Abstract
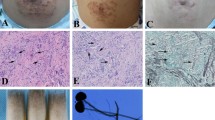
We report a case of cutaneous protothecosis due to Prototheca wickerhamii in an immunocompetent man presented with a specific eczema-like lesions. Dermatological examination revealed erythematous plaques, dark red papules with some coalescence, and a few superficial ulcerations, covered with less scales on his right side chest and neck. Fungal culture, histopathological examination and molecular identification confirmed the organism. Antifungal susceptibility testing revealed strain sensitive to amphotericin B, Fluconazole, itraconazole and voriconazole. The patient was cured by oral itraconazole capsules and topical cream ketoconazole 2 %.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roesler U, Möller A, Hensel A, Baumann D. Diversity within the current algal species Prototheca zopfii: a proposal for two Prototheca zopfii genotypes and description of a novel species, Prototheca blaschkeae sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006;56:1419–25.
Satoh K, Ooe K, Nagayama H, Makimura K. Prototheca cutis sp. nov., a newly discovered pathogen of protothecosis isolated from inflamed human skin. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2010;60(Pt 5):1236–40.
Davies RR, Spencer H, Wakelin PO. A case of human protothecosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1964;58:448–51.
Zhao J, Liu W, Lv G, Shen Y. Protothecosis successfully treated with amikacin combined with tetracyclines. Mycoses. 2004;47(3–4):156–8.
Zhang Qiang-Qiang, Li Li, Zhu Li-Ping, Zhao Ying, Wang Yun-Ru, Zhu Jun-hao, Zhu Min. Cutaneous protothecosis in patient with diabetes mellitus and review of published case reports. Mycopathologia. 2012;173:163–71.
Sha Lu, Xi Liyan, Qin Wei, Luo Yijin. Cutaneous protothecosis: two new cases in China and literature review. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:328–31.
Zhang Qiangqiang, Zhu Liping, Weng Xinhua, Li L. Meningitis due to Prototheca wickerhamii: rare case in China. Med Mycol. 2007;45(1):85–8.
Zhang Q, Weng X, Li L, Zhu L. An unusual case of granulomatous lymphadenitis due to Prototheca zopfii var. portoricensis in an immunocompetent man in China. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14(Suppl 3):e32–5.
Todd JR, King JW, Oberle A, Matsumoto T. Protothecosis: report of a case with 20-year follow-up, and review of previously published cases. Med Mycol. 2012;50(7):673–89.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Dr. Chen Min from Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Medical Mycology Shanghai, Department of Dermatology,Changzheng Hospital, Shanghai and Shanghai Institute of Medical Mycology in PCR cloning identification of organism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Li, L., Yuli, K. et al. A Case of Cutaneous Protothecosis Mimics Eczema. Mycopathologia 179, 163–166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-014-9812-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-014-9812-y