Abstract
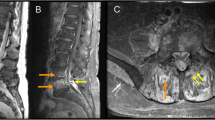
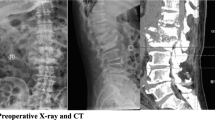
Aspergillus terreus, a saprophytic fungus, is recognized as an emerging pathogen responsible for various infections in human beings. However, bone and joint involvement is uncommon. We report a rare case of A. terreus spondylodiscitis in a 20-year-old male with a past history of recurrent, incompletely treated pulmonary tuberculosis. Clinical signs at the time of admission included cough, low-grade fever, general weakness and left-sided back pain. Histological examination of spinal biopsy samples revealed lesions of necrosis, granulomatous inflammation and septate hyphae with acute-angle branching. A. terreus was recovered from culture. The patient received antifungal therapy with voriconazole plus caspofungin and underwent surgical debridement. Further investigations revealed no cause of primary immunodeficiency such as chronic granulomatous disease, severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome or disorders of the IL-12/IFNγ signaling pathway. Moreover, HIV serological tests resulted negative and the patient was not under immunosuppressive therapy. Unfortunately, owing to precarity and medication non-adherence, vertebral sequelae occurred. This new report emphasizes the need to consider a fungal infection in patients with spondylodiscitis, regardless of the immune status.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guerado E, Cerván AM. Surgical treatment of spondylodiscitis, An update. Int Orthop. 2012;36:413–20.
Gabrielli E, Fothergill AW, Brescini L, Sutton DA, Marchionni E, Orsetti E, et al. Osteomyelitis caused by Aspergillus species: a review of 310 reported cases. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20:559–65.
Horn D, Sae-Tia S, Neofytos D. Aspergillus osteomyelitis: review of 12 cases identified by the prospective antifungal therapy alliance registry. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009;63:384–7.
Belzunegui J, Intxausti JJ, De Dios JR, Del Val N, Valverde VR, Gonzalez C, et al. Haematogenous vertebral osteomyelitis in the elderly. Clin Rheumatol. 2000;19:344–7.
McHenry MC, Easley KA, Locker GA. Vertebral osteomyelitis: long-term outcome for 253 patients from 7 Cleveland-area hospitals. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:1342–50.
Pigrau C, Almirante B, Flores X, Falco V, Rodríguez D, Gasser I, et al. Spontaneous pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis and endocarditis: incidence, risk factors, and outcome. Am J Med. 2005;118:1287.
Karadimas EJ, Bunger C, Lindblad BE, Hansen ES, Høy K, Helmig P, et al. Spondylodiscitis. A retrospective study of 163 patients. Acta Orthop. 2008;79:650–9.
Seligsohn R, Rippon JW, Lerner SA. Aspergillus terreus osteomyelitis. Arch Intern Med. 1977;137:918–20.
Glotzbach RE. Aspergillus terreus infection of pseudoaneurysm of aortofemoral vascular graft with contiguous vertebral osteomyelitis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982;77:224–7.
Brown DL, Musher DM, Taffet GE. Hematogenously acquired Aspergillus vertebral osteomyelitis in seemingly immunocompetent drug addicts. West J Med. 1987;147:84–5.
Grandière-Perez L, Asfar P, Foussard C, Chennebault JM, Penn P, Degasne I. Spondylodiscitis due to Aspergillus terreus during an efficient treatment against invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Intensive Care Med. 2000;26:1010–1.
Park KU, Lee HS, Kim CJ, Kim EC. Fungal discitis due to Aspergillus terreus in a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Korean Med Sci. 2000;15:704–7.
Maman E, Morin A-S, Soussan M, Coignard H, Lortholary O, Fain O. Multifocal bone aspergillosis by Aspergillus terreus in an apparently immunocompetent patient. Presse Medicale Paris Fr. 1983. 2015.
Gamaletsou MN, Rammaert B, Bueno MA, Moriyama B, Sipsas NV, Kontoyiannis DP, et al. Aspergillus osteomyelitis: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, management, and outcome. J Infect. 2014;68:478–93.
Arendrup MC. Update on antifungal resistance in Aspergillus and Candida. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20(Suppl 6):42–8.
Lamoth F, Alexander BD. Comparing etest and broth microdilution for antifungal susceptibility testing of the most-relevant pathogenic molds. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53:3176–81.
Steinbach WJ, Perfect JR, Schell WA, Walsh TJ, Benjamin DK. In vitro analyses, animal models, and 60 clinical cases of invasive Aspergillus terreus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:3217–25.
Lass-Flörl C, Griff K, Mayr A, Petzer A, Gastl G, Bonatti H, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of infections due to Aspergillus terreus: 10-year single centre experience. Br J Haematol. 2005;131:201–7.
Hachem R, Gomes MZR, El Helou G, El Zakhem A, Kassis C, Ramos E, et al. Invasive aspergillosis caused by Aspergillus terreus: an emerging opportunistic infection with poor outcome independent of azole therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69:3148–55.
Dotis J, Roilides E. Osteomyelitis due to Aspergillus spp. in patients with chronic granulomatous disease: comparison of Aspergillus nidulans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Int J Infect Dis. 2004;8:103–10.
Camargo JF, Husain S. Immune correlates of protection in human invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:569–77.
Hachem RY, Kontoyiannis DP, Boktour MR, Afif C, Cooksley C, Bodey GP, et al. Aspergillus terreus: an emerging amphotericin B-resistant opportunistic mold in patients with hematologic malignancies. Cancer. 2004;101:1594–600.
Walsh TJ, Anaissie EJ, Denning DW, Herbrecht R, Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, et al. Treatment of Aspergillosis: clinical practice guidelines of the infectious diseases society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:327–60.
Pascual A, Calandra T, Bolay S, Buclin T, Bille J, Marchetti O. Voriconazole therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with invasive mycoses improves efficacy and safety outcomes. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:201–11.
Barchiesi F, Spreghini E, Santinelli A, Fothergill AW, Fallani S, Manso E, et al. Efficacy of caspofungin against Aspergillus terreus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:5133–5.
Bowman JC, Abruzzo GK, Flattery AM, Gill CJ, Hickey EJ, Hsu MJ, et al. Efficacy of caspofungin against Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus terreus, and Aspergillus nidulans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:4202–5.
Felton T, Troke PF, Hope WW. Tissue penetration of antifungal agents. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014;27:68–88.
Acknowledgments
We especially thank Céline Ramanantsoa and Lucia Pérez for case consultation and critical analysis of this report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Pauline Comacle and Yohann Le Govic have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comacle, P., Le Govic, Y., Hoche-Delchet, C. et al. Spondylodiscitis Due to Aspergillus terreus in an Immunocompetent Host: Case Report and Literature Review. Mycopathologia 181, 575–581 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-0007-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-016-0007-6