar M, Khaled H, Kielanowska J, Kwan WH, Mathew BS, Mittra I, Muller B, Nicolucci A, Peralta O, Pernas F, Petruzelka L, Pienkowski T, Radhika R, Rajan B, Rubach MT, Tort S, Urrutia G, Valentini M, Wang Y, Peto R, Adjuvant Tamoxifen: Longer Against Shorter Collaborative G (2013) Long-term effects of continuing adjuvant tamoxifen to 10 years versus stopping at 5 years after diagnosis of oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: ATLAS, a randomised trial. Lancet 381: 805–816 doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61963-1
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative G, Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R, Clarke M, Cutter D, Darby S, McGale P, Pan HC, Taylor C, Wang YC, Dowsett M, Ingle J, Peto R (2011) Relevance of breast cancer hormone receptors and other factors to the efficacy of adjuvant tamoxifen: patient-level meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 378:771–784. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60993-8
Swain SM, Baselga J, Kim SB, Ro J, Semiglazov V, Campone M, Ciruelos E, Ferrero JM, Schneeweiss A, Heeson S, Clark E, Ross G, Benyunes MC, Cortes J, Group CS (2015) Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med 372:724–734. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1413513
Matsuo S, Watanabe J, Mitsuya K, Hayashi N, Nakasu Y, Hayashi M (2017) Brain metastasis in patients with metastatic breast cancer in the real world: a single-institution, retrospective review of 12-year follow-up. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-017-4107-x
Molnar IA, Molnar BA, Vizkeleti L, Fekete K, Tamas J, Deak P, Szundi C, Szekely B, Moldvay J, Vari-Kakas S, Szasz MA, Acs B, Kulka J, Tokes AM (2017) Breast carcinoma subtypes show different patterns of metastatic behavior. Virchows Arch. doi:10.1007/s00428-017-2065-7
Tham YL, Sexton K, Kramer R, Hilsenbeck S, Elledge R (2006) Primary breast cancer phenotypes associated with propensity for central nervous system metastases. Cancer 107:696–704. doi:10.1002/cncr.22041
Funding
T. J. C. W. reports consulting fees for AstraZeneca and travel expenses from Abbvie and Novocure outside the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study formal consent including for procedures is not required. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Statement of human rights
All patients were retrospectively reviewed on an IRB approved database IRB-AAAM2358, Comprehensive Brain Malignancy and Brain Tumor Clinical Database. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Anurag Saraf and Christopher S. Grubb have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saraf, A., Grubb, C.S., Hwang, M.E. et al. Breast cancer subtype and stage are prognostic of time from breast cancer diagnosis to brain metastasis development. J Neurooncol 134, 453–463 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2549-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2549-y