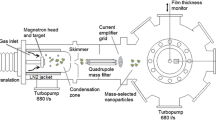
Abstract
Gas-phase aggregation of metal nanoparticles (nanoclusters), in particular, produced by magnetron sputtering, is a widely used method in research and industrial applications. Therefore, better understanding of the nucleation and growth processes as well as of nanoparticle dynamics in aggregation zone is required. One of the poorly understood issues is a charge state of nanocluster formed in magnetron-based sources. In the current work, an original approach to study charge states of silver nanoclusters after mass (size) filtering is suggested. The study reveals that particles can carry both negative and positive charges; anionic nanoparticles dominate over the cationic ones under the conditions used in our experiment. It is also found that a considerable fraction of nanoparticles has charges greater than unity, and this fraction increases with particle size. However, the tendency depends on polarity. For the cations, the doubly, triply and quadruply charged nanoclusters have very similar fractions for a given filtering condition, while for anions, an ability to carry higher than unity charges by individual particles gradually decreases. Thus, the study provides important insights on the formation of cationic and anionic nanoparticles in magnetron cluster sources as well as on the tendencies to carry multiple charges depending on particle size.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahadi AM, Hinz A, Polonskyi O, Trottenberg T, Strunskus T, Kersten H, Faupel F (2016) Modification of a metal nanoparticle beam by a hollow electrode discharge. J Vac Sci Technol A 34 (2):021301
Bins C (2001) Nanoclusters deposited on surfaces. Surf Sci Rep 44:1–49
Blom MN, Schooss D, Stairs J, Kappes MM (2006) Experimental structure determination of silver cluster ions (Agn +, 19≤n≤79). J Chem Phys 124:244308
Carchini G, Almora N, Revilla-Lopez G, Bellarosa L, García-Muelas R, García Melchor M, Pogodin S, Błonski P, Nuria López N (2013) How theoretical simulations can address the structure and activity of nanoparticles. Top Catal 56:1262–1272
Chen J, Huang J, Toma A, Zhong L, Cui Z, Shao W, Li Z, Liang W, De Angelis F, Jiang L, Chi L (2017) Modulating the spatial electrostatic potential for 1D colloidal nanoparticles assembly. Adv Mater Interfaces 4:1700505
Denison DR (1971) Operating parameters of a quadrupole in a grounded cylindrical housing. J Vac Sci Technol 8:266–269
Fojan P, Hanif M, Bartling S, Hartmann H, Barke I, Popok VN (2015) Supported silver clusters as nanoplasmonic transducers for protein sensing. Sensors Actuators B 212:377–381
Ganeva M, Pipa AV, Smirnov BM, Kashtanov PV, Hippler R (2013) Velocity distribution of mass-selected nano-size cluster ions. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 22:045011
Haberland H (1994) Experimental methods. In: Haberland H (ed) Clusters of atoms and molecules. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 205–252
Haberland H, Karrais M, Mall M (1991) A new type of cluster and cluster ion source. Z Phys D 20:413–415
Haberland H, Karrais M, Mall M, Thurner Y (1992) Thin films from energetic cluster impact: a feasibility study. J Vac Sci Technol A 10:3266–3271
Häkkinen H, Moseler M, Kostko O, Morgner N, Hoffmann MA, von Issendorff B (2004) Symmetry and electronic structure of noble-metal nanoparticles and the role of relativity. Phys Rev Lett 93:093401
Hanif M, Juluri RR, Chirumamilla M, Popok VN (2016) Poly (methyl methacrylate) composites with size-selected silver nanoparticles fabricated using cluster beam technique. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 54:1152–1159
Hartmann H, Popok VN, Barke I, von Oeynhausen V, Meiwes-Broer K-H (2012) Design and capabilities of an experimental setup based on magnetron sputtering for formation and deposition of size-selected metal clusters on ultra-clean surfaces. Rev Sci Instrum 83:073304
Huttel Y (ed) (2017) Gas-phase synthesis of nanoparticles. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Jeon TY, Kim DJ, Park S-G, Kim S-H, Kim D-H (2016) Nanostructured plasmonic substrates for use as SERS sensors. Nano Convergence 3: 18
Kousal J, Shelemin A, Schwartzkopf M, Polonskyi O, Hanus J, Solar P, Vaidulych M, Nikitin D, Pleskunov P, Krtous Z, Stunskus T, Faupel F, Roth SV, Biederman H, Choukourov A (2018) Magnetron-sputtered copper nanoparticles: lost in gas aggregation and found by in situ X-ray scattering. Nanoscale 10:18275
Liamosa D, Ruano M, Martinez L, Mayoral A, Roman E, Garcia-Hernandez M, Huttel Y (2014) The ultimate step towards a tailored engineering of core@shell and core@shell@shell nanoparticles. Nanoscale 6:13483–13486
Marom S, Plesser M, Modi R, Manini N, Di Vice M (2019) Planetary’ silver nanoparticles originating from a magnetron sputter plasma. J Phys D Appl Phys 52:095301
McKee ML, Samokhvalov A (2017) Density functional study of neutral and charged silver clusters Agn with n=2−22. Evolution of properties and structure. J Phys Chem A 121:5018–5028
Momin T, Bhowmick A (2010) A new magnetron based gas aggregationsource of metal nanoclusters coupled to adouble time-of-flight mass spectrometer system. Rev Sci Instrum 81:075110
Nikitin D, Hanuš J, Ali-Ogly S, Polonskyi O, Drewes J, Faupel F, Biederman H, Choukourov A (2019) The evolution of Ag nanoparticles inside a gas aggregation cluster source. Plasma Proc Polym in press
Novikov SM, Popok VN, Evlyukhin AB, Hanif M, Morgen P, Fiutowski J, Beermann J, Rubahn H-G, Bozhevolnyi SI (2017) Highly-stable monocrystalline silver clusters for plasmonic applications. Langmuir 33:6062–6070
Polonskyi O, Ahadi AM, Peter T, Fujioka K, Abraham JW, Vasiliauskaite E, Hinz A, Strunskus T, Wolf S, Bonitz M, Kersten H, Faupel F (2018) Plasma based formation and deposition of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles using a gas aggregation source. Eur Phys J D 72:93
Popok V (2009) Energetic cluster-surface collisions. In: Sattler KD (ed) Handbook of nanophysics, V 2, clusters and fullerenes. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 19–1–19-19
Popok VN, Hanif M, Ceynowa FA, Fojan P (2017) Immersion of low-energy deposited metal clusters into poly(methyl methacrylate). Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res B 409:91–95
Pratontep S, Sj C, Xirouchaki C, Streun M, Palmer RE (2005) Size-selected cluster beam source based on radio frequency magnetron plasma sputtering and gas condensation. Rev Sci Instrum 76:045103
Scholl JA, Koh AL, Dionne JA (2012) Quantum plasmon resonances of individual metallic nanoparticles. Nature 483:421–427
Yang X, Cai W, Shao X (2007) Structural variation of silver clusters from Ag13 to Ag160. J Phys Chem A 111:5048–5056
Zeman HD (1977) Deflection of an ion beam in the two-dimensional electrostatic quadrupole field. Rev Sci Instrum 48:1079–1085
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popok, V.N., Gurevich, L. Charge states of size-selected silver nanoparticles produced by magnetron sputtering. J Nanopart Res 21, 171 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4615-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4615-1