Abstract
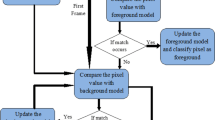
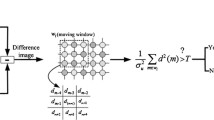
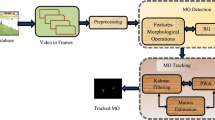
In this paper, a new algorithm for moving object detection is proposed by using unsupervised Bayesian classifier with bootstrap Gaussian expectation maximization algorithm. It consists of the following steps: the first contains of classify and estimate the motion vectors between successive frames using the Star diamond search algorithm based on unsupervised Bayesian classifier with Gaussian Expectation of Maximization algorithm, this step serves also to detect the static and dynamic blocks. In the second step, the dynamic blocks are compensated with the white pixels value and the stationary are compensated by black pixels value. In the third step, the morphological opening and closing filters are used for refining the object detected. The proposed approach is trained and evaluated using available infrared (FLIR_ADAS_v2) dataset. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsaqre FE, Baozong Y (2003) Moving object segmentation for videosurveillance and conferencing applications. In: IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology Proceedings ICCT 2003, vol. 2, pp. 1856–1859
Amine M, Djoudi K (2019, November) Vehicles detection using the MLP and the correlation measurement. In: 2019 International Conference on Advanced Electrical Engineering (ICAEE) IEEE, pp. 1–5
Banga C, Ghorbel F (1993) Optimal bootstrap sampling for fast image segmentation: application to retina image. 1993 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. IEEE, Vol. 5
Basher HA (March 2011) Two Minimum Three-Step Search Algorithm for Motion Estimation of Images from Moving IR Camera. Proceedings of IEEE Southeastcon, pp. 384–389
Boufares O, Boussif M, Aloui N (2021) Moving object detection system based on the modified temporal difference and otsu algorithm. In: 18thIEEE International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices(SSD), pp. 1378–1382
Bouwmans T, Javed S, Sultana M, Jung SK (2019) Deep neuralnetwork concepts for background subtraction: a systematic review and comparative evaluation. Neural Netw 117:8–66
Chen B, Huang S (2014) An advanced moving object detection algorithm or automatic traffic monitoring in real-world limited bandwidth networks. IEEE Trans Multimed 16:837–847
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2018) DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
De Vos L, Stegherr M (1989) Parameterizable VLSI Architectures for the Full-Search Block-Matching Algorithm. IEEE Trans Circ and Syst 36(10):1309–1316
Dou J, Qin Q, Tu Z (2019) Deep convolutional neural networks featuresfor robust foreground segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), pp. 3576–3581
El Rai MC, Aburaed N, Al-Saad M, Al-Ahmad H, Al Mansouri S, Marshall S (2020) Integrating deep learning with active contour modelsin remote sensing image segmentation. In: IEEE 27th International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), pp.1–4
Fu H, Ma Z, Zhao B, Yang Z, Jiang Y, Zhu M (2022) Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network for Foreground Segmentation, In: Proceedings of 2021 Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference, pp. 811–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6328-4_81
Gangodkar D, Kumar P, Kumar P, Mittal A (2011) Real-time motion detection using block matching algorithms on multicore processors. Int J Inf Commun Technol 3(2):131
Ghorbel F, Derrode S, Alata O (2012) Récentes avancées en reconnaissance de formes statistique. ARTS-PI éditions
Heikkila M, Pietikainen M (2006) A texture-based method for modelingthe background and detecting moving objects. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28:657–662
Kerfa D, Belbachir MF (2014) An Efficient Real Time Moving Object Detection Scheme Using Diamond Search Algorithm and Mathematical Morphology. Computers and Software, 744
Kerfa D, Faouzi Belbachir M (2016) Star diamond: an efficient algorithm for fast block matching motion estimation in H264/AVC video codec. Multimed Tools Appl 75(6):3161–3175
Kerfa D, Saidane A (2020) An efficient algorithm for fast block matching motion estimation using an adaptive threshold scheme. Multimed Tools Appl 79(33):24173–24184
Koga T (1981) Motion Compensated Inter Frame Coding for Video Conferencing. In: National Telecommunication. Conference, G5.3.1–5, New Orleans
Kurmasha HTR, Ali IH (2022) Threshold adaptation and XOR accumulation algorithm for objects detection. Int J Electr Comput Eng (2088–8708) 12(3):2517
Li R, Zeng B, Liou ML (1994) A new three-step search algorithm for block motion estimation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 4:438–442
Li C, Wang X, Zhang L, Tang J, Wu H, Lin L (2017) Weighted lowrank decomposition for robust grayscale-thermal foreground detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 27:725–738
Lim LA, Keles HY (2018) Foreground segmentation using convolutional neural networks for multiscale feature encoding. J Pattern Recognit Lett 112:256–262
Lim LA, Keles HY (2020) Learning Multi-scale Features for Foreground Segmentation. Pattern Anal Applic 23(3):1369–1380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-019-00845-9
Lim LA, Yalim Keles H (2018) Foreground segmentation using convolutional neural networks for multiscale feature encoding. Pattern Recogn Lett 112:256–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.08.002
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (Jun. 2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3431–3440. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965
Lu J, Liou ML A Simple and Efficient Search Algorithm for Block-Matching Motion Estimation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 7:429–433
Manap RA, Ranjit SSS, Basari AA, Ahmad BH (2010) Performance Analysis of Hexagon-Diamond Search Algorithm for Motion Estimation. 2nd International Conference on Computer Engineering and Technology, pp.155–159
Pan Z, Zhang R, Ku W et al (2018) Adaptive pattern selection strategy for diamond search algorithm in fast motion estimation. Multimed Tools Appl 78:2447–2464
Pan Z, Zhang R, Ku W et al (2019) Adaptive pattern selection strategy for diamond search algorithm in fast motion estimation. Multimed Tools Appl 78(2):2447–2464
Pandian SIA, Anitha J (2019) An Unvarying Orthogonal Search with Small Triangle Pattern for Video Coding. In: Smart Intelligent Computing and Applications. Springer, Singapore, pp 43–52
Pham TT (2021) Motion detection with segmentation of optical flowsfor infrared images. In: 2021 IEEE 11th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), pp. 0347–0354
Po LM, Ma WC (1996) A novel four-step search algorithm for fast block motion estimation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 6:313–317
Rashed H, El Sallab A, Yogamani S, ElHelw M (2019) Motion and depth augmented semantic segmentation for autonomous navigation. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 364–370
Richardson IEG (2010) H.264 and MPEG-4 Video Compression, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons
Rifat R, Mou JR, Shahariar R, Ahsan A (2019) A new approach of moving object detection using background subtraction method. In: IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Telecommunication Engineering (ICECTE), pp. 256–259
Saha A, Lee Y-W, Hwang Y-S et al (2018) Context-aware block-based motion estimation algorithm for multimedia internet of things (IoT) platform. Pers Ubiquit Comput 22(1):163–172
Shanableh T, Peixoto EI (2013) MPEG-2 to HEVC video transcoding with content-based modeling. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 23:1191–1196
Sultana M, Mahmood A, Javed S, Jung SK (2019) Unsupervised deep context prediction for background estimation and foreground segmentation. Mach Vis Appl 30(3):375–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-018-0993-0
Talal M, Panthakkan A, Mukhtar H, Mansour W, Almansouri S, Alahmad H (2018) Detection of water-bodies using semantic segmentation. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing and Information Security (ICSPIS), pp. 1–4
Tezcan MO, Ishwar P, Konrad J (2020) BSUV-Net: A Fully-Convolutional Neural Network for Background Subtraction of Unseen Videos, Snowmass Village CO, USA, Mar 2763 2772 https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV45572.2020.9093464
Tezcan MO, Ishwar P, Konrad J (2021) BSUV-Net 2.0: Spatio-Temporal Data Augmentations for Video-Agnostic Supervised Background Subtraction. IEEE Access 9:53849–53860. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3071163
Wang X, Wan W, Zhang J, Ma Y (Sept. 2010) Research on the Motion Estimation with a Novel Octagon Cross Diamond Search Algorithm. Asia Pacific Conference on Postgraduate Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PrimeAsia), pp. 89–92
Yao G, Lei T, Zhong J, Jiang P, Jia W (2017) Comparative evaluation of background subtraction algorithms in remote scene videos capturedby mwir sensors. Sensors 17:1–31
Yasakethu SLP, Hewage CTER (2018) Efficient decoding algorithm for 3D video over wireless channels. Multimed Tools Appl 77:30683–30701
Zha Y, Wu M, Qiu Z, Dong S, Yang F, Zhang P (2019) Distractor aware visual tracking by online Siamese network. IEEE Access 7:89777–89788
Zhao X, Chen Y, Tang M, Wang J (Jul. 2017) Joint Background Reconstruction and Foreground Segmentation via A Two-stage Convolutional Neural Network. arXiv:1707.07584 [cs], [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1707.07584. Accessed 10 Jun 2021
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, Wang X, Jia J (Jul. 2017) Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, pp. 6230–6239. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.660
Zhou Y, Maskell S (2017) Moving object detection using background subtraction for a moving camera with pronounced parallax. In: 2017 IEEE Sensor Data Fusion: Trends, Solutions, Applications (SDF), pp. 1–6
Zhu S, Ma KK (2000) A new diamond search algorithm for fast block-matching motion estimation. IEEE Trans Image Processing 9:287–290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kerfa, D. Moving objects detection in thermal scene videos using unsupervised Bayesian classifier with bootstrap Gaussian expectation maximization algorithm. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 6335–6350 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15849-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15849-1