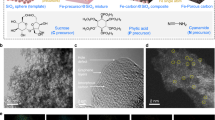
Abstract
A new kind of phosphorus-doped porous carbon framework (P-PCF) was synthesized using a simple and low-cost method and was used as a support material for loading Pd nanoparticles with an average diameter of 5~7 nm (Pd/P-PCF) for benzyl alcohol oxidation. Enhanced activity, selectivity, and stability were achieved over Pd/P-PCF in comparison to the undoped counterpart catalyst (Pd/PCF). Surface analysis of the fresh and reacted catalysts revealed that the selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol is favored using the Pd/P-PCF catalyst because of the modified electronic properties of Pd nanoparticles, the metal-support interactions, as well as the hydrophobic and basic surface properties of the catalyst, which originates from the phosphorus doping.

Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrigo R, Wrabetz S, Schuster ME, Wang D, Villa A, Rosenthal D, Girsgdies F, Weinberg G, Prati L, Schlögl R, Su DS (2012) Tailoring the morphology of Pd nanoparticles on CNTs by nitrogen and oxygen functionalization. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:10523–10532. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40861A
Batchelor-McAuley C, Shao L, Wildgoose GG, Green MLH, Compton RG (2008) An electrochemical comparison of manganese dioxide microparticles versus α and β manganese dioxide nanorods: mechanistic and electrocatalytic behaviour. New J Chem 32:1195–1203. https://doi.org/10.1039/B718862E
Chan-Thaw CE, Villa A, Katekomol P, Su D, Thomas A, Prati L (2010) Covalent triazine framework as catalytic support for liquid phase reaction. Nano Lett 10:537–541. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl904082k
Chan-Thaw CE, Villa A, Veith GM, Prati L (2015) Identifying the role of N-heteroatom location in the activity of metal catalysts for alcohol oxidation. ChemCatChem 7:1338–1346. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201402951
Chen Y, Guo Z, Chen T, Yang Y (2010) Surface-functionalized TUD-1 mesoporous molecular sieve supported palladium for solvent-free aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol. J Catal 275:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2010.07.006
Figueiredo JL, Pereira MFR, Freitas MMA, Órfão JJM (1999) Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 37:1379–1389. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(98)00333-9
Hasegawa G, Deguchi T, Kanamori K, Kobayashi Y, Kageyama H, Abe T, Nakanishi K (2015) High-level doping of nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur into activated carbon monoliths and their electrochemical capacitances. Chem Mater 27:4703–4712. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b01349
Hou H, Banks CE, Jing M, Zhang Y, Ji X (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their derivative 3D porous carbon frameworks for sodium-ion batteries with ultralong cycle life. Adv Mater 27:7861–7866. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201503816
Huang X, Shao L, She G-W, Wang M, Chen S, Meng X-M (2012) Catalyst-free synthesis of single crystalline ZnO nanonails with ultra-thin caps. CrystEngComm 14:8330. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ce26197a
Kibis LS, Stadnichenko AI, Koscheev SV, Zaikovskii VI, Boronin AI (2012) Highly oxidized palladium nanoparticles comprising Pd4+ species: spectroscopic and structural aspects, thermal stability, and reactivity. J Phys Chem C 116:19342–19348. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp305166k
Kopylovich MN, Ribeiro APC, Alegria ECBA, Martins NMR, Martins LMDRS, Pombeiro AJL (2015) Catalytic oxidation of alcohols: recent advances. In: Perez PJ (ed) Advances in organometallic chemistry, vol 63, pp 91–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.adomc.2015.02.004
Li JD, Tian QF, Jiang SY, Zhang Y, Wu YX (2016) Electrocatalytic performances of phosphorus doped carbon supported Pd towards formic acid oxidation. Electrochim Acta 213:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.06.041
Liao SX, Chi YM, Yu H, Wang HJ, Peng F (2014) Tuning the selectivity in the aerobic oxidation of cumene catalyzed by nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes. Chemcatchem 6:555–560. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201300909
Long R, Huang H, Li Y, Song L, Xiong Y (2015) Palladium-based nanomaterials: a platform to produce reactive oxygen species for catalyzing oxidation reactions. Adv Mater 27:7025–7042. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201502068
Namdeo A, Mahajani SM, Suresh AK (2016) Palladium catalysed oxidation of glycerol—effect of catalyst support. J Mol Catal A Chem 421:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2016.05.008
Niu S, Guo W, Lin T-W, Yu W, Wu Y, Ji X, Shao L (2017) Nanoscale Pd supported on 3D porous carbon for enhanced selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. RSC Adv 7:25885–25890. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA03665E
Otto K, Haack LP, deVries JE (1992) Identification of two types of oxidized palladium on γ-alumina by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl Catal B Environ 1:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-3373(92)80003-I
Parlett CMA, Bruce DW, Hondow NS, Lee AF, Wilson K (2011) Support-enhanced selective aerobic alcohol oxidation over Pd/mesoporous silicas. ACS Catal 1:636–640. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs200145n
Patel MA, Luo F, Khoshi MR, Rabie E, Zhang Q, Flach CR, Mendelsohn R, Garfunkel E, Szostak M, He H (2016) P-doped porous carbon as metal free catalysts for selective aerobic oxidation with an unexpected mechanism. ACS Nano 10:2305–2315. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b07054
Prati L, Villa A, Campione C, Spontoni P (2007) Effect of gold addition on Pt and Pd catalysts in liquid phase oxidations. Top Catal 44:319–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-007-0305-9
Sankar M, Dimitratos N, Miedziak PJ, Wells PP, Kiely CJ, Hutchings GJ (2012) Designing bimetallic catalysts for a green and sustainable future. Chem Soc Rev 41:8099–8139. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35296f
Savara A, Chan-Thaw CE, Rossetti I, Villa A, Prati L (2014) Benzyl alcohol oxidation on carbon-supported Pd nanoparticles: elucidating the reaction mechanism. ChemCatChem 6:3464–3473. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201402552
Shao L, Lin T-W, Tobias G, Green MLH (2008) A simple method for the containment and purification of filled open-ended single wall carbon nanotubes using C60 molecules Chem Commun:2164–2166. https://doi.org/10.1039/B800881G
Sharma AS, Kaur H, Shah D (2016) Selective oxidation of alcohols by supported gold nanoparticles: recent advances. RSC Adv 6:28688–28727. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra25646a
Sheldon RA, Arends IWCE, ten Brink G-J, Dijksman A (2002) Green, catalytic oxidations of alcohols. Acc Chem Res 35:774–781. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar010075n
Villa A, Plebani M, Schiavoni M, Milone C, Piperopoulos E, Galvagno S, Prati L (2012) Tuning hydrophilic properties of carbon nanotubes: a challenge for enhancing selectivity in Pd catalyzed alcohol oxidation. Catal Today 186:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2011.09.041
Villa A, Dimitratos N, Chan-Thaw CE, Hammond C, Prati L, Hutchings GJ (2015) Glycerol oxidation using gold-containing catalysts. Acc Chem Res 48:1403–1412. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar500426g
Wang D, Villa A, Porta F, Prati L, Su D (2008) Bimetallic gold/palladium catalysts: correlation between nanostructure and synergistic effects. J Phys Chem C 112:8617–8622. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp800805e
Wang X, Sun G, Routh P, Kim DH, Huang W, Chen P (2014) Heteroatom-doped graphene materials: syntheses, properties and applications. Chem Soc Rev 43:7067–7098. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00141a
Wang Y, De S, Yan N (2016) Rational control of nano-scale metal-catalysts for biomass conversion. Chem Commun (Camb) 52:6210–6224. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cc00336b
Weerachawanasak P, Hutchings GJ, Edwards JK, Kondrat SA, Miedziak PJ, Prasertham P, Panpranot J (2015) Surface functionalized TiO2 supported Pd catalysts for solvent-free selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Catal Today 250:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2014.06.005
Wu X, Radovic LR (2006) Inhibition of catalytic oxidation of carbon/carbon composites by phosphorus. Carbon 44:141–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2005.06.038
Wu G, Wang X, Guan N, Li L (2013) Palladium on graphene as efficient catalyst for solvent-free aerobic oxidation of aromatic alcohols: role of graphene support. Appl Catal B Environ 136-137:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.01.067
Zhang H, Jin MS, Xiong YJ, Lim B, Xia YN (2013) Shape-controlled synthesis of Pd nanocrystals and their catalytic applications. Acc Chem Res 46:1783–1794. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar300209w
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 21403137).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 384 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Niu, S., Ji, X. et al. Doping carbon networks with phosphorus for supporting Pd in catalyzing selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. J Nanopart Res 20, 180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4279-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4279-2