Abstract
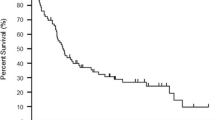
Vemurafenib is indicated for the treatment of patients with BRAF V600-mutant metastatic melanoma. We studied for the first time the characteristics of brain metastases developed during treatment with vemurafenib in real-life conditions. We included all patients treated over 3 years with vemurafenib in our department for metastatic melanoma without initial brain involvement. Our primary endpoint was to assess the incidence of brain metastases in these patients. Our secondary endpoints were to identify the risk factors for metastases occurrence and their characteristics and course. In our retrospective cohort of 86 patients, 20 % had developed brain metastases on average 5.3 months after vemurafenib initiation. The median follow-up was 9 months (1–26 months). Radiological examinations revealed multiple brain metastases in 41 % of patients. The only risk factor for metastasis occurrence identified was a high number of metastatic sites when initiating vemurafenib (p = 0.045). Metastasis development was associated with a trend toward a decrease in overall survival from 12.8 to 8.5 months (p = 0.07) and a significant decrease in progression-free survival from 7 to 5 months (p = 0.04). Among the patients who developed brain metastases, 82 % died, of whom 64 % within 3 months, versus 58 % of patients without brain metastases over the same period. The extra-cerebral disease was well controlled in 59 % of patients during brain progression. In vemurafenib-treated melanoma patients, brain metastases are frequent and associated with a particularly poor prognosis. Because of their high frequency in patients with controlled extra-cerebral disease, brain explorations should be systematically performed during treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol 22(14):2865–2872
Fonkem E, Uhlmann EJ, Floyd SR, Mahadevan A, Kasper E, Eton O, Wong ET (2012) Melanoma brain metastases: overview of current management and emerging targeted therapies. Expert Rev Neurother 12(10):1207–1215
Preusser M, Capper D, Ilhan-Mutlu A, Berghoff AS, Birner P, Bartsch R, Marosi C, Zielinski C, Mehta MP, Winkler F, Wick W, von Deimling A (2012) Brain metastases: pathobiology and emerging targeted therapies. Acta Neuropathol 123(2):205–222
Davies MA, Liu P, McIntyre S, Kim KB, Papadopoulos N, Hwu WJ, Hwu P, Bedikian A (2011) Prognostic factors for survival in melanoma patients with brain metastases. Cancer 117(8):1687–1696
Menzies AM, Long GV, Murali R (2012) Dabrafenib and its potential for the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Drug Des Devel Ther 6:391–405
Murrell J, Board R (2013) The use of systemic therapies for the treatment of brain metastases in metastatic melanoma: Opportunities and unanswered questions. Cancer Treat Rev 39(8):833–838
Long GV, Margolin KA (2013) Multidisciplinary approach to brain metastases from melanoma. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2013:393–398
Kim KB, Flaherty KT, Chapman PB, Sosman JA, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Amaravadi RK, Lee RJ, Nolop KB, Puzanov I (2011) Pattern and outcome of disease progression in phase I study of vemurafenib in patients with metastatic melanoma (MM). J Clin Oncol 29(15):1628–1634
Maleka A, Enblad G, Sjors G, Lindqvist A, Ullenhag GJ (2013) Treatment of metastatic malignant melanoma with vemurafenib during pregnancy. J Clin Oncol 31(11):e192–e193
Rochet NM, Dronca RS, Kottschade LA, Chavan RN, Gorman B, Gilbertson JR, Markovic SN (2012) Melanoma brain metastases and vemurafenib: need for further investigation. Mayo Clin Proc 87(10):976–981
Simeone E, De Maio E, Sandomenico F, Fulciniti F, Lastoria S, Aprea P, Staibano S, Montesarchio V, Palmieri G, Mozzillo N, Ascierto PA (2012) Neoplastic leptomeningitis presenting in a melanoma patient treated with dabrafenib (a V600EBRAF inhibitor): a case report. J Med Case Rep 6(1):131
Lee JM, Mehta UN, Dsouza LH, Guadagnolo BA, Sanders DL, Kim KB (2013) Long-term stabilization of leptomeningeal disease with whole-brain radiation therapy in a patient with metastatic melanoma treated with vemurafenib: a case report. Melanoma Res 23(2):175–178
Poulikakos PI, Persaud Y, Janakiraman M, Kong X, Ng C, Moriceau G, Shi H, Atefi M, Titz B, Gabay MT, Salton M, Dahlman KB, Tadi M, Wargo JA, Flaherty KT, Kelley MC, Misteli T, Chapman PB, Sosman JA, Graeber TG, Ribas A, Lo RS, Rosen N, Solit DB (2011) RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of aberrantly spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature 480(7377):387–390
Shi H, Moriceau G, Kong X, Lee MK, Lee H, Koya RC, Ng C, Chodon T, Scolyer RA, Dahlman KB, Sosman JA, Kefford RF, Long GV, Nelson SF, Ribas A, Lo RS (2012) Melanoma whole-exome sequencing identifies (V600E)B-RAF amplification-mediated acquired B-RAF inhibitor resistance. Nat Commun 3:724
Montagut C, Sharma SV, Shioda T, McDermott U, Ulman M, Ulkus LE, Dias-Santagata D, Stubbs H, Lee DY, Singh A, Drew L, Haber DA, Settleman J (2008) Elevated CRAF as a potential mechanism of acquired resistance to BRAF inhibition in melanoma. Cancer Res 68(12):4853–4861
Wagle N, Emery C, Berger MF, Davis MJ, Sawyer A, Pochanard P, Kehoe SM, Johannessen CM, Macconaill LE, Hahn WC, Meyerson M, Garraway LA (2011) Dissecting therapeutic resistance to RAF inhibition in melanoma by tumor genomic profiling. J Clin Oncol 29(22):3085–3096
Johannessen CM, Boehm JS, Kim SY, Thomas SR, Wardwell L, Johnson LA, Emery CM, Stransky N, Cogdill AP, Barretina J, Caponigro G, Hieronymus H, Murray RR, Salehi-Ashtiani K, Hill DE, Vidal M, Zhao JJ, Yang X, Alkan O, Kim S, Harris JL, Wilson CJ, Myer VE, Finan PM, Root DE, Roberts TM, Golub T, Flaherty KT, Dummer R, Weber BL, Sellers WR, Schlegel R, Wargo JA, Hahn WC, Garraway LA (2010) COT drives resistance to RAF inhibition through MAP kinase pathway reactivation. Nature 468(7326):968–972
Villanueva J, Vultur A, Lee JT, Somasundaram R, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Cipolla AK, Wubbenhorst B, Xu X, Gimotty PA, Kee D, Santiago-Walker AE, Letrero R, D’Andrea K, Pushparajan A, Hayden JE, Brown KD, Laquerre S, McArthur GA, Sosman JA, Nathanson KL, Herlyn M (2010) Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3 K. Cancer Cell 18(6):683–695
Smalley KS, Sondak VK (2010) Melanoma–an unlikely poster child for personalized cancer therapy. Engl J Med 363(9):876–878
Nazarian R, Shi H, Wang Q, Kong X, Koya RC, Lee H, Chen Z, Lee MK, Attar N, Sazegar H, Chodon T, Nelson SF, McArthur G, Sosman JA, Ribas A, Lo RS (2010) Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature 468(7326):973–977
Meier F, Forschner A, Klumpp B, Flaherty KT, Honegger JB, Witte M, Bornemann A, Dummer R, Bauer J, Tabatabai G, Weide B, Eigentler TK, Schadendorf D, Quintanilla-Fend L, Niessner H, Garbe C (2013) Targeting hyperactivation of the AKT survival pathway to overcome therapy resistance of melanoma brain metastases Cancer Med 2(1):76–85
Mittapalli RK, Vaidhyanathan S, Dudek AZ, Elmquist WF (2013) Mechanisms limiting distribution of the threonine-protein kinase B-RaF(V600E) inhibitor dabrafenib to the brain: implications for the treatment of melanoma brain metastases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 344(3):655–664
Falchook GS, Long GV, Kurzrock R, Kim KB, Arkenau TH, Brown MP, Hamid O, Infante JR, Millward M, Pavlick AC, O’Day SJ, Blackman SC, Curtis CM, Lebowitz P, Ma B, Ouellet D, Kefford RF (2012) Dabrafenib in patients with melanoma, untreated brain metastases, and other solid tumours: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet 379(9829):1893–1901
Fortin D (2012) The blood-brain barrier: its influence in the treatment of brain tumors metastases. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 12(3):247–259
Narayana A, Mathew M, Tam M, Kannan R, Madden KM, Golfinos JG, Parker EC, Ott PA, Pavlick AC (2013) Vemurafenib and radiation therapy in melanoma brain metastases. J Neurooncol 113(3):411–416
Mittapalli RK, Vaidhyanathan S, Sane R, Elmquist WF (2012) Impact of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) on the brain distribution of a novel BRAF inhibitor: vemurafenib (PLX4032). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 342(1):33–40
Durmus S, Sparidans RW, Wagenaar E, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH (2012) Oral availability and brain penetration of the B-RAFV600E inhibitor vemurafenib can be enhanced by the P-GLYCOprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) inhibitor elacridar. Mol Pharm 9(11):3236–3245
Harding JJ, Catalanotti F, Yaqubie A, McDermott GC, Kersellius R, Merghoub T (2013) Vemurafenib (VEM) in patients (pts) with BRAF-mutant melanoma and brain metastases (mets). J Clin Oncol 31:9060
Dzienis MR, Atkinson VG (2014).Response rate to vemurafenib in patients with B-RAF-positive melanoma brain metastases. Melanoma Res 24(4):349–353
Dummer R, Goldinger SM, Turtschi CP, Eggmann NB, Michielin O, Mitchell L, Veronese L, Hilfiker PR, Felderer L, Rinderknecht JD (2014) Vemurafenib in patients with BRAF mutation-positive melanoma with symptomatic brain metastases: final results of an open-label pilot study. Eur J Cancer 50(3):611–621
Baroudjian B, Boussemart L, Routier E, Dreno B, Tao Y, Deutsch E, Blanchard P, Dhermain F, Vilcot L, Vagner S, Eggermont A, Mateus C, Robert C (2014) Dramatic response to radiotherapy combined with vemurafenib. Is vemurafenib a radiosensitizer? Eur J Dermatol 24(2):265–267
Peuvrel L, Ruellan AL, Thillays F, Quereux G, Brocard A, Saint-Jean M, Aumont M, Drouet F, Dreno B (2013) Severe radiotherapy-induced extracutaneous toxicity under vemurafenib. Eur J Dermatol 23(6):879–881
Long GV, Trefzer U, Davies MA, Kefford RF, Ascierto PA, Chapman PB, Puzanov I, Hauschild A, Robert C, Algazi A, Mortier L, Tawbi H, Wilhelm T, Zimmer L, Switzky J, Swann S, Martin AM, Guckert M, Goodman V, Streit M, Kirkwood JM, Schadendorf D (2012) Dabrafenib in patients with Val600Glu or Val600Lys BRAF-mutant melanoma metastatic to the brain (BREAK-MB): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 13(11):1087–1095
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest and no funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peuvrel, L., Saint-Jean, M., Quéreux, G. et al. Incidence and characteristics of melanoma brain metastases developing during treatment with vemurafenib. J Neurooncol 120, 147–154 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1533-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1533-z