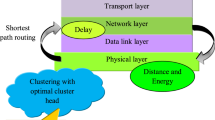
Abstract
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have recently been viewed as the foundation infrastructure that has paved the way for the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT). However, there is a challenge when integrating WSNs into the IoT due to high-energy consumption in their nodes and poor network lifespan. As a result, the fundamental issues in WSN are sensor node energy scarcity, sensor data exchange, and routing protocols. To address the aforementioned shortcomings, this paper proposes an optimized energy-efficient path-planning approach that increases network lifetime and connectivity. These applications employ large amounts of data and need a data that are more effective sensing and data transfer method. This study presents Improvised DSHR (Dual Step Hybrid Routing) - a methodology for cluster-based routing efficiency. It consists of a two-phase method designed to identify the best route taking clustering into account. In addition, it consists of cluster head selection, optimum route building, node integration with the cluster head, and sensing range optimization. Furthermore, an efficient data transmission. Improvised DSHR is evaluated considering network lifetime, communication overhead, no active nodes, and Route Length evaluated, and then the model is compared to the current Leach protocol to demonstrate its efficiency.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This research do not utilize any dataset for analysis.
References
Rani S, Ahmed SH, Talwar R, Malhotra J (2017) Can sensors collect big data? An energy-efficient big data gathering algorithm for a WSN. IEEE Trans Industr Inf 13(4):1961–1968. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2017.2656899
Ang KL-M, Seng JKP, Zungeru AM (2018) Optimizing energy consumption for big data collection in large-scale wireless sensor networks with mobile collectors. IEEE Syst J 12(1):616–626. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2016.2630691
Dao T-K, Yu J, Nguyen T-T, Ngo T-G (2020) A hybrid improved MVO and FNN for identifying collected data failure in cluster heads in WSN. IEEE Access 8:124311–124322. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005247
Wang K, Yu C-M, Wang L-C (2021) DORA: a destination-oriented routing algorithm for energy-balanced wireless sensor networks. IEEE Internet Things J 8(3):2080–2081. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3025039
Arya G, Bagwari A, Chauhan DS (2022) Performance analysis of deep learning-based routing protocol for an efficient data transmission in 5G WSN communication. IEEE Access 10:9340–9356. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3142082
Xu C, Xiong Z, Zhao G, Yu S (2019) An energy-efficient region source routing protocol for lifetime maximization in WSN. IEEE Access 7:135277–135289. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2942321
Al-Otaibi S, Al-Rasheed A, Mansour RF, Yang E, Joshi GP, Cho W (2021) Hybridization of metaheuristic algorithm for dynamic cluster-based routing protocol in wireless sensor networksx. IEEE Access 9:83751–83761. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3087602
Kaur T, Kumar D (2021) MACO-QCR: multi-objective ACO-Based QoS-Aware cross-layer routing protocols in WSN. IEEE Sens J 21(5):6775–6783. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.3038241
Ahmed Elsmany EF, Omar MA, Wan T-C, Altahir AA (2019) EESRA: energy efficient scalable routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 7:96974–96983. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2929578
Xu Y, Jiao W, Tian M (2021) An energy-efficient routing protocol for 3D Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Sens J 21(17):19550–19559. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3086806
Bai Y, Mai Y, Wang N (2017) Performance comparison and evaluation of the proactive and reactive routing protocols for MANETs. In: 2017 Wireless Telecommunications Symposium (WTS). WTS, Chicago, IL, USA, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/WTS.2017.7943538
Mohemed RE, Saleh AI, Abdelrazzak M, Samra AS (2017) Energyefficient routing protocols for solving energy hole problem in wireless sensor networks. Comput Netw 114:51–66
Razaque A, Abdulgader M, Joshi C, Amsaad F, Chauhan M (2016) PLEACH: Energy efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: Proc IEEE Long Island Syst Appl Technol Conf (LISAT), pp 1–5
Khan RA, Xin Q, Roshan N (2020) RK-energy efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. Wirel Pers Commun 116:1–13
Chang Y, Yuan X, Li B, Niyato D, Al-Dhahir N (2019) Machinelearning- based parallel genetic algorithms for multi-objective optimization in ultra-reliable low-latency WSNs. IEEE Access 7:4913–4926
Thangaramya K, Kulothungan K, Logambigai R, Selvi M, Ganapathy S, Kannan A (2019) Energy aware cluster and neuro-fuzzy based routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks in IoT. Comput Netw 151:211–223
Guo W, Yan C, Lu T (2019) Optimizing the lifetime of wireless sensor networks via reinforcement-learning-based routing. Int J Distrib Sensor Netw 15(2):155014771983354
Wang J, Cao J, Sherratt RS, Park JH (2018) An improved ant colony optimization-based approach with mobile sink for wireless sensor networks. J Supercomput 74(12):6633–6645
Alami HE, Najid A (2016) Energy-ef_cient fuzzy logic cluster head selection in wireless sensor networks. In: Proc Int Conf Inf Technol Org Develop (IT OD), Rabat, Morocco, pp 1–7
Lee J-S, Teng C-L (2017) An enhanced hierarchical clustering approach for mobile sensor networks using fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Internet Things J 4(4):1095–1103
Alami HE, Najid A (2019) ECH: An enhanced clustering hierarchy approach to maximize lifetime of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 7:107142107153
Sert SA, Yazici A (2019) Optimizing the performance of rule-based fuzzy routing algorithms in wireless sensor networks. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Fuzzy Syst (FUZZ-IEEE), New Orleans, LA, USA, pp. 16
Ma N, Zhang H, Hu H, Qin Y (2022) ESCVAD: an energy-saving routing protocol based on Voronoi adaptive clustering for Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Internet Things J 9(11):9071–9085. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3120744
Younus MU, Khan MK, Bhatti AR (2022) Improving the software-defined wireless sensor networks routing performance using reinforcement learning. IEEE Internet Things J 9(5):3495–3508. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3102130
Kumar R, Venkanna U, Tiwari V (2022) An energy optimized multi-constrained sustainable routing model for SDWSN. IEEE Trans Netw Serv Manage 19(2):1650–1661. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSM.2021.3130661
Al-Karaki JN, Al-Mashaqbeh GA (2007) SENSORIA: a new simulation platform for wireless sensor networks. 2007 International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications (SENSORCOMM 2007), pp. 424–429. https://doi.org/10.1109/SENSORCOMM.2007.4394958
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Y, K.C., M, S.B. An improvised dual step hybrid routing protocol for network lifetime enhancement in WSN-IoT environment. Multimed Tools Appl (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17823-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17823-3