Abstract
Background
Jorge Lobo’s disease (JLD) is a cutaneous chronic mycosis caused by Lacazia loboi. We studied Factor XIIIa + dermal dendrocytes (FXIIIa + DD), Langerhans cells (LC) through the expression of langerin and the expression of S100 protein.
Methods
A total of 41 biopsies and 10 normal skins (control) were developed with a polymer-based immunohistochemical method.
Results
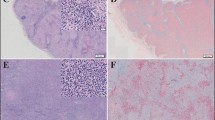
Lesions presented infiltrate comprising macrophages, some asteroid corpuscles, lymphocytes, multinucleated giant cells and a large number of fungi. LCs presented short dendrites and were scarcely distributed. Dermal langerin + cells were detected in nine JLD lesions. FXIIIa + DD were hypertrophic, visualized in the inflammatory infiltrate of JLD lesions. Cells S100+ were present in JLD and control group with a similar number of cells. A total of 14 specimens did not express FXIIIa, and this considerable number probably contributed to the statistical similarity with the control group.
Conclusions
The results indicate that LCs are present in the immune response against Lacazia loboi. Some dermal langerin + cells could be another subset of dendritic cells. Our data indicate changes of LCs in JLD cutaneous lesions and present, for the first time, results that show langerin + cells in the dermis and corroborate previous observations on the participation of FXIIIa + DD in the in situ immune response in JLD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taborda PR, Taborda VA, McGinnis MR. Lacazia loboi gen. nov., comb. nov., the etiologic agent of lobomycosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:2031–3.
Opromolla DVA, Belone AFF, Taborda PR, Rosa PS. Lymph node involvement in Jorge Lobo’s disease: report of two cases. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:938–41.
Marcos EVC, Souza FC, Torres EA, Lauris JRP, Opromolla DVA. Study of the association between human leukocyte antigens and Jorge Lobo’s disease. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2005;38:399–401.
Vilani-Moreno FR, Opromolla DVA. Determinação da viabilidade do Paracoccidioides loboi em biópsias de pacientes portadores da doença de Jorge Lobo. An Bras Dermatol. 1997;72:433–7.
Brito AC, Quaresma JAS. Lacaziosis (Jorge Lobo’s disease): review and update. An Bras Dermatol. 2007;82:461–74.
Pradinaud R, Talhari S. Lobomycose. Encyclopedie medico chirurgicale, maladies infectieuses. Paris: Elsevier; 1996. p. 1–6.
Opromolla DVA, Baruzzi RG. Doença de Jorge Lobo. In: Coura JR, editor. Dinâmica das doenças infecciosas e parasitárias. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan; 2005. p. 1185–92.
Xavier MBF, Libonati RMF, Unger D, Oliveira C, Corbett CEP, Brito AC, et al. Macrophages and TGF-beta immunohistochemical expression in Jorge Lobo’s disease. Hum Pathol. 2008;39:269–74.
Fuchs J, Milbradt R, Pecher AS. Lobomycosis (keloidal blastomycosis): case reports and overview. Cutis. 1990;46:227–34.
Opromolla DVA, Vilani-Moreno FR, Belone AFF. A doença de Jorge Lobo e a coloração pela prata metanamina. An Bras Dermatol. 1999;74:345–9.
Stoitzner P, Holzmann S, McLellan AD, Ivarsson L, Stössel H, Kapp M, et al. Visualization and characterization of migratory Langerhans cells in murine skin and lymph nodes by antibodies against Langerin/CD207. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;120:266–74.
Hunger RE, Sieling PA, Ochoa MT, Sugaya M, Burdick AE, Rea TH, et al. Langerhans cells utilize CD1a and Langerin to efficiently present nonpeptide antigens to T cells. J Clin Invest. 2004;113:701–8.
Headington JT. The dermal dendrocyte. Adv Dermatol. 1986;1:159–71.
Cerio R, Griffths CEM, Cooper KD, et al. Characterization of factor XIIIa positive dermal dendritic cells in normal and inflamed skin. Br J Dermatol. 1989;121:421–31.
Pagliari C, Sotto MN. Dendritic cells and pattern of cytokines in paracoccidioidomycosis skin lesions. Am J Dermatopatol. 2003;25:107–12.
Quaresma JAS, Unger D, Pagliari C, Sotto MN, Duarte MIS, Brito AC. Immunohistochemical study of langerhans cells in cutaneous lesions of the Jorge Lobo’s disease. Acta Trop. 2010;114:59–62.
Vilani-Moreno FR, Belone AFF, Madeira S, Opromolla DVA. Evaluation of the vital staining method for Lacazia loboi through the experimental inoculation of BALB/c mice. Med Mycol. 2003;41:211–6.
Vilani-Moreno FR, Silva LM, Opromolla DVA. Evaluation of the phagocytic activity of peripheral blood monocytes of patients with Jorge Lobo’s disease. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2004;37:165–8.
Pagliari C, Sotto MN. Correlation of factor XIIIa + dermal dendrocytes with paracoccidioidomycosis skin lesions. Med Mycol. 2002;40:407–10.
Halawi A, Abbas O, Mahalingam M. S100 proteins and the skin: a review. JEADV. 2014;28:405–14.
de Jong MA, Vriend LEM, Theelen B, Taylor ME, Fluitsma D, Boekhout T, et al. C-type lectin Langerin is a β-glucan receptor on human Langerhans cells that recognizes opportunistic and pathogenic fungi. Mol Immunol. 2010;47:1216–25.
Merad M, Manz MG. Dendritic cell homeostasis. Blood. 2009;113:3418–27.
Nagao K, Ginhoux F, Leitner WW, Motegi S, Bennett CL, Clausen BE, et al. Murine epidermal Langerhans cells and Langerin expressing dermal dendritic cells are unrelated and exhibit distinct functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:3312–7.
Romani N, Clausen BE, Stoitzner P. Langerhans cells and more: langerin-expressing dendritic cell subsets in the skin. Immunol Rev. 2010;234:120–41.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CNPq, Grant 470512/2013-0. We thank Wellington Luiz F. da Silva, BSc, for the excellent technical support.
Conflict of Interest
None of the authors have any potential conflict of interest or financial support in the subject matter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barboza, T.C., Quaresma, J.A.S., de Brito, A.C. et al. Jorge Lobo’s Disease: Immunohistochemical Characterization of Dendritic Cells in Cutaneous Lesions. Mycopathologia 179, 269–274 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-014-9836-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-014-9836-3