Abstract
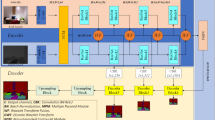
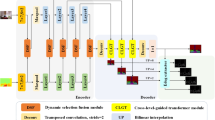
Fusing the RGB and depth information can significantly improve the performance of semantic segmentation since the depth data represents the geometric information. In this paper, we propose a novel Gate-guided Edge Distillation (GED) based approach to effectively generate edge-aware features by fusing the RGB and depth data, assisting the high-level semantic prediction. The proposed GED consists of two modules: gated fusion and edge distillation. The gated fusion module adaptively learns the relationship between RGB and depth data to generate complementary features. To address the adverse effects caused by redundant information of edge-aware features, edge distillation module enhances the semantic features of the same object while preserving the discrimination of the semantic features belonging to different objects. Besides, by using distilled edge-aware features as detailed guidance, the proposed edge-guided fusion module effectively fuses with semantic features. In addition, the complementary features are leveraged in multi-level feature fusion module to further enhance detailed information. Extensive experiments on the widely used SUN-RGBD and NYU-Dv2 datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach with ResNet-50 achieves state-of-the-art performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuna D, Kar A, Fidler S (2019) Devil is in the edges: Learning semantic boundaries from noisy annotations. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit pp. 11075–11083
Chen LC, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H (2018) Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Proc Eur Conf Comput Vis pp. 801–818. Springer
Chen Z, Cong, R, Xu Q, Huang Q (2020) Dpanet: Depth potentiality-aware gated attention network for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process
Cheng Y, Cai R, Li Z, Zhao X, Huang K (2017) Locality-sensitive deconvolution networks with gated fusion for rgb-d indoor semantic segmentation. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit pp. 3029–3037
Couprie C, Farabet C, Najman L, LeCun Y (2013) Indoor semantic segmentation using depth information. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3572
Deng L, Yang M, Li T, He Y, Wang C (2019) Rfbnet: deep multimodal networks with residual fusion blocks for rgb-d semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.00135
Eigen D, Fergus R (2015) Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis pp. 2650–2658
Geng Q, Zhang H, Qi X, Huang G, Yang R, Zhou Z (2021) Gated path selection network for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:2436–2449
Gupta S, Arbelaez P, Malik J (2013) Perceptual organization and recognition of indoor scenes from rgb-d images. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit pp. 564–571
Gupta S, Girshick R, Arbeláez P, Malik J (2014) Learning rich features from rgb-d images for object detection and segmentation. In: Proc Eur Conf Comput Vis pp. 345–360. Springer
Hazirbas C, Ma L, Domokos C, Cremers D (2016) Fusenet: Incorporating depth into semantic segmentation via fusion-based cnn architecture. In: Asian Conf Comput Vis pp. 213–228. Springer
He Y, Chiu WC, Keuper M, Fritz M (2017) Std2p: Rgbd semantic segmentation using spatio-temporal data-driven pooling. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit pp. 4837–4846. IEEE
Hu X, Yang K, Fei L, Wang K (2019) Acnet: Attention based network to exploit complementary features for rgbd semantic segmentation. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Image Process pp. 1440–1444
Jiang J, Zheng L, Luo F, Zhang Z (2018) Rednet: Residual encoder-decoder network for indoor rgb-d semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.01054
Kendall A, Gal Y, Cipolla R (2018) Multi-task learning using uncertainty to weigh losses for scene geometry and semantics. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit pp. 7482–7491. IEEE
Li W, Gu J, Dong Y, Dong Y, Han J (2020) Indoor scene understanding via rgb-d image segmentation employing depth-based cnn and crfs. Multimedia Tools and Applications 79(47):35475–35489
Li X, Zhao H, Han L, Tong Y, Yang K (2019) Gff: Gated fully fusion for semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.01803
Li Z, Gan Y, Liang X, Yu Y, Cheng H, Lin L (2016) Lstm-cf: Unifying context modeling and fusion with lstms for rgb-d scene labeling. In: Proc Eur Conf Comput Vis pp. 541–557. Springer
Lin D, Chen G, Cohen-Or D, Heng PA, Huang, H (2017) Cascaded feature network for semantic segmentation of rgb-d images. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis pp. 1311–1319. IEEE
Lin D, Huang H (2019) Zig-zag network for semantic segmentation of rgb-d images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(10):2642–2655
Lin G, Milan A, Shen C, Reid I (2017) Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1925–1934. IEEE
Liu H, Wu W, Wang X, Qian Y (2018) Rgb-d joint modelling with scene geometric information for indoor semantic segmentation. Multimedia Tools and Applications 77(17):22475–22488
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit pp. 3431–3440. IEEE
Noh H, Hong S, Han B (2015) Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis pp. 1520–1528. IEEE
Park SJ, Hong KS, Lee S (2017) Rdfnet: Rgb-d multi-level residual feature fusion for indoor semantic segmentation. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis pp. 4980–4989. IEEE
Qi X, Liao R, Jia J, Fidler S, Urtasun R (2017) 3d graph neural networks for rgbd semantic segmentation. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis pp. 5199–5208. IEEE
Ren X, Bo L, Fox D (2012) Rgb-(d) scene labeling: Features and algorithms. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit pp. 2759–2766. IEEE
Silberman N, Hoiem D, Kohli P, Fergus R (2012) Indoor segmentation and support inference from rgbd images. In: Proc Eur Conf Comput Vis pp. 746–760. Springer
Song S, Lichtenberg SP, Xiao J (2015) Sun rgb-d: A rgb-d scene understanding benchmark suite. In: Proc IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit pp. 567–576. IEEE
Takikawa T, Acuna D, Jampani V, Fidler S (2019) Gated-scnn: Gated shape cnns for semantic segmentation. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis pp. 5229–5238. IEEE
Thøgersen M, Escalera S, Gonzàlez J, Moeslund TB (2016) Segmentation of rgb-d indoor scenes by stacking random forests and conditional random fields. Pattern Recogn Lett 80:208–215
Wang J, Wang Z, Tao D, See S, Wang G (2016) Learning common and specific features for rgb-d semantic segmentation with deconvolutional networks. In: Proc Eur Conf Comput Vis pp. 664–679. Springer
Wang W, Neumann U (2018) Depth-aware cnn for rgb-d segmentation. In: Proc Eur Conf Comput Vis pp. 135–150. IEEE
Xing Y, Wang J, Chen X, Zeng G (2019) Coupling two-stream rgb-d semantic segmentation network by idempotent mappings. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Image Process pp. 1850–1854. IEEE
Yu J, Lin Z, Yang J, Shen X, Lu X, Huang TS (2019) Free-form image inpainting with gated convolution. In: Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis pp. 4471–4480. IEEE
Yu Z, Liu W, Zou Y, Feng C, Ramalingam S, Kumar B, Kautz J (2018) Simultaneous edge alignment and learning. In: Proc Eur Conf Comput Vis pp. 388–404. Springer
Zheng Y, Gao X (2017) Indoor scene recognition via multi-task metric multi-kernel learning from rgb-d images. Multimed Tools Appl 76(3):4427–4443
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants 62101344, 62171294, 61771321, 61871273, 61872429, in part by the key Project of DEGP under grants 2018KCXTD027, in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China under grants 2020A1515010959, in part by Natural Science Foundation of Shenzhen under grants JCYJ20200109105832261, JSGG20180508152022006, JCYJ20190808122409660 and in part by the Interdisciplinary Innovation Team of Shenzhen University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, W., Peng, Y., Zhang, Z. et al. RGB-D Gate-guided edge distillation for indoor semantic segmentation. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 35815–35830 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11395-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11395-w