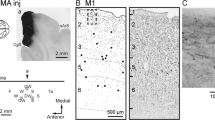
Ipsilateral associative connections between different fields in the primary sensory (S1) and primary motor (M1) areas of the cortex were studied in 25 adult cats after local coagulation and infusion of horseradish peroxidase. The distributions of associative M1 and S1 fibers were found to correspond to the margins of the somatotopic representations of different parts of the body. The fields within M1 (4y, 6ab) and S1 (1, 2, 3a, 3b), which have different morphofunctional organization, were not connected by a system of associative fibers crossing the cytoarchitonic boundaries of these fields. The primary sensory (S1) and motor (M1) areas of cortex did not have reciprocal connections. Occasional fibers connected neighboring fields in M1 and A1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. A. Badalyan, Dzh. S. Sarkisyan, and V. I. Pogosyan, “Corticocortical and thalamocortical sources of afferentation to the representation area of the radial nerve in the primary somatosensory cortex of the cat,” Biol. Zh. Armenii, 48, No. 2, 18–22 (1995).
N. M. Ipekchyan, “Characteristics of corticocortical ipsilateral connections of the primary, secondary, and tertiary sensorimotor zones in the cat brain,” Morfologiya, 139, No. 1, 22–26 (2011).
N. M. Ipekchyan and O. G. Baklavadzhyan, “The projections of fields 5 and 7 to subdivisions of the sensorimotor area of the cortex in the cat brain,” Neirofiziologiya, 20, No. 3, 319–326 (1988).
V. Mountcastle, “An organizing principle for cerebral function: the unit module and the distributed system,” in: The Mindful Brain [Russian translation], Mir, Moscow (1981), pp. 15–67.
A. A. Skoromets, A. P. Skoromets, and T. A. Skoromets, “Topical diagnosis of focal lesions of the nervous system,” in: Nervous Diseases [in Russian], MEDpressInform, Moscow (2008), pp. 197–220.
H. Asanuma, C. D. Larsen, and H. Yumiya, “Direct sensory pathways to the motor cortex in monkey:A basis of cortical reflexes,” in: Integration in Nervous System [in Russian], Igaku-Shoin, Tokyo (1979), pp. 223–238.
H. Asanuma, C. D. Larsen, and P. Zarzecki, “Peripheral input pathways projecting to the motor cortex in the cat,” Brain Res., 172, No. 2, 197–208 (1979).
H. Asanuma and I. Rosen, “Functional role of afferent input to monkey motor cortex,” Brain Res., 40, No. 1, 3–5 (1972).
C. Brodmann, Vergleichende Lokalizationslehre der Groshirnrinde in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund des Zellenbaues [in German], J. A. Barth, Leipzig, (1925).
J. Castaldo, J. Rodgers, A. Rae-Grant, et al., “Diagnosis and neuroimaging of acute stroke producing distal arm monoparesis,” J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Res., 12, No. 6, 253–258 (2003).
E. A. Fridman, T. Hanakawa, M. Chung, et al., “Reorganization of the human ipsilateral premotor cortex after stroke,” Brain, 127, No. 4, 747–758 (2004).
C. C. Gatter and T. P. S. Powell, “The intrinsic connections of the cortex of area 4 of the monkey,” Brain, 101, No. 3, 513–541 (1978).
R. Hassler and C. Muhs-Clement, “Architektonischer Aufbau des sensomotorischen und parietalen Cortex der Katze,” J. Hirnforsch., 6, No. 4, 377–420 (1964).
P. B. Johnson, A. Angelucci, R. Ziparo, et al., “Segregation and overlap of callosal and association neurons in frontal and parietal cortices of primate: a spectral and coherency analysis,” J. Neurosci., 9, No. 7, 2313–2326 (1989).
E. G. Jones, I. D. Coulter, and S. H. C. Hendry, “Intracortical connectivity of architectonic fields in the somatic sensory, motor and parietal cortex of monkeys,” J. Comp. Neurol., 181, No. 2, 291–341 (1978).
E. G. Jones and T. P. S. Powell, “The ipsilateral connexions of the somatic sensory areas in the cat,” Brain Res., 9, No. 1, 71–94 (1968).
E. G. Jones and T. P. S. Powell, “Connexions of the somatic sensory cortex of the rhesus monkey. I. Ipsilateral cortical connexions,” Brain, 19, No. 3, 477–502 (1969).
E. G. Jones and T. P. S. Powell, “An anatomical study of converging sensory pathways within the cerebral cortex of the monkey,” Brain, 93, No. 4, 790–820 (1970).
E. G. Jones and S. P. Wise, “Size, laminar and columnar distribution of efferent cells in sensory-motor cortex of monkey,” J. Comp. Neurol., 175, No. 4, 391–438 (1977).
C. Kawamura and C. Otani, “Corticocortical fiber connections in the cat cerebrum: the frontal region,” J. Comp. Neurol., 139, No. 4, 423–448 (1970).
M. M. Mesulam, “Tetramethylbenzidine for HRP neurochemistry: a non-carcinogenic blue reaction product with superior sensitivity for visualizing neural afferents and efferents,” J. Histochem. Cytochem., 26, No. 2, 106–117 (1978).
W. J. H. Nauta and P. A. Gygax, “A silver impregnation of degenerating axons in the central nervous system: a modified technic,” Stain Technol., 29, No. 1, 91–93 (1954).
A. Nieoullon and L. Rispal-Padel, “Somatotopic localization in cat motor cortex,” Brain Res., 105, No. 3, 405–422 (1976).
L. L. Porter, “Somatosensory input onto pyramidal tract neurons in rodent motor cortex,” Neuroreport, 7, No. 14, 2309–2315 (1996).
C. N. Woolsey, “Organization of somatic sensory and motor areas of the cerebral cortex,” in: Biological and Biochemical Bases of Behavior, University of Wisconsin Press, Madison (1958), pp. 63–81.
H. Yumiya and C. Chez, “Specialized subregions in the cat motor cortex: anatomical demonstration of differential projections to the rostral and causal sectors,” Exp. Brain Res., 53, No. 2, 259–276 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Morfologiya, Vol. 143, No. 2, pp. 7–12, March–April, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ipekchyan, N.M., Badalyan, S.A. The Primary Motor and the Primary Sensory Cortex – Two Local Cortical Centers of the Sensorimotor Representation of the Body. Neurosci Behav Physi 44, 455–460 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-014-9932-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-014-9932-3