Abstract
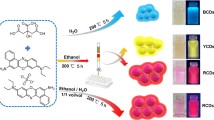
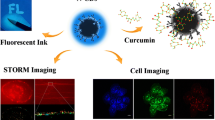
A strategy for preparing multicolor photoluminescent carbon nanodots (CNs) has been proposed. Using three types of phenylenediamine and methacrylic acid as raw materials and ethanol as a solvent, a series of novel CNs were synthesized by solvothermal one-pot method. Prepared CNs showed bright green, yellow, and indigo blue fluorescence under ultraviolet (UV) light, respectively. Three types of CNs were spherical-like nano-sized particles, and their particle sizes were approximately 5 nm, 10 nm, and 10 nm, respectively. The optical properties of CNs were characterized using ultraviolet visible spectra and fluorescence spectra. The microscopic morphology was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). The elemental composition was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS). We proposed that the different fluorescence emissions of CNs might be attributed to the surface oxygen content of the CNs. The CNs could also be applied for multicolor patterning and polymer films, invisible inks, and detection of metal ions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Awak MM, Wang P, Wang S, Tang Y, Sun Y-P, Yang L (2017) Correlation of carbon dots’ light-activated antimicrobial activities and fluorescence quantum yield. RSC Adv 7:30177–30184. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra05397e
Bao L, Liu C, Zhang ZL, Pang DW (2015) Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv Mater 27:1663–1667. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201405070
Carrara S, Arcudi F, Prato M, De Cola L (2017) Amine-rich nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots as a platform for self-enhancing electrochemiluminescence. Angew Chem 56:4757–4761. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201611879
Choudhary R, Patra S, Madhuri R, Sharma PK (2016) Equipment-free, single-step, rapid, “on-site” kit for visual detection of lead ions in soil, water, bacteria, live cells, and solid fruits using fluorescent cube-shaped nitrogen-doped carbon dots. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:5606–5617. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b01463
Ding H, Yu SB, Wei JS, Xiong HM (2016) Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 10:484–491. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b05406
Dong Y, Wang R, Li G, Chen C, Chi Y, Chen G (2012) Polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for selective and sensitive detection of copper ions. Anal Chem 84:6220–6224. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac3012126
Feng XT, Zhang F, Wang YL, Zhang Y, Yang YZ, Liu XG (2015a) Luminescent carbon quantum dots with high quantum yield as a single white converter for white light emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett 107:213102–203106. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4936234
Feng Y, Zhong D, Miao H, Yang X (2015b) Carbon dots derived from rose flowers for tetracycline sensing. Talanta 140:128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.03.038
Gao S, Chen Y, Fan H, Wei X, Hu C, Wang L, Qu L (2014) A green one-arrow-two-hawks strategy for nitrogen-doped carbon dots as fluorescent ink and oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. J Mater Chem A 2:6320–6326. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta15443b
Gong X, Zhang Q, Gao Y, Shuang S, Choi MM, Dong C (2016) Phosphorus and nitrogen dual-doped hollow carbon dot as a nanocarrier for doxorubicin delivery and biological imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:11288–11297. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b01577
Han L, Liu SG, Dong JX, Liang JY, Li LJ, Li NB, Luo HQ (2017) Facile synthesis of multicolor photoluminescent polymer carbon dots with surface-state energy gap-controlled emission. J Mater Chem C 5:10785–10793. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tc03314a
Hu S, Liu J, Yang J, Wang Y, Cao S (2011) Laser synthesis and size tailor of carbon quantum dots. J Nanopart Res 13:7247–7252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0638-y
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L, Lu Y, Wu A, Cai C, Lin H (2015) Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew Chem 54:5360–5363. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201501193
Kozák O, Datta KKR, Greplová M, Ranc V, Kašlík J, Zbořil R (2013) Surfactant-derived amphiphilic carbon dots with tunable photoluminescence. J Phys Chem C 117:24991–24996. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4040166
Kumar A, Chowdhuri AR, Laha D, Mahto TK, Karmakar P, Sahu SK (2017) Green synthesis of carbon dots from Ocimum sanctum for effective fluorescent sensing of Pb 2+ ions and live cell imaging. Sensors Actuators B Chem 242:679–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.109
Li Q, Ohulchanskyy TY, Liu R, Koynov K, Wu D, Best A, Kumar R, Bonoiu A, Prasad PN (2010) Photoluminescent carbon dots as biocompatible nanoprobes for targeting cancer cells in vitro. J Phys Chem C 114:12062–12068. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp911539r
Li W, Zhang Z, Kong B, Feng S, Wang J, Wang L, Yang J, Zhang F, Wu P, Zhao D (2013) Simple and green synthesis of nitrogen-doped photoluminescent carbonaceous nanospheres for bioimaging. Angew Chem 52:8151–8155. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201303927
Li L, Yu B, You T (2015) Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots for highly selective and sensitive detection of Hg (II) ions. Biosens Bioelectron 74:263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.06.050
Liang Z, Zeng L, Cao X, Wang Q, Wang X, Sun R (2014) Sustainable carbon quantum dots from forestry and agricultural biomass with amplified photoluminescence by simple NH4OH passivation. J Mater Chem C 2:9760–9766. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tc01714e
Lim SY, Shen W, Gao Z (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:362–381. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00269e
Liu S, Tian J, Wang L, Luo Y, Sun X (2012) A general strategy for the production of photoluminescent carbon nitride dots from organic amines and their application as novel peroxidase-like catalysts for colorimetric detection of H2O2and glucose. RSC Adv 2:411–413. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ra00709b
Liu Y, Zhou L, Li Y, Denga R, Zhang H (2016) Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots with excellent thermal and photo stability applied as invisible ink for loading important information and anti-counterfeiting. Nanoscale 9:491–496. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR07123F
Ma Z, Ming H, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang Z (2012) One-step ultrasonic synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from glucose and their visible-light sensitive photocatalytic ability. New J Chem 36:861–864. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nj20942j
Mewada A, Pandey S, Thakur M, Jadhav D, Sharon M (2014) Swarming carbon dots for folic acid mediated delivery of doxorubicin and biological imaging. J Mater Chem B 2:698–705. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb21436b
Pan D, Zhang J, Li Z, Wu M (2010) Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv Mater 22:734–738. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200902825
Peng J, Gao W, Gupta BK, Liu Z, Romero-Aburto R, Ge L, Song L, Alemany LB, Zhan X, Gao G, Vithayathil SA, Kaipparettu BA, Marti AA, Hayashi T, Zhu JJ, Ajayan PM (2012) Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett 12:844–849. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl2038979
Qiao ZA, Wang Y, Gao Y, Li H, Dai T, Liu Y, Huo Q (2010) Commercially activated carbon as the source for producing multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots by chemical oxidation. Chem Commun 46:8812–8814. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc02724c
Qu S, Wang X, Lu Q, Liu X, Wang L (2012) A biocompatible fluorescent ink based on water-soluble luminescent carbon nanodots. Angew Chem 51:12215–12218. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201206791
Ravindran S, Chaudhary S, Colburn B, Ozkan M, CSO (2003) Covalent coupling of quantum dots to multiwalled carbon nanotubes for electronic device applications. Nano Lett 3:447–453. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0259683
Sahu S, Behera B, Maiti TK, Mohapatra S (2012) Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem Commun 48:8835–8837. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc33796g
Sarkar S, Banerjee D, Ghorai UK, Das NS, Chattopadhyay KK (2016) Size dependent photoluminescence property of hydrothermally synthesized crystalline carbon quantum dots. J Lumin 178:314–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2016.05.033
Shi L et al (2015) Facile and eco-friendly synthesis of green fluorescent carbon nanodots for applications in bioimaging, patterning and staining. Nanoscale 7:7394–7401. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr00783f
Shi L et al (2016) Carbon dots with high fluorescence quantum yield: the fluorescence originates from organic fluorophores. Nanoscale 8:14374–14378. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr00451b
Tao S, Song Y, Zhu S, Shao J, Yang B (2017) A new type of polymer carbon dots with high quantum yield: from synthesis to investigation on fluorescence mechanism. Polymer 116:472–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.02.039
Wang L, Zhou HS (2014) Green synthesis of luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots from milk and its imaging application. Anal Chem 86:8902–8905. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac502646x
Wang X, Cao L, Yang ST, Lu F, Meziani MJ, Tian L, Sun KW, Bloodgood MA, Sun YP (2010) Bandgap-like strong fluorescence in functionalized carbon nanoparticles. Angew Chem 49:5310–5314. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201000982
Wang F, Xie Z, Zhang H, Liu C-Y, Zhang Y-G (2011a) Highly luminescent organosilane-functionalized carbon dots. Adv Funct Mater 21:1027–1031. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201002279
Wang X, Qu K, Xu B, Ren J, Qu X (2011b) Microwave assisted one-step green synthesis of cell-permeable multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots without surface passivation reagents. J Mater Chem 21:2445–2450. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm02963g
Wang TY, Chen CY, Wang CM, Tan YZ, Liao WS (2017) Multicolor functional carbon dots via one-step refluxing synthesis. ACS Sensors 2:354–363. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.6b00607
Xu Y, Wu M, Liu Y, Feng XZ, Yin XB, He XW, Zhang YK (2013) Nitrogen-doped carbon dots: a facile and general preparation method, photoluminescence investigation, and imaging applications. Chemistry 19:2276–2283. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201203641
Xue M, Zhan Z, Zou M, Zhang L, Zhao S (2016) Green synthesis of stable and biocompatible fluorescent carbon dots from peanut shell for multicolor living cell imaging. New J Chem 40:1698–1703. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ02181B
Yan F, Zou Y, Wang M, Mu X, Yang N, Chen L (2014) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots-based fluorescent chemosensors for sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions and application of imaging in living cells. Sens Actuators B Chem 192:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.11.041
Yu X, Liu R, Zhang G, Cao H (2013) Carbon quantum dots as novel sensitizers for photoelectrochemical solar hydrogen generation and their size-dependent effect. Nanotechnology 24:335401. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/33/335401
Yuan M, Zhong R, Gao H, Li W, Yun X, Liu J, Zhao X, Zhao G, Zhang F (2015) One-step, green, and economic synthesis of water-soluble photoluminescent carbon dots by hydrothermal treatment of wheat straw, and their bio-applications in labeling, imaging, and sensing. Appl Surf Sci 355:1136–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.07.095
Zhang Z, Sun W, Wu P (2015) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots derived from egg white: facile and green synthesis, photoluminescence properties, and multiple applications. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:1412–1418. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00156
Zhu L, Yin Y, Wang C-F, Chen S (2013a) Plant leaf-derived fluorescent carbon dots for sensing, patterning and coding. J Mater Chem C 1:4925–4932. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tc30701h
Zhu S et al (2013b) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 125:4045–4049. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA16233A
Zhu J-H, Li M-M, Liu S-P, Liu Z-F, Li Y-F, Hu X-L (2015) Fluorescent carbon dots for auramine O determination and logic gate operation. Sensors Actuators B Chem 219:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.05.032
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41576098, 81773483), the Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province of China (2016C33176, LGF18B070002), the Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo city (2017A610231, 2017A610228, 2017A610069), and the K.C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 6049 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, B., Xie, H., Wang, S. et al. Multicolor photoluminescent carbon nanodots regulated by degree of oxidation for multicolor patterning, invisible inks, and detection of metal ions. J Nanopart Res 21, 76 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4515-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4515-4