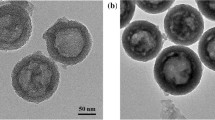
Abstract
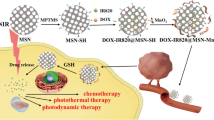
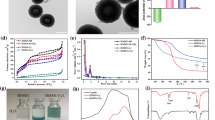
The synergistic treatment combining chemotherapy and hyperthermy, as a promising strategy, can improve the therapeutic efficiency of tumor therapy. The glutathione-responsive, chemotherapeutic and photothermal synergistic drug delivery systems (DDS) were developed using degradable dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles (DDMSNs) as carriers, camptothecin (CPT) as antitumor drug, and bovine serum albumin (BSA)/CuS as photothermal reagents (denoted as DDMSNs-CPT-CuS). BSA/CuS can prevent the premature drug release during the delivery process, and convert light energy into heat under photothermal treatment. The DDMSNs-CPT-CuS composites ranging from 100 to 200 nm had a loading capacity of 150 μg mg−1 for CPT and performed excellent GSH-triggered drug release behavior under condition of pH (5.0) and glutathione (GSH, 10 mM). The photothermal conversion efficiency (η) of DDMSNs-CuS was 38.8% with 808 nm laser irradiation for 10 min (2.5 W cm−2). The engineered DDMSNs-CuS showed the low protein adsorption capacity (140–230 μg mg−1), hemolysis rate of 5% (200 μg mL−1), and weak cytotoxicity for A549 and Hela cells with a cell viability of more than 75% (50 μg mL−1), indicating that the developed drug carriers displayed superior biocompatibility. There were significant differences between the cell viabilities treated with DDMSNs-CPT-CuS under NIR laser irradiation and that of without NIR laser irradiation when the loaded-CPT concentration was more than 6 μg mL−1. The proposed DDMSNs-CPT-CuS exhibited well performances, such as easy preparation, low cytotoxicity and high photothermal conversion efficiency. The results illustrated that DDS can achieve the synergistic treatment of photothermal therapy and chemotherapy for tumor cells. Therefore, this work provides a promising strategy to design multi-responsive and synergistic treatment DDS, and the developed DDMSNs-CPT-CuS present great potential for tumor treatment.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azizi S, Nosrati H, and Danafar H (2020) Simple surface functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles with methotrexate-conjugated bovine serum albumin as a biocompatible drug delivery vehicle[J]. Appl Organomet Chem 34(4)
Bai S, Ma X, Shi X, Shao J, Zhang T, Wang Y, Cheng Y, Xue P, Kang Y, Xu Z (2019) Smart unimolecular micelle-based polyprodrug with dual-redox stimuli response for tumor microenvironment: enhanced in vivo delivery efficiency and tumor penetration[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(39):36130–36140
Bai S, Jia D, Ma X, Liang M, Xue P, Kang Y, Xu Z (2021) Cylindrical polymer brushes-anisotropic unimolecular micelle drug delivery system for enhancing the effectiveness of chemotherapy[J]. Bioact Mater 6(9):2894–2904
Bao H, Zhang Q, Yan Z (2019) The impact of camptothecin-encapsulated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles on the activity of cytochrome P450 in vitro[J]. Int J Nanomedicine 14:383–391
Cheng X, Li D, Lin A, Xu J, Wu L, Gu H, Huang Z, Liu J, Zhang Y, Yin X (2018) Fabrication of multifunctional triple-responsive platform based on CuS-capped periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for chemo-photothermal therapy[J]. Int J Nanomedicine 13:3661–3677
de Solorzano IO, Alejo T, Abad M, Bueno-Alejo C, Mendoza G, Andreu V, Irusta S, Sebastian V, Arruebo M (2019) Cleavable and thermo-responsive hybrid nanoparticles for on-demand drug delivery[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci 533:171–181
Giuseppe P, Scott MT, Kevin W, Zhuang L, Andrew PG, Li Z, Joy H, Dai H (2009) PEG branched polymer for functionalization of nanomaterials with ultralong blood circulation[J]. J Am Chem Soc 131:4783–4787
He R-X, Wang Q, Li B, Jia J, Lu W-J, Shuang S-M (2020) Construction of protein-mediated copper sulfide bonded mesoporous silica nanoparticles vector for chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of cancer[J]. Chinese J Anal Chem 48(2):197–205
Huang J, Zhou J, Zhuang J, Gao H, Huang D, Wang L, Wu W, Li Q, Yang DP, Han MY (2017) Strong near-infrared absorbing and biocompatible CuS nanoparticles for rapid and efficient photothermal ablation of gram-positive and -negative bacteria[J]. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9(42):36606–36614
Huo M, Wang L, Chen Y, Shi J (2017) Tumor-selective catalytic nanomedicine by nanocatalyst delivery[J]. Nat Commun 8(1):357
Jafari S, Derakhshankhah H, Alaei L, Fattahi A, Varnamkhasti BS, Saboury AA (2019) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for therapeutic/diagnostic applications[J]. Biomed Pharmacother 109:1100–1111
Ji Y, Song S, Li X, Lv R, Wu L, Wang H, Cao M (2021) Facile fabrication of nanocarriers with yolk-shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles for effective drug delivery[J]. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 63:102531
Jia D, Ma X, Lu Y, Li X, Hou S, Gao Y, Xue P, Kang Y, Xu Z (2021) ROS-responsive cyclodextrin nanoplatform for combined photodynamic therapy and chemotherapy of cancer[J]. Chin Chem Lett 32(1):162–167
Li X, Garamus VM, Li N, Gong Y, Zhe Z, Tian Z, Zou A (2018) Preparation and characterization of a pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle dual-modified with biopolymers[J]. Colloid Surface A 548:61–69
Li T, Shi S, Goel S, Shen X, Xie X, Chen Z, Zhang H, Li S, Qin X, Yang H, Wu C, Liu Y (2019) Recent advancements in mesoporous silica nanoparticles towards therapeutic applications for cancer[J]. Acta Biomater 89:1–13
Li D, Zhang T, Min C, Huang H, Tan D, Gu W (2020) Biodegradable theranostic nanoplatforms of albumin-biomineralized nanocomposites modified hollow mesoporous organosilica for photoacoustic imaging guided tumor synergistic therapy[J]. Chem Eng J 388:124253
Liu HJ, Xu P (2019) Smart mesoporous silica nanoparticles for protein delivery[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel) 9(4):511
Maity A, Polshettiwar V (2017) Dendritic fibrous nanosilica for catalysis, energy harvesting, carbon dioxide mitigation, drug delivery, and sensing[J]. Chemsuschem 10(20):3866–3913
Moreira AF, Dias DR, Correia IJ (2016) Stimuli-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy: a review[J]. Micropor Mesopor Mat 236:141–157
Park JH, Gu L, von Maltzahn G, Ruoslahti E, Bhatia SN, Sailor MJ (2009) Biodegradable luminescent porous silicon nanoparticles for in vivo applications[J]. Nat Mater 8(4):331–336
Passi M, Shahid S, Chockalingam S, Sundar IK, Packirisamy G (2020) Conventional and nanotechnology based approaches to combat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: implications for chronic airway diseases[J]. Int J Nanomed 15:3803–3826
Saeed RMY, Bano Z, Sun J, Wang F, Ullah N, Wang Q (2019) CuS-functionalized cellulose based aerogel as biocatalyst for removal of organic dye[J]. J Appl Polym Sci 136(15):47404
Shao M, Chang C, Liu Z, Chen K, Zhou Y, Zheng G, Huang Z, Xu H, Xu P, Lu B (2019) Polydopamine coated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-sensitive nanocarriers for overcoming multidrug resistance[J]. Colloid Surface B 183:110427
Shi J, Kantoff PW, Wooster R, Farokhzad OC (2017) Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities[J]. Nat Rev Cancer 17(1):20–37
Li S, Ma N, Zhang Y, Liu W, Zhang X, Chen Z, Fu J, Huang Y, Yang J (2017) Synthesis and drug releasing effectiveness of hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres with ordered mesochannels[J]. J Chin Ceram Soc 45(03):327–332
Song S, Li X, Ji Y, Lv R, Wu L, Wang H, Cao M, Xu Z (2021) GSH/pH dual-responsive and HA-targeting nano-carriers for effective drug delivery and controlled release[J]. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 62:102327
Su X, Zhao F, Wang Y, Yan X, Jia S, Du B (2017) CuS as a gatekeeper of mesoporous upconversion nanoparticles-based drug controlled release system for tumor-targeted multimodal imaging and synergetic chemo-thermotherapy[J]. Nanomedicine-uk 13(5):1761–1772
Venkatesan P, Thirumalaivasan N, Yu H-P, Lai P-S, Wu S-P (2019) Redox stimuli delivery vehicle based on transferrin-capped MSNPs for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy[J]. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2(4):1623–1633
Wan X, Liu M, Ma M, Chen D, Wu N, Li L, Li Z, Lin G, Wang X, Xu G (2019) The ultrasmall biocompatible CuS@BSA nanoparticle and its photothermal effects[J]. Front Pharmacol 10:141
Wang D, Xu Z, Chen Z, Liu X, Hou C, Zhang X, Zhang H (2014) Fabrication of single-hole glutathione-responsive degradable hollow silica nanoparticles for drug delivery[J]. Acs Appl Mater Inter 6(15):12600–12608
Xiao Y, Peng J, Liu Q, Chen L, Shi K, Han R, Yang Q, Zhong L, Zha R, Qu Y, Qian Z (2020) Ultrasmall CuS@BSA nanoparticles with mild photothermal conversion synergistically induce MSCs-differentiated fibroblast and improve skin regeneration[J]. Theranostics 10(4):1500–1513
Xu C, Wang Y, Wang E, Yan N, Sheng S, Chen J, Lin L, Guo Z, Tian H, Chen X (2020) Effective eradication of tumors by enhancing photoacoustic-imaging-guided combined photothermal therapy and ultrasonic therapy[J]. Adv Func Mater 31(10):2009314
Yang Y, Wan J, Niu Y, Gu Z, Zhang J, Yu M, Yu C (2016) Structure-dependent and glutathione-responsive biodegradable dendritic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for safe protein delivery[J]. Chem Mater 28(24):9008–9016
Yang Y, Lu Y, Abbaraju PL, Zhang J, Zhang M, Xiang G, Yu C (2017a) Multi-shelled dendritic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres: roles of composition and architecture in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56(29):8446–8450
Yang Y, Lin Y, Di D, Zhang X, Wang D, Zhao Q, Wang S (2017b) Gold nanoparticle-gated mesoporous silica as redox-triggered drug delivery for chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy[J]. J Colloid Interf Sci 508:323–331
Yang J, Dai D, Lou X, Ma L, Wang B, Yang YW (2020) Supramolecular nanomaterials based on hollow mesoporous drug carriers and macrocycle-capped CuS nanogates for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy[J]. Theranostics 10(2):615–629
Zhang C, Fu YY, Zhang X, Yu C, Zhao Y, Sun SK (2015) BSA-directed synthesis of CuS nanoparticles as a biocompatible photothermal agent for tumor ablation in vivo[J]. Dalton T 44(29):13112–13118
Zhang Q, Shen C, Zhao N, Xu F-J (2017) Redox-responsive and drug-embedded silica nanoparticles with unique self-destruction features for efficient gene/drug codelivery[J]. Adv Func Mater 27(10):1606229
Zhang J, Shen B, Chen L, Chen L, Meng Y, Feng J (2019) A dual-sensitive mesoporous silica nanoparticle based drug carrier for cancer synergetic therapy[J]. Colloid Surface B 175:65–72
Zhang T, Xiong H, Ma X, Gao Y, Xue P, Kang Y, Sun ZJ, Xu Z (2021) Supramolecular Tadalafil Nanovaccine for cancer immunotherapy by alleviating myeloid-derived suppressor cells and heightening immunogenicity[J]. Small Methods 5(6):2100115
Zhao Y, Cai Q, Qi W, Jia Y, Xiong T, Fan Z, Liu S, Yang J, Li N, Chang B (2018) BSA-CuS nanoparticles for photothermal therapy of diabetic wound infection in vivo[J]. ChemistrySelect 3(32):9510–9516
Zhou M, Du X, Li W, Li X, Huang H, Liao Q, Shi B, Zhang X, Zhang M (2017) One-pot synthesis of redox-triggered biodegradable hybrid nanocapsules with a disulfide-bridged silsesquioxane framework for promising drug delivery[J]. J Mater Chem B 5(23):4455–4469
Funding
This work was supported by the Zhongjing Young Scholars Research Funding (B) of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, the Key Science and Technology Program of Henan Province (212102311049), National Natural Sciences Foundation for Young Scientists of China (No. 21505034), Scientific Research Nursery Project of Henan University of Chinese Medicine (MP2020-23, MP2020-107), and Henan College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program of Henan University of Chinese Medicine (202110471007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Lv, R., Wang, H. et al. Facile fabrication of glutathione-responsive and photothermal nanocarriers with dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled drug delivery. J Nanopart Res 24, 128 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05498-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05498-0