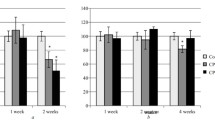
The effects of chronic (17 days) intranasal administration of low (50 IU/kg) and intermediate (8000 IU/kg) doses of human interferon-α (IA) on behavioral indicators of anxiety and depression and the monoaminergic system of the brain were studied in rats. Control rats received the same volume of intranasal physiological saline. IA was found to have any ambiguous effects on anxiety levels. Thus, anxiety in the open field test increased after administration of both doses of IA and decreased in the light-dark test and elevated plus maze test after small doses of IA. In the forced swimming test, administration of both doses of IA was followed by an increase in the duration of immobility (a behavioral symptom of depression). Administration of the intermediate (but not the small) dose of IA was followed by increases in the contents of dopamine and its metabolites in the olfactory bulb and decreases in the nucleus accumbens; the noradrenaline content decreased in the prefrontal cortex. It is suggested that these neurochemical changes in the brain may underlie the behavioral symptoms of depression induced by intranasal administration of intermediate doses of IA. Depression-like behavioral symptoms occurring after administration of small doses of IA were evidently not linked with changes in brain monoaminergic systems but could be due to other mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. S. Kudrin, P. M. Klodt, V. B. Narkevich, I. A. Shipilov, V. I. Poseva, G. M. Molodavkin, and T. A. Voronina, “Behavioral and neurochemical aspects of the antidepressant actions of GSB-106 – a dipeptide fragment of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF),” Eksperim. Klin. Farmakol., 75, No. 10, 41–45 (2012).
E. V. Loseva, N. A. Loginova, and I. G. Akmaev, “Neuroimmunomodulatory interferon-α and its dose-dependent action on behavior in humans and animals,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh. im. I. M. Sechenova, 95, No. 12, 1397–1406 (2009).
E. V. Loseva, N. A. Loginova, and I. G. Akmaev, “The role of interferon-α in the regulation of nervous system functions,” Usp. Fiziol. Nauk., 39, No. 2, 31–45 (2008).
E. V. Loseva, N. A. Loginova, L. M. Biryukova, V. N. Mats, and N. V. Pasikova, “Acquisition of feeding conditioned reflexes in young and old rats in controls and after administration of small doses of interferon-α,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh. im. I. M. Sechenova, 93, No. 4, 386–393 (2007).
E. V. Loseva, N. A. Loginova, V. V. Neklyudov, V. N. Mats, O. V. Kurskaya, and N. V. Pasikova, “Effects of human and rat interferon-α on behavior in rats of different ages and comparison of their amino acid sequence homologies,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat. I. P. Pavlova, 59, No. 4, 461–472 (2009).
E. V. Loseva, M. V. Mezentseva, L. I. Russu, N. A. Loginova, N. V. Panov, M. N. Shchetvin, and I. A. Suetina, “Suppression of cytokine synthesis in the spleen and brain and minor changes in c-fos expression in the brain in rats given intranasal administration of single-layer carbon nanotubes,” Ros. Nanotekhnol., 11, No. 3–4, 80–86 (2016).
E. V. Loseva, N. V. Pasikova, N. A. Loginova, L. M. Biryukova, and V. N. Mats, “Effects of intranasal administration of small doses of human interferon-α on behavior in rats of different ages,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat. I. P. Pavlova, 57, No. 3, 323–335 (2007).
E. V. Obraztsova, L. V. Osidak, E. G. Golovacheva, O. I. Afanas’eva, K. K. Mil’kint, E. G. Koroleva, S. A. Tarasov, M. V. Kachanova, V. P. Drinevskii, and I. A. Vasil’eva, “Interferon status in children with acute respiratory infections. Interferon therapy,” Byull. Eksperim. Biol. Med., Supplement Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology of Ultralow Doses of Antibodies to Endogenous Function Regulators, 22–26 (2009).
K. Yu. Sarkisova, M. A. Kulikov, V. S. Kudrin, V. B. Narkevich, I. S. Midzyanovskaya, L. M. Biryukova, A. A. Folomkina, and A. S. Bazyan, “Neurochemical mechanisms of depression-like behavior in WAG/Rij rats,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat. I. P. Pavlova, 63, No. 3, 303–315 (2013).
G. M. Asnis and R. De La Garza, 2nd, “Interferon-induced depression in chronic hepatitis C: a review of its prevalence, risk factors, biology, and treatment approaches,” J. Clin. Gastroenterology, 40, No. 4, 322–335 (2006).
S. Bhatt, P. Kilambi, P. Patel, N. Patel, A. Panchal, G. Shah, and S. Goswami, “Beneficial effect of aspirin against interferon-β-2b-induced depressive behavior in Sprague Dawley rats,” Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. (2016), doi: 10.111/1440-1681.12660.2016.
L. Capuron, G. Neurauter, D. L. Musselman, D. H. Lawson, C. B. Nemeroff, D. Fuchs, and A. H. Miller, “Interferon-alpha-induced changes in tryptophan metabolism. Relationship to depression and paroxetine treatment,” Biol. Psychiatry, 54, No. 9, 906–914 (2003).
I. E. Cicek, E. Cicek, F. Kayhan, F. Uguz, I. Erayman, S. Kurban, F. H. Yerlikaya, and N. Kaya, “The roles of BDNF, S100B, and oxidative stress in interferon-induced depression and the effect of antidepressant treatment in patients with chronic viral hepatitis: a prospective study,” J. Psychosom. Res., 76, No. 3, 227–232 (2014).
L. Danielyan, S. Beer-Hammer, A. Stolzing, R. Schäfer, G. Siegel, C. Fabian, P. Kahle, T. Biedermann, A. Lourhmati, M. Buadze, A. Novakovic, B. Proksch, C. H. Gleiter, W. H. Frey, 2nd, and M. Schwab, “Intranasal delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, macrophages, and microglia to the brain in mouse models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease,” Cell Transplant., 23, Suppl. 1, S123–S139 (2014).
R. De La Garza, 2nd and G. M. Asnis, “The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac sodium attenuates IFN-alpha induced alterations to monoamine turnover in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus,” Brain Res., 977, No. 1, 70–79 (2003).
R. De La Garza, 2nd, G. M. Asnis, E. Pedrosa, C. Stearns, A. L. Migdal, J. F. Reinus, R. Paladugu, and S. Vemulapalli, “Recombinant human interferon-alpha does not alter reward behavior, or neuroimmune and neuroendocrine activation in rats,” Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 29, No. 5, 781–792 (2005).
M. Dec and A. Puchalski, “Use of oromucosally administered interferon-alpha in the prevention and treatment of animal diseases,” Pol. J. Vet. Sci., 11, No. 2, 175–186 (2008).
S. V. Dhuria, L. R. Hanson, and W. H. Frey, 2nd, “Intranasal delivery to the central nervous system: mechanisms and experimental considerations,” J. Pharm. Sci., 99, No. 4, 1654–1673 (2010).
O. Dipasquale, E. A. Cooper, J. Tibbie, V. Voon, F. Baglio, G. Baselli, M. Cercignani, and N. A. Harrison, “Interferon-β acutely impairs whole-brain functional connectivity network architecture – A preliminary study,” Brain Behav. Immun., 58, 31–39 (2016).
A. Dunn, “Effects of cytokines and infections on brain neurochemistry,” J. Clin. Neurosci. Res., 6, No. 1–2, 52–68 (2006).
G. Dusheiko, “Side effects of alpha interferon in chronic hepatitis,” Hepatology, 26, No. 3, Suppl. 1, 112S–121S (1997).
B. Fahey, B. Hickey, D. Kelleher, A. M. O’Dwyer, and S. M. O’Mara, “The widely-used antiviral drug interferon-alpha induces depressive-and anxiogenic-like effects in healthy rats,” Behav. Brain Res., 182, No. 1, 80–87 (2007).
J. C. Felger, O. Alagbe, F. Hu, D. Mook, A. A. Freeman, M. M. Sanchez, N. H. Kalin, E. Ratti, C. B. Nemeroff, and A. H. Miller, “Effects of interferon-alpha on rhesus monkeys: a nonhuman primate model of cytokine-induced depression,” Biol. Psychiatry, 62, No. 11, 1324–1333 (2007).
J. C. Felger, L. Li, P. J. Marvar, B. J. Woolwine, D. G. Harrison, C. L. Raison, and A. H. Miller, “Tyrosine metabolism during interferon-alpha administration: Association with fatigue and CSF dopamine concentrations,” Brain Behav. Immun., 31, 153–160 (2013).
C. W. Fischer, A. Eskelund, D. P. Budac, S. Tillmann, N. Liebenberg, B. Elfving, and G. Wegener, “Interferon-alpha treatment induces depression-like behaviour accompanied by elevated hippocampal quinolinic acid levels in rats,” Behav. Brain Res., 293, 166–172 (2015).
L. Gao, S. Yu, Q. Chen, Z. Duan, J. Zhou, C. Mao, D. Yu, W. Zhu, J. Nie, and Y. Hou, “A randomized controlled trial of low-dose recombinant human interferons alpha-2b nasal spray to prevent acute viral respiratory infections in military recruits,” Vaccine, 28, No. 28, 4445–4451 (2010).
S. G. Helton and F. W. Lohoff, “Serotonin pathway polymorphisms and the treatment of major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders,” Pharmacogenomics, 16, No. 5, 541–553 (2015).
C. Hoyo-Becerra, A. Huebener, M. Trippler, M. Lutterbeck, Z. J. Liu, K. Truebner, T. Bajanowski, G. Gerken, D. M. Hermann, and J. F. Schlaak, “Concomitant interferon-alpha stimulation and TLR3 activation induces neuronal expression of depression-related genes that are elevated in the brain of suicidal persons,” PLoS One, 8, No. 12, e83149 (2013).
J. Ishikawa, A. Ishikawa, and S. Nakamura, “Interferon-alpha reduces the density of monoaminergic axons in the rat brain,” Neuroreport, 18, No. 2, 137–140 (2007).
O. A. Kalyoncu, D. Tan, H. Mirsal, O. Pektas, and M. Beyazyurek, “Major depressive disorder with psychotic features induced by interferon-alpha treatment for hepatitis C in a polydrug abuser,” J. Psychopharmacology, 19, No. 1, 102–105 (2005).
M. Kamata, H. Higuchi, M. Yoshimoto, K. Yoshida, and T. Shimizu, “Effect of single intracerebroventricular injection of alpha-interferon on monoamine concentrations in the rat brain,” Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 10, No. 2, 129–132 (2000).
J. Kaufman, C. DeLorenzo, S. Choudhury, and R. V. Parsey, “The 5-HT1A receptor in major depressive disorder,” Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 26, No. 3, 397–410 (2016).
C. Kiank, J. P. Zeden, S. Drude, G. Domanska, G. Fusch, W. Otten, and C. Schuett, “Psychological stress-induced, IDO1-dependent tryptophan catabolism: implications on immunosuppression in mice and humans,” PLoS One, 5, No. 7, e11825 (2010).
I. J. Kopin, K. S. Bankiewicz, and J. Harvey-White, “Assessment of brain dopamine metabolism from plasma HVA and MHPG during debrisoquin treatment: validation in monkeys treated with MPTP,” Neuropsychopharmacology, 1, No. 2, 119–125 (1988).
M. Kosel, A. Bilkei-Gorzo, R. Zawatzky, A. Zimmer, and T. E. Schlaepfer, “Pegylated human interferon-alpha 2a does not induce depression-associated changes in mice,” Psychiatry Res., 185, No. 1–2, 243–247 (2011).
D. Kugel, G. Kochs, K. Obojes, J. Roth, G. P. Kobinger, D. Kobasa, O. Haller, P. Staeheli, and V. von Messling, “Intranasal administration of alpha interferon reduces seasonal influenza A virus morbidity in ferrets,” J. Virol., 83, No. 8, 3843–3851 (2009).
K. Kuter, W. Kolasiewicz, K. Golembiowska, A. Dziubina, G. Schulze, K. Berghauzen, J. Wardas, and K. Ossowska, “Partial lesion of the dopaminergic innervation of the ventral striatum induces ‘depressive-like’ behavior of rats,” Pharmacol. Rep., 63, No. 6, 1383–1392 (2011).
N. Mayr, J. Zeitlhofer, L. Deecke, E. Fritz, H. Ludwig, and H. Gisslinger, “Neurological function during long-term therapy with recombinant interferon alpha,” J. Neuropsych. Clin. Neurosci., 11, No. 3, 343–348 (1999).
S. Mehta, S. Mukherjee, D. Balasubramanian, and A. Chowdhary, “Evaluation of neuroimmunomodulatory activity of recombinant human interferon-α,” Neuroimmunomodulation, 21, No. 5, 250–256 (2014).
E. Palazidou, “The neurobiology of depression,” Br. Med. Bull., 101, 127–145 (2012).
C. L. Raison, A. S. Borisov, B. J. Woolwine, B. Massung, G. Vogt, and A. H. Miller, “Interferon-alpha effects on diurnal hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity: relationship with proinflammatory cytokines and behavior,” Mol. Psychiatry, 15, No. 5, 535–547 (2010).
C. L. Raison, L. Capuron, and A. H. Miller, “Cytokines sing the blues: inflammation and the pathogenesis of depression,” Trends Immunol., 27, No. 1, 24–31 (2006).
C. L. Raison, M. Demetrashvili, L. Capuron, and A. H. Miller, “Neuropsychiatric adverse effects of interferon-alpha: recognition and management,” CNS Drugs, 19, No. 2, 105–123 (2005).
J. Reichen, L. Bianchi, P. C. Frei, P. J. Mal, D. Lavanchy, and M. Schmid, “Efficacy of steroid withdrawal and low-dose interferon treatment in chronic active hepatitis. Results of a randomized multicenter trial. Swiss Association for the Study of the Liver,” J. Hepatol., 20, No. 2, 168–174 (1994).
C. Reyes-Vázquez, B. Prieto-Gómez, and N. Dafny, “Interferon modulates central nervous system function,” Brain Res., 1442, 76–89 (2012).
A. B. Richards and E. Sherwood (inventors), Amarillo Biosciences, Inc. (assignee), United States Patent 6036949, “Treatment of fibromyalgia with low interferon doses.”
Y. Rotman, B. B. Borg, A. Soza, J. J. Feld, A. A. Modi, R. Loomba, G. Lutchman, E. Rivera, E. Doo, M. G. Ghany, T. Heller, A. U. Neumann, T. J. Liang, and J. H. Hoofnagle, “Low-and standard-dose peginterferon alfa-2a for chronic hepatitis C, genotype 2 or 3: efficacy, tolerability, viral kinetics and cytokine response,” Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther., 31, No. 9, 1018–1027 (2010).
Yu. K. Sarkisova, I. S. Midzianovskaia, and M. A. Kulikov, “Depressive-like behavioral alterations and c-fos expression in the dopaminergic brain regions in WAG/Rij rats with genetic absence epilepsy,” Behav. Brain Res., 144, No. 1–2, 211–226 (2003).
Yu. K. Sarkisova and M. A. Kulikov, “Behavioral characteristics of WAG/Rij rats susceptible and non-susceptible to audiogenic seizures,” Behav. Brain Res., 166, No. 1, 9–18 (2006).
K. Sarkisova and G. van Luijtelaar, “The WAG/Rij strain: a genetic animal model of absence epilepsy with comorbidity of depression. Review article,” Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 35, 854–876 (2011).
H. Shuto, Y. Kataoka, T. Horikawa, N. Fujihara, and R. Oishi, “Repeated interferon-alpha administration inhibits dopaminergic neural activity in the mouse brain,” Brain Res., 747, No. 2, 348–351 (1997).
J. W. Slaton, T. Karahima, P. Perrotte, K. Inoue, S. J. Kim, J. Izawa, D. Kedar, D. J. McConkey, R. Millikan, P. Sweeney, C. Yoshikawa, T. Shuin, and C. P. Dinney, “Treatment with low-dose interferon-alpha restores the balance between matrix metalloproteinase-9 and E-cadherin expression in human transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder,” Clin. Cancer Res., 7, No. 9, 2840–2853 (2001).
S. Sockalingam, P. S. Links, and S. E. Abbey, “Suicide risk in hepatitis C and during interferon-alpha therapy: a review and clinical update,” J. Viral. Hepat., 18, No. 3, 153–160 (2011).
B. M. Spruijt and W. H. van Hooff Gispen, “Ethology and neurobiology of grooming behavior,” Physiol. Rev., 72, 825–853 (1992).
M. M. Wen, “Olfactory targeting through intranasal delivery of biopharmaceutical drugs to the brain -current development,” Discov. Med., 11, No. 61, 497–503 (2011).
M. C. Wichers, G. Kenis, G. H. Koek, G. Robaeys, N. A. Nicolson, and M. Maes, “Interferon-alpha-induced depressive symptoms are related to changes in the cytokine network but not to cortisol,” J. Psychosom. Res., 62, No. 2, 207–214 (2007).
J. P. Yang, H. J. Liu, S. M. Cheng, Z. L. Wang, X. Cheng, H. X. Yu, and X. F. Liu, “Direct transport of VEGF from the nasal cavity to brain,” Neurosci. Lett., 449, No. 2 108–111 (2009).
L. S. Zheng, S. Hitoshi, N. Kaneko, K. Takao, T. Miyakawa, Y. Tanaka, H. Xia, U. Kalinke, K. Kudo, S. Kanba, K. Ikenaka, and K. Sawamoto, “Mechanisms for interferon-α-induced depression and neural stem cell dysfunction,” Stem Cell Rep., 3, No. 1, 73–84 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
P. M. Klodt is deceased.
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 103, No. 4, pp. 417–431, April, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loseva, E.V., Loginova, N.A., Sarkisova, K.Y. et al. Behavioral Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression and Brain Monoamine Contents in Rats after Chronic Intranasal Administration of Interferon-α. Neurosci Behav Physi 48, 954–962 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-018-0655-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-018-0655-8