Abstract
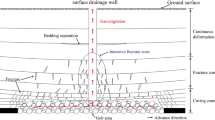
Fracture is an important factor controlling mineralization and ore distribution in metallic deposits. Fracture also affects mechanical stability of drifts. A plausible three-dimensional discrete fracture network (DFN) was constructed using GEOFRAC, a geostatistical method of conditioning directions (strikes and dips) and locations of sample fractures. The northern part of the Gejiu tin district, southwest China, was selected, using 10,212 fractures sampled on drift roofs at five different levels and along a 5463 m length. Key parameters of this DFN are fracture density, direction, and the connective condition of disks that form a fracture plane. The simulated fractures were verified by good correspondence of their directions with those of the sample fractures; furthermore, continuous fractures longer than 1 km matched the faults observed in outcrops. The most notable result was clarification of fracture control by the orebody shape: Simulated gentle fractures (30° dips or less) formed layered orebodies and created boundaries between each layer, while steep fractures (60° dips or more) displaced the layers by acting as faults. Such fault-type fractures and the densely fractured portions require caution with respect to mining safety. It was concluded that GEOFRAC is useful for three-dimensional DFN modeling in underground mines.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuna, J. A., & Yortsos, Y. C. (1995). Application of fractal geometry to the study of networks of fractures and their pressure transient. Water Resources Research, 31(3), 527–540.
Cheng, Y. B., Mao, J. W., Chang, Z. S., & Pirajno, F. (2013). The origin of the world class tin-polymetallic deposits in the Gejiu district, SW China: Constraints from metal zoning characteristics and 40Ar–39Ar geochronology. Ore Geology Review, 53, 50–62.
Chiu, S. N., Stoyan, D., Kendall, W. S., & Mecke, J. (2013). Stochastic geometry and its applications (pp. 297–302). Hoboken: Wiley.
Clemo, T., & Smith, L. (1997). A hierarchical model for solute transport in fractured media. Water Resources Research, 33(8), 1763–1783.
De Dreuzy, J. R., Pichot, G., Poirriez, B., & Erhel, J. (2013). Synthetic benchmark for modeling flow in 3D fractured media. Computers & Geosciences, 50, 59–71.
Erhel, J., de Dreuzy, J. R., & Poirriez, B. (2009). Flow simulation in three-dimensional discrete fracture networks. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 31(4), 2688–2705.
Ivanova, V. M. (1998). Geologic and stochastic modeling of fracture systems in rocks, Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Ivanova, V. M., & Einstein, H. H. (2004). Three-dimensional hierarchical stochastic modeling of fracture systems—An example from the Yates field, In: Proceedings of the 6th North American rock mechanics symposium (NARMS), Gulf Rocks 2004, Houston, TX.
Ivanova, V. M., Sousa, R., Murrihy, B., & Einstein, H. H. (2014). Mathematical algorithm development and parametric studies with the GEOFRAC three-dimensional stochastic model of natural rock fracture systems. Computers & Geosciences, 67(3), 100–109.
Koike, K., & Ichikawa, Y. (2006). Spatial correlation structures of fracture systems for identifying a scaling law and modeling fracture distributions. Computers & Geosciences, 32(8), 1079–1095.
Koike, K., Kubo, T., Liu, C. X., Masoud, A., Amano, K., & Kurihara, A. (2015). 3D geostatistical modeling of fracture system in a granitic massif to characterize hydraulic properties and fracture distribution. Tectonophysics, 660, 1–16.
Koike, K., Liu, C. X., & Sanga, T. (2012). Incorporation of fracture directions into 3D geostatistical methods for a rock fracture system. Environmental Earth Sciences, 66(8), 1403–1414.
Lai, D. X. (2005). Geological characteristics and ore prospecting orientation of Damalu inter layer oxidized deposit in Gejiu tin mine. Miner Resources Geol., 1, 25–28. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liao, S. L., Chen, S. Y., Deng, X. H., Li, P., Zhao, J. N., & Liao, Y. Z. (2014). Fluid inclusion characteristics and geological significance of the Xi’ao copper–tin polymetallic deposit in Gejiu, Yunnan Province. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79, 455–467.
Liu, R. C., Li, B., Jiang, Y. J., & Huang, N. (2016). Review: Mathematical expressions for estimating equivalent permeability of rock fracture networks. Hydrogeology Journal, 24, 1623–1649.
Liu, C. X., Ni, C. Z., Yan, Y. F., & Tan, L. (2013). Three-dimensional simulation of rock fractures by geostatistical method: A case study of Gaosong field in Yunnan province. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 34(3), 347–353. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, C. X., Ni, C. Z., Yan, Y. F., & Tan, L. (2014). Automatically extraction of lineaments from DEM. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 29(2), 273–277. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, C. X., Qin, D. X., Dang, Y. T., & Tan, S. C. (2003). Synthesis information based mineral resource prediction of Gaosong field in Gejiu Tin-deposit. Advance in Earth Sciences, 18(6), 921–927. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mooney, C. R., & Boisvert, J. B. (2016). Using a discrete fracture network and spatial point processes to populate veins and model grade in a coarse gold deposit. Nature Resources Research, 25(3), 255–268.
Mustapha, H. (2011). G23FM: A tool for meshing complex geological media. Computater & Geosciences, 15(3), 385–397.
Qin, D. X., Li, Y. S., Fan, Z. G., Chen, A. B., Tan, S. C., Hong, T., et al. (2006). The geochemistry and mineralization evolvement of Gejiu tin ore deposits. Engineering Science, 1, 30–39. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Riley, M. S. (2004). An algorithm for generating rock fracture patterns: Mathematical analysis. Mathematical Geology, 36(6), 683–702.
Soleimani, M., Shokri, B. J., & Rafiei, M. (2017). Integrated petrophysical modeling for a strongly heterogeneous and fractured reservoir, Sarvak Formation, SW Iran. Nature Resources Research, 26(1), 75–88.
Terzaghi, R. D. (1965). Sources of error in joint surveys. Géotechnique, 15, 287–304.
Zhang, H., Tong, X., Wu, J. D., Luo, T. Y., Tai, Y., & Zhu, D. (2007). Gejiu tin-polymetallic ore deposit: An example of landing of red sea-type submarine hydrothermal deposition. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 27(3/4), 335–341. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhuang, Y. Q., Wang, R. Z., Zheng, S. P., & Yin, J. (1996). Tin-copper-polymetallic deposit in Gejiu, Yunnan. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Projects (NSFC) [Grant Numbers 40902058 and 41562017] and partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI [Grant Numbers 26120519 and 16H01545]. Sincere thanks are extended to the two anonymous reviewers and editors for their valuable comments and suggestions that helped improve the clarity of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Kubo, T., Lu, L. et al. Spatial Simulation and Characterization of Three-Dimensional Fractures in Gejiu tin District, Southwest China, Using GEOFRAC. Nat Resour Res 28, 99–108 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-018-9381-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-018-9381-8