Abstract
The bituminous-to-sub-bituminous quality feed coals of thermal power plants contain several environmental-concern trace elements (As, Se, Ni, Cr, Zn, Pb, Cu, Cd, Co and Mn). During combustion, these elements are enriched or depleted in the major coal combustion residues (CCR, fly and bottom ash). The analyzed elements are classified into three different groups according to the estimated enrichment ratio and relative enrichment index. Class I contains the volatile elements As, Se, both of which are depleted in fly and bottom ash. Class II contains the semi-volatile elements Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Cd and Pb, which are more enriched in finer fly ash than coarse bottom ash. In contrast, the less volatile Class III elements Co and Mn are equally enriched in fly and bottom ash. The major CCR containing heavy load of these elements (about 1826 t/year) are gradually exposed to the different segments of environment such as air, water and soil. These elements may have a possibility to be bioavailable in the food chain, which may give harmful influence to the ecological receptors. As per risk assessment code, the analyzed elements As, Se, Cr and Ni have low-risk character, while rest of the elements Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn, Co and Mn are safe for the environment. Laboratory water leaching experiment of elements in fly ash and bottom ash shows that these combustion residues are non-hazardous and may be used in various sectors such as construction field, land filled materials, mine reclamation and also in agriculture field. An understanding of regular monitoring and skillful management for the disposal practice as well as environmentally safe utilization of combustion residues generated from thermal power plants is a crucial issue from public health viewpoint.







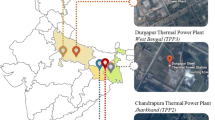
Source: Central electricity authority, Govt. India
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Baba, A., & Kaya, A. (2004). Leaching characteristics of solid wastes from thermal power plants of western Turkey and composition of toxicity methodologies. Journal of Environmental Management, 73, 199–207.
Basu, M., Pande, M., Bhadoria, P. B. S., & Mahapatra, S. C. (2009). Potential fly ash utilisation in agriculture: A global review. Progress in Natural Science, 19, 1173–1186.
Bhangare, R. C., Ajmal, P. Y., Sahu, S. K., Pandit, G. G., & Puranik, V. D. (2011). Distribution of trace elements in coal and combustion residues from five thermal power Plants in India. International Journal of Coal Geology, 86, 349–356.
Bhattacharyya, S., Donahoe, R. J., & Patel, D. (2009). Experimental study of chemical treatment of coal fly ash to reduce the mobility of priority of trace elements. Fuel, 88, 1173–1183.
Central Authority of Electricity Report, Govt. of India, 2016–2017.
Eskanazy, G., Finkelman, R. B., & Chatterjee, S. (2010). Some considerations concerning the use of correlation coefficients and cluster analysis in interpreting coal geochemistry data. International Journal of Coal Geology, 83, 491–493.
European Council Decision 2003/33/EC. Official Journal of the European communities, 16, 27–49.
Finkelman, R. B. (2004). Potential health impacts of burning coal beds and waste banks. International Journal of Coal Geology, 59, 19–24.
Hower, J. C., Robertson, J. D., Thomas, G. A., Wong, A. S., Schram, W. H., Graham, U. M., et al. (1996). Characterisation of fly ash from Kentucky power plants. Fuel, 75, 403–411.
Hu, G., Liu, G., Wu, D., & Fu, B. (2018). Geochemical behaviour of hazardous volatile elements in coals with different geological origin during combustion. Fuel, 233, 361–367.
Huggins, F., & Goodarzi, F. (2009). Environmental assessment of elements and polyaromatic hydrocarbons emitted from a Canadian coal fired power plant. International Journal of Coal Geology, 77, 282–288.
Izquierdo, M., & Querol, X. (2012). Leaching behaviour of elements from coal combustion fly ash: An overview. International Journal of Coal Geology, 94, 54–66.
Jankowski, J., Ward, C. R., French, D., & Groves, S. (2006). Mobility of trace elements from selected Australian fly ashes and its potential impact on aquatic ecosystem. Fuel, 85, 243–256.
Karayigit, A. I., Gayer, R. A., Querol, X., & Onacak, T. (2000). Contents of major and trace elements in feed coals from Turkish coal-fired power plants. International Journal of Coal Geology, 44, 169–184.
Li, X., Dai, S., Zhang, W., Li, T., Zheng, X., & Chen, W. (2014). Determination of As and Se in coal and coal combustion products using closed vessel microwave digestion and collision/reaction cell technology (CCT) of inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS). International Journal of Coal Geology, 124, 1–4.
Li, J., Zhuang, X., Querol, X., Font, O., Moreno, N., & Zhou, J. (2012). Environmental geochemistry of the feed coals and their combustion by-products from two coal-fired power plants in Xinjiang Province, Northwest China. Fuel, 95, 446–456.
Markich, S. J., & Jeffree, R. A. (1994). Absorption of divalent trace metals as analogue of calcium by Australian fresh water bivalves: an explanation of how water hardness reduces metal toxicity. Aquatic Toxicology, 29, 257–290.
Markwiese, J. T., Rogers, W. J., Carriker, N. E., Thal, D. I., Vitale, R. J., Gruzalski, J. G., et al. (2014). Natural attenuation of coal combustion waste in river sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 5235–5246.
Mukerjee, A. B., & Zevenhoven, R. (2006). Mercury in coal ash and its fate in the Indian subcontinent: A synoptic review. Science of the Total Environment, 368, 384–392.
Pandey, V. C., Singh, J. S., Singh, R. P., Singh, N., & Yunus, M. (2011). Arsenic hazards in coal fly ash and its fate in Indian scenario. Resource Conservation and Recycling, 55, 819–835.
Pendias, A. K. (2004). Soil-plant transfer of trace elements: An environmental issue. Geoderma, 122, 143–149.
Querol, X., Turel, J. L. F., & Soler, A. L. (1995). Trace elements in coal and their behaviour during combustion in a large power station. Fuel, 74, 331–343.
Rowe, C. L., Hopkins, W. A., & Congdon, J. D. (2002). Ecotoxicological implications of aquatic disposal of coal combustion residues in the United States: A review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 80, 207–276.
Sanders, J. G., & Riedel, G. F. (1998). Metal accumulation and impacts in phytoplankton. In W. J. Langston & M. J. Bebianno (Eds.), Metal metabolism in aquatic environments. Dordrecht: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4419-4731-4.
Saqib, N., & Backstrom, M. (2016). Chemical association and mobility of trace elements in 13 different fuel incineration fly ashes. Fuel, 165, 193–204.
Shim, Y. S., Rhee, S. W., & Lee, W. K. (2005). Comparison of leaching characteristics of heavy metals from bottom and fly ashes in Korea and Japan. Waste Management, 25, 473–480.
Spears, D. A., & Tarrazona, M. R. M. (2004). Trace elements in combustion residues from a UK power station. Fuel, 83, 2265–2270.
Sun, R., Liu, G., Zheng, L., & Chou, C. L. (2010). Geochemistry of trace elements in coals from the Zhuji Mine, Huainan coal field Anhui, China. International Journal of coal geology, 81, 81–96.
Sushil, S., & Batra, V. S. (2006). Analysis of fly ash heavy metal content and disposal in three thermal power plants in India. Fuel, 85, 2676–2679.
Swaine, J. D. (2000). Why trace elements are important. Fuel Processing Technology, 65–66, 21–33.
Swaine, J. D., & Goodarzi, F. (1995). Environmental aspects of trace elements in coal., Energy and Environment Dordrecht: Spirnger. ISBN 9780792336662.
Tang, Q., Liu, G., Zhou, C., & Sun, R. (2012). Distribution and fate of environmentally sensitive elements (arsenic, mercury, stibium and selenium) in coal-fired power plants at Huainan, Anhui, China. Fuel, 95, 334–339.
Tang, Q., Liu, G., Zhou, C., & Sun, R. (2013). Distribution of trace elements in feed coal and combustion residues from two coal-fired power plants at Huainan, Anhui, China. Fuel, 107, 315–322.
Taylor, G. H., Teichmuller, M., Davis, A., Diessel, C. F. K., Littke, R., & Robert, P. (1998). Organic petrology: A new handbook incorporating some revised parts of Stach’s textbook of coal petrology. Stuttgart: Gebrüder Borntraeger. ISBN 978-3-443-01036-2.
Tiwari, M. K., Bajpai, S., Dewangan, U. K., & Tamrakar, R. K. (2015). Suitability of leaching test methods for fly ash and slag: A review. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 8, 523–537.
Tiwari, M., Sahu, S. K., Bhangare, R. C., Ajmal, P. Y., & Pandit, G. G. (2014). Elemental characterisation of coal, fly ash, and bottom ash using energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence technique. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 90, 53–57.
Vassilev, S. V., & Vassileva, C. G. (1996). Mineralogy of combustion wastes from coal-fired power stations. Fuel Processing Technology, 47, 261–280.
Vassilev, S. V., & Vassileva, C. G. (1997). Geochemistry of coals, coal ashes and combustion wastes from coal-fired power stations. Fuel Processing Technology, 51, 19–45.
Vejahati, F., Zhenghe, X., & Gupta, R. (2010). Trace elements in coal: Associations with coal minerals and their behavior during coal utilization—A review. Fuel, 89, 904–911.
Verma, S. K., Masto, R. E., Gautam, S., Choudhury, D. P., Ram, L. C., Maiti, S. K., et al. (2015). Investigation of PAHs and trace elements in coal and its combustion residues from a power plant. Fuel, 162, 138–147.
Xu, M., Yan, R., Zheng, C., Qiao, Y., Han, J., & Sheng, C. (2003). Status of trace element emission in coal combustion process: A review. Fuel Processing Technology, 85, 215–237.
Yan, R., Gauthier, D., & Flamant, G. (2001). Volatility and chemistry of trace elements in a coal combustor. Fuel, 80, 2217–2226.
Yan, C. Z., Li, Q. Z., Zhang, X., & Li, G. X. (2010). Mobility and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediment of Xiamen Bay and its adjacent areas, China. Environmental Earth Science, 60, 1469–1479.
Yao, Z. T., Ji, X. S., Sarker, P. K., Tang, J. H., Ge, L. Q., Xia, M. S., et al. (2015). A comprehensive review on the application of coal fly ash. Earth-Science Reviews, 141, 105–121.
Zhang, J. Y., Zheng, C. G., Ren, D. Y., Chou, C. L., Liu, J., Zeng, R. S., et al. (2004). Distribution of potentially hazardous trace elements in coals from Shanxi province, China. Fuel, 83, 129–135.
Zhao, S., Duan, Y., Lu, J., Gupta, R., Pudasainee, D., Liu, S., et al. (2018a). Thermal stability, chemical speciation and leaching characteristics of hazardous trace elements in FGD gypsum from coal-fired power plants. Fuel, 231, 94–100.
Zhao, S., Duan, Y., Lu, J., Gupta, R., Pudasainee, D., Liu, S., et al. (2018b). Chemical speciation and leaching characteristics of hazardous trace elements in coal and fly ash from coal fired power plants. Fuel, 232, 463–469.
Zhou, Y., Ning, X., Liao, X., Lin, M., Liu, J., & Wang, J. (2013). Characterization and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals found in fly ashes from waste filter bags obtained from Chinese steel plant. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 95, 130–136.
Acknowledgments
The authors duly acknowledge the support of DST-PURSE and UGC-SAP program to carry out the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, D., Chatterjee, D., Chakravarty, S. et al. Investigation of Environmental-Concern Trace Elements in Coal and Their Combustion Residues from Thermal Power Plants in Eastern India. Nat Resour Res 28, 1505–1520 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09451-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09451-2