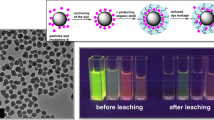
Abstract
The synthesis of fluorophore-doped silica nanoparticles (FDS NPs) with two conventional approaches, Stöber and microemulsion, as well as a novel amino acid-catalyzed seeds regrowth technique (ACSRT) is presented. The efficiency of each applied synthesis route toward incorporation of selected hydrophilic fluorophores, including rhodamine B isothiocyanate and fluorescein isothiocyanate, without and with an amine-containing crosslinker, into silica matrix was systematically studied. Our results clearly highlight the advantages of ACSRT to obtain FDS NPs with a remarkable encapsulation efficiency, high quantum yield, and enhanced stability against bleaching and dye leaking due to efficient embedding of the dyes inside silica network even without the amine-containing silane reagent. Moreover, evaluation of photostability of FDNPs internalized in human bone cells demonstrates the merits of ACSRT.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberto G, Caputo G, Viscardi G, Coluccia S, Martra G (2012) Molecular engineering of hybrid dye–silica fluorescent nanoparticles: influence of the dye structure on the distribution of fluorophores and consequent photoemission brightness. Chem Mater 24:2792–2801
Al-Rawi M, Diabaté S, Weiss C (2011) Uptake and intracellular localization of submicron and nano-sized SiO2 particles in HeLa cells. Arch Toxicol 85:813–826
Auger A, Samuel J, Poncelet O, Raccurt O (2011) A comparative study of non-covalent encapsulation methods for organic dyes into silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:1–12
Bagwe R, Yang C, Hilliard L, Tan W (2004) Optimization of dye-doped silica nanoparticles prepared using a reverse microemulsion method. Langmuir 20:8336–8342
Bass J, Grosso D, Boissiere C, Belamie E, Coradin T, Sanchez C (2007) Stability of mesoporous oxide and mixed metal oxide materials under biologically relevant conditions. Chem Mater 19:4349–4356
Bäumler W, Penzkofer A (1990) Fluorescence spectroscopic analysis of N and P isomers of DODCI. Chem Phys 140:75–97
Blechinger J, Herrmann R, Kiener D, García-García F, Scheu C, Reller A, Bräuchle C (2010) Perylene-labeled silica nanoparticles: synthesis and characterization of three novel silica nanoparticle species for live-cell imaging. Small 6:2427–2435
Canton C, Riccò R, Marinello F, Carmignato S, Enrichi F (2011) Modified Stöber synthesis of highly luminescent dye-doped silica nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 13:4349–4356
Costa C, Leite C, Galembeck F (2003) Size dependence of Stöber silica nanoparticle microchemistry. J Phys Chem B 107:4747–4755
Costa C, Valadares L, Galembeck F (2007) Stöber silica particle size effect on the hardness and brittleness of silica monoliths. Colloids Surf A 302:371–376
Daberkow T, Meder F, Treccani L, Schowalter M, Rosenauer A, Rezwan K (2012) Fluorescence labeling of colloidal core–shell particles with defined isoelectric points for in vitro studies. Acta Biomater 8:1–8
Ethiraj A, Hebalkar N, Kharrazi S, Urban J, Sainkar S, Kulkarni S (2005) Photoluminescent core-shell particles of organic dye in silica. J Lumin 114:15–23
Finnie K, Bartlett J, Barbé C, Kong L (2007) Formation of silica nanoparticles in microemulsions. Langmuir 23:3017–3024
Finnie K, Waller D, Perret F, Krause-Heuer A, Lin H, Hanna J, Barbe C (2009) Biodegradability of sol–gel silica microparticles for drug delivery. Sol-Gel Sci Technol 49:12–18
Fouilloux S, Tache O, Spalla O, Thill A (2011) Nucleation of silica nanoparticles measured in situ during controlled supersaturation increase. Restructuring toward a monodisperse nonspherical shape. Langmuir 27:12304–12311
Fuller J, Zugates G, Ferreira L, Ow H, Nguyen N, Wiesner U, Langer R (2008) Intracellular delivery of core-shell fluorescent silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 29:1526–1532
Gao F, Tang L, Dai L, Wang L (2007) A fluorescence ratiometric nano-pH sensor based on dual-fluorophore-doped silica nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta Part A 67:517–521
Gao X, He J, Deng L, Cao H (2009) Synthesis and characterization of functionalized rhodamine B-doped silica nanoparticles. Opt Mater 31:1715–1719
Ha S-W, Camalier C-E, Beck GR Jr, Lee J-K (2009) New method to prepare very stable and biocompatible fluorescent silica nanoparticles Chem Commun 20:2881–2883
Imhof A, Megens M, Engelberts J, de Lang D, Sprik R, Vos W (1999) Spectroscopy of fluorescein (FITC) dyed colloidal silica spheres. J Phys Chem B 103:1408–1415
Liang J, Xue Z, Xu J, Li J, Zhang H, Yang W (2013) Highly efficient incorporation of amino-reactive dyes into silica particles by a multi-step approach. Colloids Surf A 426:33–38
Liong M et al (2008) Multifunctional inorganic nanoparticles for imaging, targeting, and drug delivery. ACS Nano 2:889–896
Mahon E, Hristov D, Dawson K (2012) Stabilising fluorescent silica nanoparticles against dissolution effects for biological studies. Chem Commun 48:7970–7972
Montalti M et al (2006) Size effect on the fluorescence properties of dansyl-doped silica nanoparticles. Langmuir 22:5877–5881
Nakamura M, Shono M, Ishimura K (2007) Synthesis, characterization, and biological applications of multifluorescent silica nanoparticles. Anal Chem 79:6507–6514
Nan A, Bai X, Son S, Lee S, Ghandehari H (2008) Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of silica nanotubes. Nano Lett 8:2150–2154
Rampazzo E et al (2010) Energy transfer from silica core-surfactant shell nanoparticles to hosted molecular fluorophores. J Phys Chem B 114:14605–14613
Salvati A, Åberg C, dos Santos T, Varela J, Pinto P, Lynch I, Dawson K (2011) Experimental and theoretical comparison of intracellular import of polymeric nanoparticles and small molecules: toward models of uptake kinetics. Nanomedicine 7:1–9
Santra S, Zhang P, Wang K, Tapec R, Tan W (2001) Conjugation of biomolecules with luminophore-doped silica nanoparticles for photostable biomarkers. Anal Chem 73:4988–4993
Shahabi S, Treccani L, Dringen R, Rezwan K (2015a) Dual fluorophore doped silica nanoparticles for cellular localization studies in multiple stained cells. Acta Biomater 14:208–216
Shahabi S, Treccani L, Dringen R, Rezwan K (2015b) Modulation of silica nanoparticle uptake into human osteoblast cells by variation of the ratio of amino and sulfonate surface groups: effects of serum. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:13821–13833
Shahabi S, Treccani L, Rezwan K (2015c) Amino acid-catalyzed seed regrowth synthesis of photostable high fluorescent silica nanoparticles with tunable sizes for intracellular studies. J Nanopart Res 17:1–15
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26:62–69
van Blaaderen A, Vrij A (1992) Synthesis and characterization of colloidal dispersions of fluorescent, monodisperse silica spheres. Langmuir 8:2921–2931
van Blaaderen A, Vrij A (1993) Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse colloidal organo-silica spheres. Colloid Interface Sci 156:1–18
Watanabe R, Yokoi T, Kobayashi E, Otsuka Y, Shimojima A, Okubo T, Tatsumi T (2011) Extension of size of monodisperse silica nanospheres and their well-ordered assembly. J Colloid Interface Sci 360:1–7
Yokoi T (2012) Syntheses and applications of well-ordered porous silicas by using anionic surfactants and basic amino acids. J Jpn Petrol Inst 55:13–26
Yokoi T et al (2009) Mechanism of formation of uniform-sized silica nanospheres catalyzed by basic amino acids. Chem Mater 21:3719–3729
Zhao X, Bagwe R, Tan W (2004) Development of organic-dye- doped silica nanoparticles in a reverse microemulsion. Adv Mater 16:173–176
Acknowledgments
We greatly thank Dr. Jan Köser of Zentrale Analytik, University of Bremen for DLS measurements. This work was supported by the European Research Council within the SIRG Project “BiocerEng” Project No. 205509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahabi, S., Treccani, L. & Rezwan, K. A comparative study of three different synthesis routes for hydrophilic fluorophore-doped silica nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 18, 28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3334-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3334-0