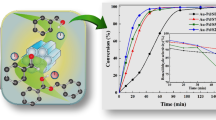
Abstract
Mesoporous TiO2-sphere-supported Au-nanoparticles (Au/m-TiO2-spheres) catalysts have been synthesized by a simple method using tetrabutyl titanate as TiO2 precursor and characterized with XRD, BET, ICP, SEM, TEM, UV-Vis DRS, XPS, as well as FT-IR. The samples with the size in the range of 200–400 nm were almost perfectly spherical. The average diameter of pores was about 3.6 nm, and the mesopore size distribution was in the range of 2–6 nm with a narrow distribution. When the catalyst was calcined at 300 °C, the Au NPs with the size ca. 5 nm were highly dispersed on the surfaces of m-TiO2 spheres and partially embedded in the supports. Remarkably, the specific surface area of the Au/m-TiO2-spheres was as high as 117 m2 g−1. The CO-adsorbed catalyst showed an apparent IR adsorption peak at 1714 cm−1 that matched with bridging model CO. It means the catalysts should be of high catalytic activity for the CO oxidation due to they could adsorb and activate CO commendably. When Au-content was 0.48 wt.%, the Au/m-TiO2-spheres could convert CO completely into CO2 at ambient temperature.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrii S, Morfin F, Renouprez AJ, Rousset JL (2004) Oxidation of CO on gold supported catalysts prepared by laser vaporization: direct evidence of support contribution. J Am Chem Soc 126(4):1199–1205. doi:10.1021/ja036352y
Cai J, Wu X, Li S, Zheng F, Zhu L, Lai Z (2015) Synergistic effect of double-shelled and sandwiched TiO2@Au@C hollow spheres with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(6):3764–3772. doi:10.1021/am508554t
Chen D, Cao L, Huang F, Imperia P, Cheng Y, Caruso RA (2010a) Synthesis of monodisperse mesoporous titania beads with controllable diameter, high surface areas, and variable pore diameters (14–23 nm). J Am Chem Soc 132(12):4438–4444. doi:10.1021/ja100040p
Chen J, Hua Z, Yan Y, Zakhidov AA, Baughman RH, Xu L (2010b) Template synthesis of ordered arrays of mesoporous titania spheres. Chem Commun 46(11):1872–1874. doi:10.1039/b915706a
Chen Y, Deng Y, Pu Y, Tang B, Su Y, Tang J (2016) One pot preparation of silver nanoparticles decorated TiO2 mesoporous microspheres with enhanced antibacterial activity. Mater Sci Eng C 65:27–32. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2016.04.028
Denkwitz Y, Makosch M, Geserick J, Hörmann U, Selve S, Kaiser U, Hüsing N, Behm RJ (2009) Influence of the crystalline phase and surface area of the TiO2 support on the CO oxidation activity of mesoporous Au/TiO2 catalysts. Appl Catal B 91(1–2):470–480. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.06.016
Ding S, Yin X, Lü X, Wang Y, Huang F, Wan D (2012) One-step high-temperature solvothermal synthesis of TiO2/sulfide nanocomposite spheres and their solar visible-light applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(1):306–311. doi:10.1021/am201343q
Fu Q, Saltsburg H, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M (2003) Active nonmetallic Au and Pt species on ceria-based water-gas shift catalysts. Science 301(5635):935–938. doi:10.1126/science.1085721
Gaur S, Wu H, Stanley GG, More K, Kumar CS, Spivey JJ (2013) CO oxidation studies over cluster-derived Au/TiO2 and AUROlite™ Au/TiO2 catalysts using DRIFTS. Catal Today 208:72–81. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2012.10.029
Haruta M, Daté M (2001) Advances in the catalysis of Au nanoparticles. Appl Catal A 222(1–2):427–437. doi:10.1016/S0926-860X(01)00847-X
Herzing AA, Kiely CJ, Carley AF, Landon P, Hutchings GJ (2008) Identification of active gold nanoclusters on iron oxide supports for CO oxidation. Science 321(5894):1331–1335. doi:10.1126/science.1159639
Hutchings GJ, Hall MS, Carley AF, Landon P, Solsona BE, Kiely CJ, Herzing A, Makkee M, Moulijn JA, Overweg A, Fierro-Gonzalez JC, Guzman J, Gates BC (2006) Role of gold cations in the oxidation of carbon monoxide catalyzed by iron oxide-supported gold. J Catal 242(1):71–81. doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2006.06.001
Idakiev V, Dimitrov D, Tabakova T, Ivanov K, Yuan Z, Su B (2015) Catalytic abatement of CO and volatile organic compounds in waste gases by gold catalysts supported on ceria-modified mesoporous titania and zirconia. Chin J Catal 36(4):579–587. doi:10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60283-7
Li S, Zhu H, Qin Z, Wang G, Zhang Y, Wu Z, Li Z, Chen G, Dong W, Wu Z, Zheng L, Zhang J, Hu T, Wang J (2014) Morphologic effects of nano CeO2–TiO2 on the performance of Au/CeO2–TiO2 catalysts in low-temperature CO oxidation. Appl Catal B 144:498–506. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.049
Liu B, Liu L, Lang X, Wang H, Lou X, Aydil ES (2014) Doping high-surface-area mesoporous TiO2 microspheres with carbonate for visible light hydrogen production. Energy Environ Sci 7(8):2592–2597. doi:10.1039/c4ee00472h
Liu C, Tan Y, Lin S, Li H, Wu X, Li L, Pei Y, Zeng X (2013) CO self-promoting oxidation on nanosized gold clusters: triangular Au3 active site and CO induced O–O scission. J Am Chem Soc 135(7):2583–2595. doi:10.1021/ja309460v
Li X, Zhu Z, Zhao Q, Liu S (2011) FT-IR study of the photocatalytic degradation of gaseous toluene over UV-irradiated TiO2 microballs: enhanced performance by hydrothermal treatment in alkaline solution. Appl Surf Sci 257(10):4709–4714. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.12.133
Lv Q, Meng M, Zha Y (2006) Preparation and characterization of nano-structured Au/TiO2 catalyst with high thermal stability. Chin J Catal 27(12):1111–1116
Ma Z, Dai S (2011) Design of novel structured gold nanocatalysts. ACS Catal 1(7):805–818. doi:10.1021/cs200100w
Qi C, Su H, Guan R, Xu X (2012) An investigation into phosphate-doped Au/alumina for low temperature CO oxidation. J Phys Chem C 116(33):17492–17500. doi:10.1021/jp301807j
Rico-Oller B, Boudjemaa A, Bahruji H, Kebir M, Prashar S, Bachari K, Fajardo M, Gómez-Ruiz S (2016) Photodegradation of organic pollutants in water and green hydrogen production via methanol photoreforming of doped titanium oxide nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 563–564:921–932. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.101
Schubert G, Gazsi A, Solymosi F (2014) Photocatalytic decomposition and oxidation of dimethyl ether over Au/TiO2. J Catal 313:127–134. doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2014.03.005
Shi Y, Hu X, Zhao J, Zhou X, Zhu B, Zhang S, Huang W (2015) CO oxidation over Cu2O deposited on 2D continuous lamellar g-C3N4. New J Chem 39(8):6642–6648. doi:10.1039/c5nj00621j
Trang NTH, Ali Z, Kang DJ (2015) Mesoporous TiO2 spheres interconnected by multiwalled carbon nanotubes as an anode for high-performance lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(6):3676–3683. doi:10.1021/am508158v
Wang G, Wang X, Liu J, Sun X (2012) Mesoporous Au/TiO2 nanocomposite microspheres for visible-light photocatalysis. Chem Eur J 18(17):5361–5366. doi:10.1002/chem.201101410
Wang L, Wang H, Rice AE, Zhang W, Li X, Chen M, Meng X, Lewis JP, Xiao F (2015) Design and preparation of supported Au catalyst with enhanced catalytic activities by rationally positioning Au nanoparticles on anatase. J Phys Chem Lett 6(12):2345–2349. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b00655
Xie K, Sun L, Wang C, Lai Y, Wang M, Chen H, Lin C (2010) Photoelectrocatalytic properties of Ag nanoparticles loaded TiO2 nanotube arrays prepared by pulse current deposition. Electrochim Acta 55(24):721–7218. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2010.07.030
Yamada Y, Mizutani M, Nakamura T, Yano K (2010) Mesoporous microcapsules with decorated inner surface: fabrication and photocatalytic activity. Chem Mater 22(5):1695–1703. doi:10.1021/cm9031072
Yang K, Huang K, He Z, Chen X, Fu X, Dai W (2014) Promoted effect of PANI as electron transfer promoter on CO oxidation over Au/TiO2. Appl Catal B 158–159:250–257. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.028
Yao Q, Wang C, Wang H, Yan H, Lu J (2016) Revisiting the Au particle size effect on TiO2-coated Au/TiO2 catalysts in CO oxidation reaction. J Phys Chem C 120(17):9174–9183. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b12712
Yoshitake H, Saito N (2013) Selective hydrogenation of crotonaldehyde on Au supported on mesoporous titania. Microporous and Mesoporous Mater 168:51–56. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.09.031
Zhang P, Guo J, Zhao P, Zhu B, Huang W, Zhang S (2015) Promoting effects of lanthanum on the catalytic activity of Au/TiO2 nanotubes for CO oxidation. RSC Adv 5(16):11989–11995. doi:10.1039/c4ra14133d
Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Xiang S, Zhou S, Sheng X (2014) Encapsulation of Au nanoparticles with well crystallized anatase TiO2 mesoporous hollow spheres for increased thermal stability. RSC Adv 4(14):7313–7320. doi:10.1039/c3ra47535b
Zhou L, Chen M, Wang Y, Su Y, Yang X, Chen C, Xu J (2014a) Au/mesoporous-TiO2 as catalyst for the oxidation of alcohols to carboxylic acids with molecular oxygen in water. Appl Catal A 475:347–354. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2014.01.042
Zhou N, He B, Wang X, Hu Z (2014b) Preparation and characterization of Au@TiO2 core–shell hollow nanoparticles with CO oxidation performance. J Nanopart Res 16:2676. doi:10.1007/s11051-014-2676-8
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21373120, 21301098, 21071086, and 21271110), MOE Innovation Team (IRT13022) of China, and the Applied Basic Research Programs of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Tianjin (13JCQNJC02000 and 12JCYBJC13100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Huang, S., Zhu, B. et al. Preparation and characterization of mesoporous TiO2-sphere-supported Au-nanoparticle catalysts with high activity for CO oxidation at ambient temperature. J Nanopart Res 18, 323 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3620-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3620-x