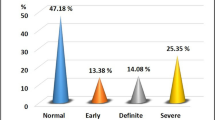
Objectives. To study neurological complications in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM 1) receiving different methods of insulin therapy. Materials and methods. A total of 34 patients aged 18–40 years with DM 1 for 14.25 ± 9.25 years and receiving insulin therapy were studied. At the time of the study, patients of group 1 had been receiving insulin therapy by continuous subcutaneous infusion therapy (insulin pump) for 4.5 ± 1.5 years; the duration of the preceding period of standard therapy by repeated s.c. injections (basal-bolus therapy) was 11.3 ± 5.4 years. Patients of group 2 had been on basal-bolus therapy for 12.7 ± 7.7 years. Clinical evaluation of neurological status, autonomic changes, and testing on the MMSE, MoCA, HADS, TSS, NSS, and NDS were performed in patients of both groups. Results and conclusions. Patients of group 1, as compared with those of group 2, had less severe neuropathic, cognitive, and autonomic disorders and had a more favorable emotional background, indicating that the first treatment was more effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Diabetes Association, Diabetes Statistics for Youth (2004), http//w.niddk.nih.gov/news/reserch-updates/Pages/Rates-of-Diabetes-Increasing-in-U-S--Youth.aspx, acc. Aug. 30, 2015.
Yu. I. Suntsov, L. L. Bolotskaya, O. V. Maslova, and I. V. Kazakov, “Epidemiology of diabetes mellitus and prediction of its prevalence in the Russian Federation,” Sakhar. Diabet, No. 1, 15–18 (2011), doi: https://doi.org/10.14341/2072-0351-6245.
L. Norgren, W. Hiatt, J. Dormandy, et al., “Inter-Society Consensus for the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease (TASC II),” Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg., 23, No. 1, 1–75 (2007), doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2006.09.024.
E. L. Feldman, Stevens, M. J., et al., “Somatosensory neuropathy,” in: Elltenberg and Rifkin’s Diabetes Mellitus, D. Porte, R. S. Sherwin, and A. Baron, (eds.), McGraw Hill, New York (2002).
A. L. Vinik et al., “Diabetic autonomic neuropathy,” in: Elltenberg and Rifkin’s Diabetes Mellitus, D. Porte, R. S. Sherwin, and A. Baron, (eds.), McGraw Hill, New York (2002).
P. Narendran, S. J. Creely, A. Syed, et al., “Aggressive and devastating neuropathy, the consequence of untreated slow-onset type 1 diabetes,” Q. J. Med., 523–526 (2011), doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcq133.
E. V. Spitsyna, Studies of the Associations of a Number of Candidate Genes with Diabetic Polyneuropathy in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Auth. Abstr. Master’s Thesis in Med. Sci., Moscow (2008), www.genetika.ru›aaa genetika/Ucheniy sovet…Spicina.doc.
I. A. Strokov, T. R. Bursa, E. V. Zotova, et al., “Association of polymorphisms of the SOD2 gene and the SOD3 gene with diabetic polyneuropathy n type 1 diabetes mellitus,” Sakhar. Diabet, 2003, No. 2, 3–5 (2003), doi: https://doi.org/10.14341/2072-0351-5924.
E. Sabbath, K. Savola, T. Evening, et al., “Genetic, autoimmune, and clinical characteristics of childhood and adult onset type 1 diabetes,” Diabetes Care, No. 23, 1326–1332 (2000), doi: https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.23. 9.1326.
I. V. Gur’eva, E. Yu. Komelyagina, I. V. Kuzina, and A. S. Ametov, Diabetic Peripheral Sensorimotor Neuropathy. Pathogenesis, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis, Meditsina, Moscow (2004).
P. Rosen, P. P. Nawroth, G. King, et al., “The role of oxidative stress in the onset and progression of diabetes and its complications,” Diab. Metab. Res. Rev., No. 17, 189–212 (2001), doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.196.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group, “Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes, UKPDS 38,” BMJ, 317, No. 7160, 703–713 (1998), doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.317.7160.703.
DCCT Research Group, “The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus,” New Engl. J. Med., 70, 1009–1018 (1993), doi: 10. 1056/nejm199309303291401.
V. M. Prikhozhan, “Classification of diabetic neuropathy,” Probl. Endokrinol., 33, No. 3, 79–85 (1987).
S. V. Kotov, A. P. Kalinin, I. G. Rybakova, Diabetic Neuropathy, Meditsina (2000).
S. P. Markin, Nervous System Lesions in Diabetes Mellitus, Meditsina, Moscow (2008).
E. Litmanovich, R. Geva, and M. Rachmiel, “Short and long-term neurological-behavioral alterations in type 1 diabetes mellitus pediatric population,” World J. Diabetes, 6, No. 2, 259–270 (2015), doi: https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i2.259.
A. J. Boulton, F. A. Gries, and J. A. Jervell, “Guidelines for the diagnosis and outpatient management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy,” Diabet. Med., 15, No. 6, 508–514 (1998), doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-9136(199806)15,6508::aid-dia6133.0.co,2-l.
Zh. S. Al’bekova, The Prevalence of Diabetic Polyneuropathy in Patient with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. A Clinical-Electrophysiological and Genetic Study, Moscow, (2011), www.endocrincentr.ru/images/material-images/2809.docx, acc. Aug. 30, 2015.
P. J. Dyck, J. L. Karnes, and P. S. O’Brien, “The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study, reassessment of tests and criteria for diagnosis and staged severity,” Neurology, No. 42, 1164–1170 (1992), doi:https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.42.6.1164.
P. J. Dyck, W. J. Litchy, N. A. Lehman, et al., “Variables influencing neuropathic endpoints: The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study of Healthy Subjects,” Neurology, No. 45, 1115–1121 (1995), doi: https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.45.6.1115.
A. M. Vein (ed.), Autonomic Disorders, Med. Inform. Agentstvo, Moscow (2000).
A. L. Vertkin, O. N. Tkacheva, Kh. M. Torshkhoeva, et al., Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy: Prevalence, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis. Methodological Guidelines, GEOTAR-Media, Moscow (2005).
V. V. Zakharov, “Neurophysiological tests. The need and potential for use,” Consil. Medicum, 13, No. 2, 82–90 (2011).
E. A. Trifonova, Clinical-Psychological Factors in Impairments to Mental Adaptation and the Quality of Life in Patients with Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus: Auth. Abstr. Master’s Thesis in Psychol. Sci., www.rsl.ru. acc. Aug. 30, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S. S. Korsakova, Vol. 116, No. 9, Iss. 1, pp. 13–17, September, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimkina, N.F., Nad’, Y.G. & Barantsevich, E.R. Neurological Complications in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus with Different Methods of Insulin Therapy. Neurosci Behav Physi 48, 69–73 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-017-0532-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-017-0532-x