Abstract
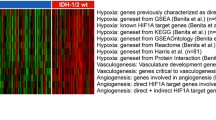
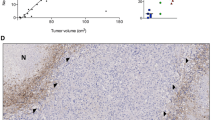
There is little data on why glioblastomas (GBM) hemorrhage and how it may affect patient outcomes. The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanisms of hemorrhage in glioblastoma by examining molecular and genetic features by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and mRNA expression profiles in association with imaging and clinical outcomes. An observational retrospective cohort analysis was performed on 43 FFPE GBM tissue samples. MR images were assessed for the presence of hemorrhage and extent of resection. Specimens were examined for CD34 and CD105 expression using IHC. Tumor mRNA expression profiles were analyzed for 92 genes related to angiogenesis and vascularity. Forty-three specimens were analyzed, and 20 showed signs of hemorrhage, 23 did not. The average OS for patients with GBM with hemorrhage was 19.12 months (95% CI 10.39–27.84), versus 13.85 months (95% CI 8.85–18.85) in those without hemorrhage (p > 0.05). Tumors that hemorrhaged had higher IHC staining for CD34 and CD105. mRNA expression analysis revealed tumor hemorrhage was associated with increased expression of HIF1α and MDK, and decreased expression of F3. Hemorrhage in GBM was not associated with worsened OS. Increased expression of angiogenic factors and increased CD34 and CD105 IHC staining in tumors with hemorrhage suggests that increased hypoxia-induced angiogenesis and vessel density may play a role in glioblastoma hemorrhage. Characterizing tumors that are prone to hemorrhage and mechanisms behind the development of these hemorrhages may provide insights that can lead to the development of targeted, individualized therapies for glioblastoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watanabe K, Wakai S, Okuhata S (1997) Gliomas presenting with basal ganglionic haemorrhage. Report of two cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 139:787–788
Johnson DR, O’Neill BP (2012) Glioblastoma survival in the United States before and during the temozolomide era. J Neurooncol 107:359–364
Wakai S, Yamakawa K, Manaka S, Takakura K (1982) Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage caused by brain tumor: its incidence and clinical significance. Neurosurgery 10:437–444
Yuguang L, Meng L, Shugan Z, Yuquan J, Gang L, Xingang L, Chengyuan W (2002) Intracranial tumoural haemorrhage–a report of 58 cases. J Clin Neurosci 9:637–639
Liwnicz BH, Wu SZ, Tew JM Jr (1987) The relationship between the capillary structure and hemorrhage in gliomas. J Neurosurg 66:536–541
Kondziolka D, Bernstein M, Resch L, Tator CH, Fleming JF, Vanderlinden RG, Schutz H (1987) Significance of hemorrhage into brain tumors: clinicopathological study. J Neurosurg 67:852–857
Weisberg LA (1986) Hemorrhagic primary intracranial neoplasms: clinical-computed tomographic correlations. Comput Radiol 10:131–136
Cemil B, Tun K, Polat O, Ozen O, Kaptanoglu E (2009) Glioblastoma multiforme mimicking arteriovenous malformation. Turk Neurosurg 19:433–436
Kase CS, Louis DN (1990) Case 26-1990—A 68-year old man with a right hemiparesis, abulia, and multiple intracerebral hemorrhages. N Engl J Med 322:1866–1878
Khanna A, Venteicher AS, Walcott BP, Kahle KT, Mordes DA, William CM, Ghogawala Z, Ogilvy CS (2013) Glioblastoma mimicking an arteriovenous malformation. Front Neurol 4: 144
Kim IY, Jung S, Jung TY, Kang SS, Choi C (2008) Primary central nervous system lymphoma presenting as an acute massive intracerebral hemorrhage: case report with immunohistochemical study. Surg Neurol 70:308–311
Li X, Wang K, Zhang A, Song Z, Yang S, Qian C, Wang Y (2013) Glioblastoma mimicking a cerebral contusion: a case report. Oncol Lett 6: 1499–1501
Little JR, Dial B, Belanger G, Carpenter S (1979) Brain hemorrhage from intracranial tumor. Stroke 10:283–288
Padt J, De Reuck, J, Eecken, H vander: Intracerebral hemorrhage as initial cymptom of a brain tumor. Acta Neurol Belg 73: 241–251, 1973
Viratchai C, Shuangshoti S (1978) Massive spontaneous hemorrhage in primary intracranial neoplasms. J Med Assoc Thai 61:115–122
De Waele JW, De Reuck J, Vandekerckhove T (1986) Clinical pathological conference. An unusual cause of a spontaneous intracerebral haematoma. Acta Neurol Belg 86:145–151
Liebelt BD, Boghani Z, Takei H, Fung SH, Britz GW (2015) Epithelioid glioblastoma presenting as massive intracerebral hemorrhage: case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol Int 6:S97–S100
Benveniste RJ, Manzano G, Petito CK (2008) Multifocal glioblastoma multiforme with synchronous spontaneous hemorrhage: case report. J Neurooncol 89:55–58
Burges RCL (1926) Subarachnoid haemorrhage as the first effect of a cerebral tumour. Br Med J 2:887
Grimm SA, DeAngelis LM (2007) Intratumoral hemorrhage after thrombolysis in a patient with glioblastoma multiforme. Neurology 69:936
Inamasu J, Kuramae T, Nakatsukasa M (2009) Glioblastoma masquerading as a hypertensive putaminal hemorrhage: a diagnostic pitfall. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 49:427–429
Inamasu J, Nakamura Y, Saito R, Kuroshima Y, Mayanagi K, Ichikizaki K (2005) Rebleeding from a primary brain tumor manifesting as intracerebral hemorrhage (CNN 04/077, revised version). Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108:105–108
Kazim SF, Bhatti AU (2011) Glioblastoma multiforme masquerading as intracerebral haemorrhage: a diagnostic dilemma. J Pak Med Assoc 61:196–197
Kimura N, Ishibashi M, Masuda T, Morishige M, Abe T, Fujiki M, Kashima K, Kumamoto T (2009) Primary central nervous system lymphoma with cortical laminar hemorrhage. J Neurol Sci 287:281–284
Misra BK, Steers AJ, Miller JD, Gordon A (1988) Multicentric glioma presenting with hemorrhage. Surg Neurol 29:73–76
Oldberg E (1933) Hemorrhage into gliomas: a review of eight hundred and thirty-two consecutive verified cases of glioma. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 30:1061–1073
Ragland RL, Wagner LD, Huang YP, Som PM, Teal JS, Handler MS (1990) Streaming hypointensity in hemorrhagic glioblastoma multiforme. An illustrative case. Neuroradiology 32:241–243
Scott M (1975) Spontaneous intracerebral hematoma caused by cerebral neoplasms. Report of eight verified cases. J Neurosurg 42:338–342
Sell M, Huber-Schumacher S, van Landeghem FK (2006) Congenital glioblastoma multiforme with abnormal vascularity presenting as intracranial hemorrhage in prenatal ultrasound. Childs Nerv Syst 22:729–733
Shuangshoti S, Dharmmaponpilas J (1978) Supratentorial glioblastoma multiforme and infratentorial ependymoma with repeated hemorrhages. J Med Assoc Thai 61:489–496
Skultety FM (1968) Meningioma simulating ruptured aneurysm. Case report. J Neurosurg 28:380–382
Taniura S, Okamoto H, Tanabe M, Kurosaki M, Mizushima M, Watanabe T (2007) Huge lobar intracerebral hemorrhage by glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 82:117–118
Manganiello LO (1949) Massive spontaneous hemorrhage in gliomas; a report of seven verified cases. J Nerv Ment Dis 110:277–298
Cheng SY, Nagane M, Huang HS, Cavenee WK (1997) Intracerebral tumor-associated hemorrhage caused by overexpression of the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF121 and VEGF165 but not VEGF189. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12081–12087
Reiss Y, Machein MR, Plate KH (2005) The role of angiopoietins during angiogenesis in gliomas. Brain Pathol 15:311–317
Jiang WG, Davies G, Martin TA, Parr C, Watkins G, Mansel RE, Mason MD (2005) The potential lymphangiogenic effects of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med 16:723–728
Emdad L, Das SK, Dasgupta S, Hu B, Sarkar D, Fisher PB (2013) AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC: signaling pathways, downstream genes, interacting proteins, and regulation of tumor angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res 120:75–111
Abounader R, Laterra J (2005) Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in brain tumor growth and angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol 7:436–451
Schmidt NO, Westphal M, Hagel C, Ergun S, Stavrou D, Rosen EM, Lamszus K (1999) Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in human gliomas and their relation to angiogenesis. Int J Cancer 84:10–18
Jung S, Moon KS, Jung TY, Kim IY, Lee YH, Rhu HH, Sun HS, Jeong YI, Kim KK, Kang SS (2006) Possible pathophysiological role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in metastatic brain tumor-associated intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurooncol 76:257–263
Harris AL, Fox S, Leek R, Zhang H, Scott P, Bicknell R, Gatter K (1995) Breast cancer angiogenesis: therapy target and prognostic factor. Eur J Cancer 31A:831–832
Halin C, Zardi L, Neri D (2001) Antibody-based targeting of angiogenesis. News Physiol Sci 16:191–194
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Fox SB, Turner GD, Leek RD, Whitehouse RM, Gatter KC, Harris AL (1995) The prognostic value of quantitative angiogenesis in breast cancer and role of adhesion molecule expression in tumor endothelium. Breast Cancer Res Treat 36:219–226
Fox SB, Leek RD, Weekes MP, Whitehouse RM, Gatter KC, Harris AL (1995) Quantitation and prognostic value of breast cancer angiogenesis: comparison of microvessel density, Chalkley count, and computer image analysis. J Pathol 177:275–283
Fox SB, Gatter KC, Altman DG, Leek RD, Harris AL: Re: Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic assay for invasive ductal breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 87: 1798–1799; author reply 1801–1792, 1995
Vitolo D, Paradiso P, Uccini S, Ruco LP, Baroni CD (1996) Expression of adhesion molecules and extracellular matrix proteins in glioblastomas: relation to angiogenesis and spread. Histopathology 28:521–528
Bratton SL, Odetola FO, McCollegan J, Cabana MD, Levy FH, Keenan HT (2005) Regional variation in ICU care for pediatric patients with asthma. J Pediatr 147:355–361
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J (1991) Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis–correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324:1–8
Stummer W, Reulen HJ, Meinel T, Pichlmeier U, Schumacher W, Tonn JC, Rohde V, Oppel F, Turowski B, Woiciechowsky C, Franz K, Pietsch T, Group AL-GS (2008) Extent of resection and survival in glioblastoma multiforme: identification of and adjustment for bias. Neurosurgery 62:564–576 (discussion 564–576)
Chaichana KL, Chaichana KK, Olivi A, Weingart JD, Bennett R, Brem H, Quinones-Hinojosa A (2011) Surgical outcomes for older patients with glioblastoma multiforme: preoperative factors associated with decreased survival. Clinical article. J Neurosurg 114:587–594
Rao A, Rao G, Gutman DA, Flanders AE, Hwang SN, Rubin DL, Colen RR, Zinn PO, Jain R, Wintermark M, Kirby JS, Jaffe CC, Freymann J, Group TGPR (2015) A combinatorial radiographic phenotype may stratify patient survival and be associated with invasion and proliferation characteristics in glioblastoma. J Neurosurg 1–10
Salo J, Niemela A, Joukamaa M, Koivukangas J (2002) Effect of brain tumour laterality on patients’ perceived quality of life. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72:373–377
Inskip PD, Tarone RE, Hatch EE, Wilcosky TC, Selker RG, Fine HA, Black PM, Loeffler JS, Shapiro WR, Linet MS (2003) Laterality of brain tumors. Neuroepidemiology 22:130–138
Duff SE, Li C, Garland JM, Kumar S (2003) CD105 is important for angiogenesis: evidence and potential applications. FASEB J 17:984–992
Maschio LB, Madallozo BB, Capellasso BA, Jardim BV, Moschetta MG, Jampietro J, Soares FA, Zuccari DA (2014) Immunohistochemical investigation of the angiogenic proteins VEGF, HIF-1alpha and CD34 in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Acta Histochem 116:148–157
Tatusova T, Ciufo S, Fedorov B, O’Neill K, Tolstoy I (2015) RefSeq microbial genomes database: new representation and annotation strategy. Nucleic Acids Res 43:3872
Ponnaluri VK, Vavilala DT, Prakash S, Mukherji M (2013) Hypoxia mediated expression of stem cell markers in VHL-associated hemangioblastomas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 438:71–77
Hao H, Maeda Y, Fukazawa T, Yamatsuji T, Takaoka M, Bao XH, Matsuoka J, Okui T, Shimo T, Takigawa N, Tomono Y, Nakajima M, Fink-Baldauf IM, Nelson S, Seibel W, Papoian R, Whitsett JA, Naomoto Y (2013) Inhibition of the growth factor MDK/midkine by a novel small molecule compound to treat non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 8:e71093
Alliot F, Rutin J, Leenen PJ, Pessac B (1999) Pericytes and periendothelial cells of brain parenchyma vessels co-express aminopeptidase N, aminopeptidase A, and nestin. J Neurosci Res 58:367–378
Rao A, Manyam G, Rao G, Jain R (2016) Integrative analysis of mRNA, microRNA, and protein correlates of relative cerebral blood volume values in GBM reveals the role for modulators of angiogenesis and tumor proliferation. Cancer Inform 15:29–33
Rao A, Rao G, Gutman DA, Flanders AE, Hwang SN, Rubin DL, Colen RR, Zinn PO, Jain R, Wintermark M, Kirby JS, Jaffe CC, Freymann J (2016) A combinatorial radiographic phenotype may stratify patient survival and be associated with invasion and proliferation characteristics in glioblastoma. J Neurosurg 124:1008–1017
Wang Y, Xing D, Zhao M, Wang J, Yang Y (2016) The role of a single angiogenesis inhibitor in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: a meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS ONE 11:e0152170
Chinot OL, Nishikawa R, Mason W, Henriksson R, Saran F, Cloughesy T, Garcia J, Revil C, Abrey L, Wick W (2016) Upfront bevacizumab may extend survival for glioblastoma patients who do not receive second-line therapy: an exploratory analysis of AVAglio. Neuro-Oncol
Funding
Shoemaker Prize for Neurodegenerative Research. University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Medicine Summer Research Grant. UNMC Eppley Institute Cancer Biology Training Grant (T32CA009476). Fred & Pamela Buffet Cancer Center Support Grant (P30 CA036727).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Ben G. McGahan and Beth K. Neilsen contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGahan, B.G., Neilsen, B.K., Kelly, D.L. et al. Assessment of vascularity in glioblastoma and its implications on patient outcomes. J Neurooncol 132, 35–44 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2350-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2350-3