Abstract
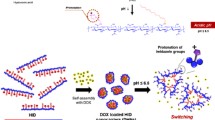
In this article, we prepared a multifunctional oligosaccharides of hyaluronan (oHA) conjugates, oHA-histidine-menthone 1,2-glycerol ketal (oHM). The oHM conjugates possess pH-sensitive menthone 1,2-glycerol ketal (MGK) as hydrophobic moieties and oHA as the target of CD44 receptor. The polymeric mPEG-Chitosan-Ketal (PCK) carrying pH-sensitive ketal group as hydrophobic moieties and PEG group as hydrophilic moieties were synthesized. The two pH-sensitive ketal derivatives were employed to fabricate nanoparticles for anti-tumor drug delivery. The oHM-PCK nanoparticles (oHPN) can spontaneously self-assemble into mixed micellar structure with nano-sized spherical shape of 100–200 nm at pH 7.4 PBS conditions. The oHPN could release encapsulated curcumin with 92.6 % at pH 5.0 compared with 55.3 % at pH 7.4. The results of cytotoxicity assay indicated that encapsulated curcumin in oHPN (Cur-oHPN) have less toxicity compared to curcumin suspension. The anti-tumor efficacy in vivo suggested that Cur-oHPN suppressed tumor growth most efficiently. These results present the promising potential of oHPN as an effective nano-sized pH-sensitive drug delivery system for intracellular delivery.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camenisch TD, McDonald JA (2000) Hyaluronan: is bigger better? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 3:431–433
Chen D, Wang H (2014) Novel pH-sensitive biodegradable polymeric drug delivery systems based on ketal polymers. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14(983–989):7
Chen D, Jiang X, Liu J, Jin X, Zhang C, Ping Q (2010) In vivo evaluation of novel pH-sensitive mPEG-Hz-chol conjugate in liposomes: pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, efficacy assessment. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol 38:136–142
Chen D, Liu W, Shen Y, Mu H, Zhang Y, Liang R et al (2011) Effects of a novel pH-sensitive liposome with cleavable esterase-catalyzed and pH-responsive double smart mPEG lipid derivative on ABC phenomenon. Int J Nanomed 6:2053–2061
Chen D, Sun K, Mu H, Tang M, Liang R, Wang A et al (2012) pH and temperature dual-sensitive liposome gel based on novel cleavable mPEG-Hz-CHEMS polymeric vaginal delivery system. Int J Nanomed 7:2621–2630
Chen D, Mu H, Sun K, Liu W (2013a) Synthesis, anticoagulant activity and potential drug carrier of biomimetic N-cholesteryl hemisuccinate-O-sulfate chitosan polymer of blood cell membrane. J Control Release. 172:e25
Chen D, Yu H, Mu H, Wei J, Song Z, Shi H et al (2013b) Novel chitosan derivative for temperature and ultrasound dual-sensitive liposomal microbubble gel. Carbohydr Polym 94:17–23
Duncan R (2006) Polymer conjugates as anticancer nanomedicines. Nat Rev Cancer 6:688–701
Hobbs SK, Monsky WL, Yuan F, Roberts WG, Griffith L, Torchilin VP et al (1998) Regulation of transport pathways in tumor vessels: role of tumor type and microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4607–4612
Hou L, Yao J, Zhou J, Zhang Q (2012) Pharmacokinetics of a paclitaxel-loaded low molecular weight heparin-all-trans-retinoid acid conjugate ternary nanoparticulate drug delivery system. Biomaterials 3:5431–5440
Kim JH, Kim YS, Kim S, Park JH, Kim K, Choi K et al (2006) Hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles as carriers for paclitaxel. J Control Release 111:228–234
Kothapalli D, Flowers J, Xu T, Puré E, Assoian RK (2008) Differential activation of ERK and Rac mediates the proliferative and anti-proliferative effects of hyaluronan and CD44. J Biol Chem 283:31823–31829
Park K, Kim JH, Nam YS, Lee S, Nam HY, Kim K et al (2007) Effect of polymer molecular weight on the tumor targeting characteristics of self-assembled glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J Control Release 122:305–314
Slevin M, Krupinski J, Gaffney J, Matou S, West D, Delisser H et al (2006) Hyaluronan-mediated angiogenesis in vascular disease: uncovering RHAMM and CD44 receptor signaling pathways. Matrix Biol 26:58–68
Yang C, Cao M, Liu H, He Y, Xu J, Du Y et al (2012) The high and low molecular weight forms of hyaluronan have distinct effects on CD44 clustering. J Biol Chem 287:43094–43107
Yu H, Mu H, Xiu L, Sun K, Liu W, Chen D (2013) A novel ketal-based chitosan as nano-vehicles for potential pH-sensitive nanomedicine delivery. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 5:1007–1011
Acknowledgments
This study is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no.81302718), Taishan Scholar Project (To Dr. Zimei Wu), Young Core Instructor Visitor Foundation of Shandong Province, China (2014), Young Core Instructor Training Program of Yantai University, China (2014).
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Daquan Chen and Zimei Wu have contributed to this work equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Sun, J., Lian, S. et al. Dual pH-responsive and CD44 receptor targeted multifunctional nanoparticles for anticancer intracellular delivery. J Nanopart Res 16, 2743 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2743-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2743-1