Abstract
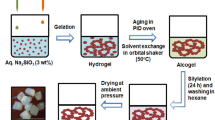
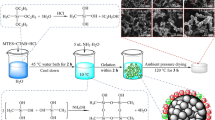
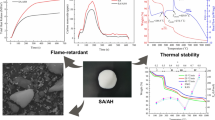
Silica aerogel (SA) is a nanoporous material and has attracted increasing attention in the field of thermal insulation in recent years. In this work, the thermal stability and pyrolysis characteristics of the methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS) silica aerogel (MSA) prepared in pure water were investigated experimentally. The MSA shows a high thermal stability with the onset and peak temperature (Tonset and Tpeak) about 417 °C and 476 °C, respectively, in the pyrolysis process. The oxidation kinetics reveals that the pyrolysis of MSA can be divided into three stages with the average apparent activation energy (E) of each stage being 382.8 kJ/mol, 364.4 kJ/mol, and 328.9 kJ/mol, respectively. The pre-exponential factor (A) has the same tendency with the E. The TG-FTIR analysis demonstrates that the CO2 and H2O are the main volatiles during the pyrolysis process and all of them increase against the temperature. It is further observed that the production of CO2 presents a linear increase, and the H2O shows an obvious two-stage form along with the temperature. Compared with other hydrophobic SAs, the MSA has a larger Tonset and Tpeak and much larger E, indicating better thermal safety. The research outcomes provide a technical guide to analyze the thermal pyrolysis of hydrophobic SA and put a new insight to reduce their thermal hazards, which is beneficial to the development of higher-performance nanoporous silica aerogels for the thermal insulation field.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad MS, Mehmood MA, Taqvi STH, Elkamel A, Liu C-G, Xu J, Rahimuddin SA, Gull M (2017) Pyrolysis, kinetics analysis, thermodynamics parameters and reaction mechanism of Typha latifolia to evaluate its bioenergy potential. Bioresour Technol 245(December):491–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.162
Bigda R, Mianowski A (2006) Influence of heating rate on kinetic quantities of solid phase thermal decomposition. J Therm Anal Calorim 84(2):453–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-7378-0
Cai L, Shan G (2015) Elastic silica aerogel using methyltrimethoxysilane precusor via ambient pressure drying. J Porous Mater 22:1455–1463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-0026-6
Chen HB, Wang YZ, Schiraldi DA (2014) Preparation and flammability of poly(vinyl alcohol) composite aerogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(9):6790–6796. https://doi.org/10.1021/am500583x
Cheng X, Li C, Shi X, Li Z, Gong L, Zhang H (2017) Rapid synthesis of ambient pressure dried monolithic silica aerogels using water as the only solvent. Mater Lett 204(October):157–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.05.107
Collazzo GC, Broetto CC, Perondi D, Junges J, Dettmer A, Dornelles Filho AA, Foletto EL, Godinho M (2017) A detailed non-isothermal kinetic study of elephant grass pyrolysis from different models. Appl Therm Eng 110(January):1200–1211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.09.012
Cuce E, Cuce PM, Wood CJ, Riffat SB (2014) Toward aerogel based thermal superinsulation in buildings: a comprehensive review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 34:273–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.03.017
Ding Y, Ezekoye OA, Lu S, Wang C (2016) Thermal degradation of beech wood with thermogravimetry/Fourier transform infrared analysis. Energy Convers Manag 120(July):370–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.05.007
Doyle CD (1962) Estimating isothermal life from thermogravimetric data. J Appl Polym Sci 6(24):639–642. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1962.070062406
Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi R, Abbasi MH (2008) Evaluation of reliability of Coats-Redfern method for kinetic analysis of non-isothermal TGA. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 18(1):217–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(08)60039-4
Finlay K, Gawryla MD, Schiraldi DA (2008) Biologically based fiber-reinforced/clay aerogel composites. Ind Eng Chem Res 47(3):615–619. https://doi.org/10.1021/Ie0705406
Guo J, Nguyen BN, Li L, Meador MAB, Scheiman DA, Cakmak M (2013) Clay reinforced polyimide/silica hybrid aerogel. J Mater Chem A 1:7211. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta00439b
Gurav JL, Venkateswara Rao A, Parvathy Rao A, Nadargi DY, Bhagat SD (2009) Physical properties of sodium silicate based silica aerogels prepared by single step sol–gel process dried at ambient pressure. J Alloys Compd 476(1):397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.09.029
He S, Chen X (2017) Flexible silica aerogel based on methyltrimethoxysilane with improved mechanical property. J Non-Cryst Solids 463(May):6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.02.014
He S, Li Z, Shi X, Yang H, Gong L, Cheng X (2015) Rapid synthesis of sodium silicate based hydrophobic silica aerogel granules with large surface area. Adv Powder Technol 26(2):537–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2015.01.002
He S, Sun G, Cheng X, Dai H, Chen X (2017) Nanoporous SiO 2 grafted aramid fibers with low thermal conductivity. Compos Sci Technol 146(July):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.04.021
He S, Huang Y, Chen G, Feng M, Dai H, Yuan B, Chen X (2019) Effect of heat treatment on hydrophobic silica aerogel. J Hazard Mater 362(January):294–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.087
Huang D, Guo C, Zhang M, Shi L (2017) Characteristics of nanoporous silica aerogel under high temperature from 950°C to 1200°C. Mater Des 129(September):82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.05.024
Huang S, Wu X, Li Z, Shi L, Zhang Y, Liu Q (2020) Rapid synthesis and characterization of monolithic ambient pressure dried MTMS aerogels in pure water. J Porous Mater 27(4):1241–1251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-020-00902-3
Huber L, Zhao S, Malfait WJ, Vares S, Koebel MM (2017) Fast and minimal-solvent production of superinsulating silica aerogel granulate. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 56(17):4753–4756. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201700836
Hüsing N, Schubert U (1998) Aerogels—airy materials: chemistry, structure, and properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 37(1–2):22–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980202)37:1/2<22::AID-ANIE22>3.0.CO;2-I
Jiang L, Xiao H-H, He J-J, Sun Q, Liang G, Sun J-H (2015) Application of genetic algorithm to pyrolysis of typical polymers. Fuel Process Technol 138:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.05.001
Kanamori K, Nakanishi K (2011) Controlled pore formation in organotrialkoxysilane-derived hybrids: from aerogels to hierarchically porous monoliths. Chem Soc Rev 40(2):754–770. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00068j
Kim YS, Kim YS, Kim SH (2010) Investigation of thermodynamic parameters in the thermal decomposition of plastic waste−waste lube oil compounds. Environmental Science & Technology 44(13):5313–5317. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101163e
Kistler SS (1931) Coherent expanded aerogels and jellies. Nature 127(3211):741. https://doi.org/10.1038/127741a0
Kistler SS (1932) Coherent expanded-aerogels. J Phys Chem 1(36):52–64
Koebel MM, Huber L, Zhao S, Malfait WJ (2016) Breakthroughs in cost-effective, scalable production of superinsulating, ambient-dried silica aerogel and silica-biopolymer hybrid aerogels: from laboratory to pilot scale. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 79(2):308–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4012-5
Li Z, Cheng X, Shi L, He S, Gong L, Li C, Zhang H (2016) Flammability and oxidation kinetics of hydrophobic silica aerogels. J Hazard Mater 320(December):350–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.054
Li C, Cheng X, Li Z, Pan Y, Huang Y, Gong L (2017) Mechanical, thermal and flammability properties of glass fiber film/silica aerogel composites. J Non-Cryst Solids 457(February):52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.11.017
Li Z, Cheng X, Gong L, Liu Q, Li S (2018) Enhanced flame retardancy of hydrophobic silica aerogels by using sodium silicate as precursor and phosphoric acid as catalyst. J Non-Cryst Solids 481(August 2017):267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.10.053
Li Z, Huang S, Shi L, Li Z, Liu Q, Li M (2019) Reducing the flammability of hydrophobic silica aerogels by doping with hydroxides. J Hazard Mater 373(July):536–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.112
Li Z, Zhao S, Koebel MM, Malfait WJ (2020) Silica aerogels with tailored chemical functionality. Materials & Design 193:108833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108833
Liu Q, Wang S, Zheng Y, Luo Z, Cen K (2008) Mechanism study of wood lignin pyrolysis by using TG–FTIR analysis. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 82(1):170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2008.03.007
Luo Y, Li Z, Zhang W, Yan H, Wang Y, Li M, Liu Q (2019) Rapid synthesis and characterization of ambient pressure dried monolithic silica aerogels in ethanol/water co-solvent system. J Non-Cryst Solids 503–504(January):214–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2018.09.049
Maia AAD, de Morais LC (2016) Kinetic parameters of red pepper waste as biomass to solid biofuel. Bioresour Technol 204(March):157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.12.055
Martinez G, Roberto EG, Reichenauer G, Zhao S, Koebel M, Barrio A (2016) Thermal assessment of ambient pressure dried silica aerogel composite boards at laboratory and field scale. Energy and Buildings 128:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.06.071
Meador MAB, Weber AS, Hindi A, Naumenko M, McCorkle L, Quade D, Vivod SL, Gould GL, White S, Deshpande K (2009) Structure−{property} {relationships} in {porous} 3D {nanostructures}: {epoxy}-{cross}-{linked} {silica} {aerogels} {produced} {using} {ethanol} as the {solvent}. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1(4):894–906. https://doi.org/10.1021/am900014z
Motahari S, Motlagh GH, Moharramzadeh A (2015) Thermal and flammability properties of polypropylene/silica aerogel composites. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part B 54(9):1081–1091. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2015.1078619
Randall JP, Meador MA, Jana SC (2011) Tailoring mechanical properties of aerogels for aerospace applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(3):613–626. https://doi.org/10.1021/am200007n
Santos JCO, Santos IMG, Conceiçăo MM, Porto SL, Trindade MFS, Souza AG, Prasad S, Fernandes VJ, Araújo AS (2004) Thermoanalytical, kinetic and rheological parameters of commercial edible vegetable oils. J Therm Anal Calorim 75(2):419–428. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JTAN.0000027128.62480.db
Turmanova S, Ch S, Genieva D, Dimitrova AS, Vlaev LT (2008) Non-isothermal degradation kinetics of filled with rise husk ash Polypropylene composites. Express Polym Lett 2(2):133–146. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2008.18
Vlaev LT, Georgieva VG, Genieva SD (2007) Products and kinetics of non-isothermal decomposition of vanadium(IV) oxide compounds. J Therm Anal Calorim 88(3):805–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-7149-y
Wang S, Guo X, Wang K, Luo Z (2011) Influence of the interaction of components on the pyrolysis behavior of biomass. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 91(1):183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2011.02.006
Wang Y, Li Z, Huber L, Wu X, Huang S, Zhang Y, Huang R, Liu Q (2020) Reducing the thermal hazard of hydrophobic silica aerogels by using dimethyldichlorosilane as modifier. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 93(1):111–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05170-5
Wu X, Fan M, Shen X, Cui S, Tan G (2018) Silica aerogels formed from soluble silicates and methyl trimethoxysilane (MTMS) using CO2 gas as a gelation agent. Ceram Int 44(1):821–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.005
Wu X, Huang S, Zhang Y, Shi L, Luo Y, Deng X, Liu Q, Li Z (2020a) Flame retardant polyurethane sponge/MTMS aerogel composites with improved mechanical properties under ambient pressure drying. J Nanopart Res 22(8):221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-04958-9
Wu X, Li Z, Joao G, Zhang Y, Huang S, Liu Q (2020b) Reducing the flammability of hydrophobic silica aerogels by tailored heat treatment. J Nanopart Res 22(4):83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-04822-w
Xu Y, Chen B (2013a) Investigation of thermodynamic parameters in the pyrolysis conversion of biomass and manure to biochars using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol 146(10):485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.086
Xu Y, Chen B (2013b) Investigation of thermodynamic parameters in the pyrolysis conversion of biomass and manure to biochars using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol 146(October):485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.086
Yuan X, He T, Cao H, Yuan Q (2017) Cattle manure pyrolysis process: kinetic and thermodynamic analysis with isoconversional methods. Renew Energy 107(July):489–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.02.026
Zhang W, Li Z, Shi L, Li Z, Luo Y, Liu Q, Huang R (2019) Methyltrichlorosilane modified hydrophobic silica aerogels and their kinetic and thermodynamic behaviors: graphical abstract. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 89(2):448–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4882-9
Zhao S, Jiang B, Maeder T, Muralt P, Kim N, Matam SK, Jeong E, Han YL, Koebel MM (2015) Dimensional and structural control of silica aerogel membranes for miniaturized motionless gas pumps. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(33):18803–18814. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b05462
Zhuravlev LT (2000) The surface chemistry of amorphous silica. Zhuravlev Model. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 173(1):1–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(00)00556-2
Funding
The authors deeply appreciate the supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51904336), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 2020JJ4714), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 202501003 and 202045001), the Innovation-Driven Project of Central South University (No. 2018CX025), and the Independent Exploration and Innovation Project for Graduate Students of Central South University (2020zzts704).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Huang, S. et al. Thermal stability and pyrolysis characteristics of MTMS aerogels prepared in pure water. J Nanopart Res 22, 334 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05062-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05062-8