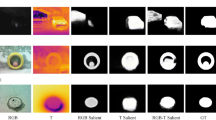
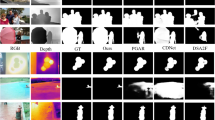
Abstract
The purpose of RGB-Thermal salient object detection (RGB-T SOD) is to segment the common salient objects or regions of the visible light image and the corresponding thermal-infrared image. Thermal-infrared information can provide more effective clues for finding prominent objects in complex environments. How to exploit the potential of multi-modal complementarity, make full use of the significant information provided by the dominant modality, and accurately locate the salient objects is still a problem worth exploring. In this paper, we first make a visual modal analysis of the complementarity between thermal-infrared images and visible images and then based on the analysis results, we propose a Transformer-based adaptive interactive network (AINet). In specific, we design a modal interaction module (MIM) with two parallel units to effectively use complementary modal information to fully complete modal information interaction. The spatial interaction unit (SIU) is responsible for directly completing modal interaction and integration in a weighted manner, and completing modal complementarity at the spatial level. The self-reinforcement unit (SRU) is responsible for enhancing the two single-modality features, strengthening the role of dominant modal features, and completing modal complementarity at the channel level. Besides, we propose a double mapping query-location module (QLM) for high-level features to complete global analysis and accurately confirm the location of salient objects. Finally, we adopt a re-calibration dual branch decoder (RCDB) to integrate the output features. We carry out sufficient experiments on RGB-T SOD datasets, and the results demonstrate that the proposed method performs outstanding against the other 13 state-of-the-art methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Zhou Z, Guo Y, Huang J, Dai M, Deng M, Yu Q (2022) Superpixel attention guided network for accurate and real-time salient object detection. Multimedia Tools Appl 81(27):38921–38944
Yang N, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Yang H, Du L (2022) A benchmark dataset and baseline model for co-salient object detection within RGB-D images. Multimedia Tool Appl 81(25):35831–35842
Wang Y, Zhou T, Li Z, Huang H, Qu B (2022) Salient object detection based on multi-feature graphs and improved manifold ranking. Multimedia Tools Appl 81(19):27551–27567
Tu Z, Li Z, Li C, Lang Y, Tang J (2021) Multi-interactive dual-decoder for RGB-thermal salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:5678–5691
Fan D-P, Lin Z, Zhang Z, Zhu M, Cheng M-M (2020) Rethinking RGB-D salient object detection: models, datasets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst
Song S, Yu H, Miao Z, Fang J, Zheng K, Ma C, Wang S (2020) Multi-spectral salient object detection by adversarial domain adaptation. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence 34:12023–12030
Liu Y, Zhang Q, Zhang D, Han J (2019) Employing deep part-object relationships for salient object detection, vol 2019-October, pp 1232–1241
Liu Y, Zhang D, Zhang Q, Han J (2022) Part-object relational visual saliency. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(7):3688–3704
Liu Y, Zhang D, Liu N, Xu S, Han J (2022) Disentangled capsule routing for fast part-object relational saliency. IEEE Trans Image Process 31:6719–6732
Cheng M-M, Zhang F-L, Mitra NJ, Huang X, Hu S-M (2010) Repfinder: finding approximately repeated scene elements for image editing. ACM Trans Graph 29(4)
Chen T, Cheng M-M, Tan P, Shamir A, Hu S-M (2009) Sketch2photo: internet image montage. ACM Trans Graph 28(5):1–10
Mahadevan V, Vasconcelos N (2009) Saliency-based discriminant tracking. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1007–1013
Chen S, Li Z, Tang Z (2020) Relation R-CNN: a graph based relation-aware network for object detection. IEEE Signal Process Lett 27:1680–1684
Quan Y, Li Z, Chen S, Zhang C, Ma H (2021) Joint deep separable convolution network and border regression reinforcement for object detection. Neural Comput Appl 33(9):4299–4314
Wang H, Zhu J, Dai W, Liu J (2019) A Re-ID and tracking-by-detection framework for multiple wildlife tracking with artiodactyla characteristics in ecological surveillance. In: Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on real-time computing and robotics (RCAR), pp 901–906
Zhu J, Wang H, Han D, Liu J (2018) Smart surveillance: a nature ecological intelligent surveillance system with robotic observation cameras and environment factors sensors. In: Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on CYBER technology in automation, control, and intelligent systems (CYBER), pp 451–456
Wang G, Li C, Ma Y, Zheng A, Tang J, Luo B (2018) RGB-T saliency detection benchmark: dataset, baselines, analysis and a novel approach. In: Image Graph Technol Appl (IGTA), pp 359–369
Tang J, Fan D, Wang X, Tu Z, Li C (2020) RGBT salient object detection: benchmark and a novel cooperative ranking approach. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 30(12):4421–4433
Tu Z, Xia T, Li C, Lu Y, Tang J (2019) M3S-NIR: multi-modal multi-scale noise-insensitive ranking for RGB-T saliency detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on multimedia information processing and retrieval (MIPR), pp 141–146
Tu Z, Xia T, Li C, Wang X, Ma Y, Tang J (2020) rGB-T image saliency detection via collaborative graph learning. Trans Multimedia 22(1):160–173
Tu Z, Ma Y, Li Z, Li C, Xu J, Liu Y (2020) RGBT salient object detection: a large-scale dataset and benchmark. arXiv:2007.03262
Zhang Q, Huang N, Yao L, Zhang D, Shan C, Han J (2020) RGB-T salient object detection via fusing multi-level CNN features. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:3321–3335
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS (2018) CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceeding of the Europeon conference on computer vision (ECCV)
Zhu C, Cai X, Huang K, Li TH, Li G (2019) PDNet: prior-model guided depth-enhanced network for salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME), pp 199–204
Chen Z, Cong R, Xu Q, Huang Q (2021) DPANet: depth potentiality-aware gated attention network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:7012–7024
Li G, Liu Z, Ye L, Wang Y, Ling H (2020) Cross-modal weighting network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the Europeon conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 665–681
Pang Y, Zhang L, Zhao X, Lu H (2020) Hierarchical dynamic filtering network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the Europeon conference on computer vision (ECCV)
Jiang B, Zhou Z, Wang X, Tang J, Luo B (2021) cmSalGAN: RGB-D salient object detection with cross-view generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans Multimedia 23:1343–1353
Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, He K (2018) Non-local neural networks. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 7794–7803
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser L, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Proceeding of the conference on neural information processing systems (NeurIPS)
Mallick R, Benois-Pineau J, Zemmari A (2022) I saw: a self-attention weighted method for explanation of visual transformers. In: 2022 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp 3271–3275
Zhao X, Zhang L, Pang Y, Lu H, Zhang L (2020) A single stream network for robust and real-time RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the Europeon conference on computer vision (ECCV)
Wang W, Xie E, Li X, Fan D-P, Song K, Liang D, Lu T, Luo P, Shao L (2021) Pyramid vision transformer: a versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In: Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV)
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceeding of the international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 9992–10002
Zhang J, Liu H, Yang K, Hu X, Liu R, Stiefelhagen R (2023) CMX: cross-modal fusion for RGB-X semantic segmentation with transformers. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 1–16
Shin U, Lee K, Kweon IS (2023) Complementary random masking for RGB-thermal semantic segmentation
Liu N, Zhang N, Wan K, Shao L, Han J (2021) Visual saliency transformer. In: Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 4702–4712
Zhu J, Zhang X, Fang X, Dong F, Qiu Y (2021) Modal-adaptive gated recoding network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Signal Process Lett 1–1
Wang W, Xie E, Li X, Fan D-P, Song K, Liang D, Lu T, Luo P, Shao L (2021) PVTv2: improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer. arXiv:2106.13797
Park J, Woo S, Lee J, Kweon IS (2018) BAM: bottleneck attention module. In: Proceeding of the British machine vision conference (BMVC), p 147
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, Uszkoreit J, Houlsby N (2021) An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: International conference on learning representations (ICLR)
Rahman MA, Wang Y (2016) Optimizing intersection-over-union in deep neural networks for image segmentation. In: Proceeding of the international symposium on visual computing (ISVC)
Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q (2020) F3Net: fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (AAAI)
Perazzi F, Krahenbuhl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A (2012) Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 733–740
Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, Susstrunk S (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1597–1604
Fan D-P, Cheng M-M, Liu Y, Li T, Borji A (2017) Structure-measure: a new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 4558–4567
Fan D, Gong C, Cao Y, Ren B, Cheng M, Borji A (2018) Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. In: Proceeding of the joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI), pp 698–704
Piao Y, Ji W, Li J, Zhang M, Lu H (2019) Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for saliency detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 7253–7262
Liu N, Zhang N, Han J (2020) Learning selective self-mutual attention for RGB-D saliency detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Deng Z, Hu X, Zhu L, Xu X, Qin J, Han G (2018) R3Net: recurrent residual refinement network for saliency detection. In: Proceeding of the international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI), pp 684–690
Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, Gao C, Dehghan M, Jagersand M (2019) BASNet: boundary-aware salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Liu J-J, Hou Q, Cheng M-M, Feng J, Jiang J (2019) A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Wu Z, Su L, Huang Q (2019) Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3902–3911
Zhao J-X, Liu J-J, Fan D-P, Cao Y, Yang J, Cheng M-M (2019) EGNet:edge guidance network for salient object detection. In: Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV)
Zhou H, Tian C, Zhang Z, Li C, Ding Y, Xie Y, Li Z (2023) Position-aware relation learning for rgb-thermal salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 32:2593–2607
Huo F, Zhu X, Zhang L, Liu Q, Shu Y (2022) Efficient context-guided stacked refinement network for RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(5):3111–3124
Gao W, Liao G, Ma S, Li G, Liang Y, Lin W (2022) Unified information fusion network for multi-modal RGB-D and RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(4):2091–2106
Zhou T, Fan D-P, Cheng M-M, Shen J, Shao L (2021) RGB-D salient object detection: a survey. Comput Vis Media 7(4)
Chen G, Shao F, Chai X, Chen H, Jiang Q, Meng X, Ho Y-S (2022) CGMDRNet: cross-guided modality difference reduction network for RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(9):6308–6323
Liu Z, Tan Y, He Q, Xiao Y (2022) Swinnet: swin transformer drives edge-aware RGB-D and RGB-T salient object detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(7):4486–4497
Pang Y, Zhao X, Zhang L, Lu H (2023) Caver: cross-modal view-mixed transformer for bi-modal salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 32:892–904
Ju R, Liu Y, Ren T, Ge L, Wu G (2015) Depth-aware salient object detection using anisotropic center-surround difference. Signal Process Image Commun 38:115–126
Peng H, Li B, Xiong W, Hu W, Ji R (2014) RGBD salient object detection: a benchmark and algorithms. In: Proceeding of the Europeon conference on computer vision (ECCV)
Li G, Zhu C (2017) A three-pathway psychobiological framework of salient object detection using stereoscopic technology. In: Proceeding of the IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCVW), pp 3008–3014
Niu Y, Geng Y, Li X, Liu F (2012) Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In: Proceeding of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 454–461
Ji W, Li J, Zhang M, Piao Y, Lu H (2020) Accurate rgb-d salient object detection via collaborative learning. In: Proceeding of the Europeon conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 52–69
Jiang B, Zhou Z, Wang X, Tang J, Luo B (2021) cmsalgan: Rgb-d salient object detection with cross-view generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans Multimedia 23:1343–1353
Zhu J, Zhang X, Dong F, Yan S, Meng X, Li Y, Tan P (2022) Transformer-based Adaptive Interactive Promotion Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. In: 2022 34th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), pp. 1989–1994. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCDC55256.2022.10034159
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2023M741952, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant U21B6001, and the Tianjin Graduate Scientific Research Innovation Project under Grant 2021YJSO2S02. A preliminary version of this work has appeared in CCDC 2022 [68].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, F., Wang, Y., Zhu, J. et al. Adaptive interactive network for RGB-T salient object detection with double mapping transformer. Multimed Tools Appl (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17747-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17747-y