Abstract
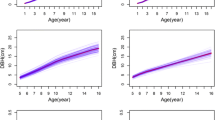
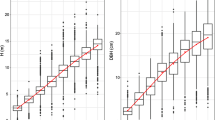
Genetic parameters were estimated for tree height (H), diameter at breast height (DBH), and volume from a progeny trial conducted in Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi) in Liaoning, China. A 12 × 12 full-diallel mating design with selfing was adopted, and data were collected in 2005 and 2014 at 20 and 29 years after planting. Based on an analysis of 55 of 144 potential crosses, general combining ability (GCA) and specific combining ability (SCA) were statistically significant for these traits. Variance was larger in SCA than in GCA in 2005, and the ratio of SCA to GCA was lower in 2014. Estimates of narrow-sense heritability were low to moderate, ranging from 0.10 for DBH to 0.14 for H, in 2005 and decreased in all traits except H as the trees aged. The reciprocal effect was not significant. Selfed progeny did not show severe inbreeding depression for survival or growth. The results of this study will facilitate the development of breeding and deployment strategies to increase the efficiency of genetic improvement in Japanese larch.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balocchi CE, Bridgwater FE, Zobel BJ, Jahromi S (1993) Age trends in genetic parameters for tree height in a non-selected population of loblolly pine. For Sci 39:231–251
Borralho NMG, Dutkowski GW (1998) Comparison of rolling front and discrete generation breeding strategies for trees. Can J For Res 28:987–993. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-28-7-987
Bouvet J-MM, Saya A, Vigneron P (2009) Trends in additive, dominance and environmental effects with age for growth traits in Eucalyptus hybrid populations. Euphytica 165:35–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9746-x
Burgess IP, Williams ER, Bell JC et al (1996) The effect of outcrossing rate on the growth of selected families of Eucalyptus grandis. Silvae Genet 45:97–100
Butler DG, Cullis BR, Gilmour AR, Gogel BJ (2009) ASReml-R reference manual. The State of Queensland, Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries, Brisbane
Byram T, Lowe WJ (1986) General and specific combining ability estimates for growth in loblolly pine. In: Proceeding of the IUFRO conference on breeding theory, progeny testing and seed orchards. Williamsburg, VA, pp 352–360
Carson MJ (1975) Control-pollinated seed orchards of best general combiners—a new strategy for radiata pine improvement. In: Proceedings of the DSIR plant breeding symposium, pp 144–149
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Cram WH (1984) Some effects of self-, cross-, and open-pollinations in Picea pungens. Can J Bot 62:392–395. https://doi.org/10.1139/b84-059
Diao S, Hou Y, Xie Y, Sun X (2016) Age trends of genetic parameters, early selection and family by site interactions for growth traits in Larix kaempferi open-pollinated families. BMC Genet 17:104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0400-7
Dieters MJ, White TL, Hodge GR (1995) Genetic parameter estimates for volume from fuil-sib tests of slash pine (Pinus elliottii). Can J For Res 25:1397–1408. https://doi.org/10.1139/x95-152
Du FX, Hoeschele I (2000) Estimation of additive, dominance and epistatic variance components using finite locus models implemented with a single-site Gibbs and a descent graph sampler. Genet Res 76:187–198. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016672300004614
Fukatsu E, Hiraoka Y, Matsunaga K et al (2015) Genetic relationship between wood properties and growth traits in Larix kaempferi obtained from a diallel mating test. J Wood Sci 61:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10086-014-1436-9
Gould PJ, Calir JBSt, Anderson PD (2011) Performance of full-sib families of Douglas-fir in pure-family and mixed-family deployments. For Ecol Manag 262:1417–1425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2011.06.042
Hayashi Y (1960) Taxonomical and phytogeographical study of Japanese conifers. Norin-Shuppan, Tokyo (in Japanese)
Henderson CR (1975) Best linear unbiased estimation and prediction under a selection model. Biometrics 31:423. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529430
Jansson G, Li B (2004) Genetic gains of full-sib families from disconnected diallels in loblolly pine. Silvae Genet 53:60–64. https://doi.org/10.1515/sg-2004-0011
Johnsen K, Major JE, Maier CA (2003) Selfing results in inbreeding depression of growth but not of gas exchange of surviving adult black spruce trees. Tree Physiol 23:1005–1008
Kusnandar D, Galmwey NW, Hertzler GL, Butcher TB (1998) Age trends in variance and heritabilities for diameter and height in maritime pine (Pinus pinaster AIT.) in western Australia. Silvae Genet 47:136–141
Lai M, Sun X, Chen D et al (2014) Age-related trends in genetic parameters for Larix kaempferi and their implications for early selection. BMC Genet 15:S10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-15-S1-S10
Samuel CJA, Johnstone RCB, Fletcher AM (1972) A diallel cross in Sitka spruce assessment of first year characters in an early glasshouse test. Theor Appl Genet 61:53–61
Snyder EB (1972) Notes: five-year performance of self-pollinated slash pines. For Sci 18:246
Wang JJ, Weng YH, Krasowski M et al (2018) Genetic parameters of growth and stem forking for black spruce progeny tested in New Brunswick, Canada. New For 49:265–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-017-9618-0
Weng YH, Lu P, Meng QF, Krasowski M (2015) Genetic resistance to western gall rust in jack pine and its relationship with tree height growth. Can J For Res 45:970–977. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2014-0535
White TL, Adams WT, Neale DB (2007) Forest genetics, 1st edn. CABI, Cambridge
White T, Davis J, Gezan S et al (2014) Breeding for value in a changing world: past achievements and future prospects. New For 45:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-013-9400-x
Williams CG, Savolainen O (1996) Inbreeding depression in conifers: implications for breeding strategy. For Sci 42:102–117
Woods JH, Heaman JC (1989) Effect of different inbreeding levels on filled seed production in Douglas-fir. Can J For Res 19:54–59
Wu HX, Matheson AC (2004) General and specific combining ability from partial diallels of radiata pine: implications for utility of SCA in breeding and deployment populations. Theor Appl Genet 108:1503–1512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1598-8
Wu HX, Matheson AC, Spencer D (1998) Inbreeding in Pinus radiata. I. The effect of inbreeding on growth, survival and variance. Theor Appl Genet 97:1256–1268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051018
Xiang B, Li B, Isik F (2003) Time trend of genetic parameters in growth traits of Pinus taeda L. Silvae Genet 52:114–121
Yanchuk AD (1996) General and specific combining ability from disconnected partial diallels of coastal Douglas-fir. Silvae Genet 45:37–45
Yao WH, Zhang YD, Kang MS et al (2013) Diallel analysis models: a comparison of certain genetic statistics. Crop Sci 53:1481–1490. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2013.01.0027
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Forestry Industry Research Special Funds for Public Welfare Projects (201504104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Xie, Y. & Sun, X. Full-diallel-based analysis of genetic parameters for growth traits in Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi). New Forests 51, 261–271 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-019-09729-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-019-09729-6