Abstract
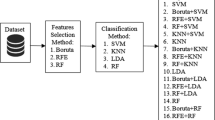
Human age is a crucial factor in social interaction. It determines the way we interact with others. It is also a relevant forensic issue that can provide helpful information in legal and criminal investigations. Thus, human age estimation has a wide range of real-world applications related to human computer interaction and forensic sciences. Based on auditory perception, in this paper, we investigate a new biometric trait for human age classification and estimation. For this purpose, several techniques of Machine Learning, including Random Forests (RF), Support Vector Machines (SVM), Linear Regression (LR), Polynomial Regression (PR), Ridge Regression (RR) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), are used to estimate the age of the volunteers. To evaluate the performances of our experiment, a dataset of 837 tests have been collected with different ages ranging from 6 to 60 years. The results show a good accuracy between 86% and 92% of reasonable classification and 98.2% of good age estimation with a root-mean-square error of 2.6 years. Results are found to be significant and show that auditory perception is one of the practical interests in real-world applications. The dataset we used will be made publicly available online.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anguita D, Ghio A, Ridella S, Sterpi D (2009) K-fold cross validation for error rate estimate in support vector machines. In: Proc of the Int Conf on Data Mining, pp 291–297
Barbosa de Sá LC, Lima MAMT, Tomita S, Frota SMMC, Santos GA, Garcia TR (2007) Analysis of high frequency auditory thresholds in individuals aged between 18 and 29 years with no ontological complaints. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 73:2
Boser BE, Guyon IM, Vapnik VN (1992) A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In: Proce of the fifth ann work on Comp learn theo ACM, pp 144–152
Breiman L (2011) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:123–140
Bukar AM, Ugail H (2017) Automatic age estimation from facial profile view. IET Comp Vis 11(8):650–655
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-Vector Networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Cortes C, Mohri M, Rostamizadeh A (2009) L2 regularization for learning kernels proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence .109-116 AUAI Press
Ceyhan EB, Saĝiroĝlu Ş, Atagün E (2014) Age estimation from fingerprints: Examination of the population in Turkey. In: IEEE 13th Inter Conf Mach Learn Appl IEEE, pp 478–481
Dobry G, Hecht RM, Avigal M, Zigel Y (2011) Supervector dimension reduction for efficient speaker age estimation based on the acoustic speech signal. IEEE Trans on Audio Spe and Lang Proc 19(7):1975–1985
Dietterich TG (1998) Approximate statistical tests for comparing supervised classification learning algorithms. Neucomput 10(7):1895–1923
Dornaika F, Bekhouche SE, Arganda-Carreras I (2020) Robust regression with deep CNNs for facial age estimation: An empirical study. Expert Systems with Applications 141:112942
Eidinger E, Enbar R, Hassner T (2014) Age and gender estimation of unfiltered faces. IEEE Trans Info Forens Secur 1(12):2170–2179
Freire-Aradas A, Phillips C, Lareu MV (2017) Forensic individual age estimation with DNA: from initial approaches to methylation tests Foren sci rev 29 2
Fisher RA (1936) The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Annal Eug 7:179–188
Farhadian M, Salemi F, Saati S, Nafisi N (2019) Dental age estimation using the pulp-to-tooth ratio in canines by neural networks. Imaging science in dentistry 49 (1):19–26
Geoffrey A, Manley DPV (2016) Frequency selectivity of the human cochlea: Suppression tuning of spontaneous otoacoustic emissions. Hear Res 336:53–62
Guyon I, Saffari A, Dror G, Cawley G (2010) Model selection: beyond the bayesian–frequentist divide. JMLR 11:61–87
Haraksim R, Galbally J, Beslay L (2019) Fingerprint growth model for mitigating the ageing effect on children’s fingerprints matching. Pattern Recognition 88:614–628
Ilyas M, Othmani A, Nait-Ali A (2017) Human age estimation using auditory system through dynamic frequency sound.IEEE 2nd BioSMART conf: 1-3
Ilyas M, Alice O, Amine NA (2018) Prediction of hearing loss based on auditory perception: a preliminary study inter work on pre intel med. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Ilyas M, Othmani A, Fournier R, Nait-ali A (2019) Auditory perception based Anti-Spoofing system for human age verification. Electro 8(11):1313
Ilyas M, Othmani A, Nait-ali A (2020) Age Estimation Using Sound Stimulation as a Hidden Biometrics Approach. Springer, Singapore, pp 113–125
Jagannath A, Tsuchido T (2003) Validation of a polynomial regression model: the thermal inactivation of Bacillus subtilis spores in milk. Letters in applied microbiology 37(5):399–404
Lanitis A, Draganova C, Christodoulou C (2004) Comparing different classifiers for automatic age estimation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybernetics 34 (1):621–628
Li G, Borj PR, Bergeron L, Bours P (2019) Exploring Keystroke Dynamics and Stylometry Features for Gender Prediction on Chat Data. In: 42nd International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electro Microelectron MIPRO, 1049–1054
Li X, Makihara Y, Xu C, Yagi Y, Ren M (2018) Gait-based human age estimation using age group-dependent manifold learning and regression. Multimedia Tools and Applications 77(21):28333–28354
Li X (2018) Gait-based human age estimation using age group-dependent manifold learning and regression. Multi Tools Appl 77:28333–28354
Liu KH, Tsung JL (2019) Structure-Based Human Facial Age Estimation Framework under a Constrained Condition. IEEE Trans Image Proc 28:5187
Moyse E (2014) Age estimation from faces and voices: a review. Psychologica Belgica 54(3):255–265
Metze F, Ajmera J, Englert R, Bub U, Burkhardt F, Stegmann J, Littel B (2007) Comparison of four approaches to age and gender recognition for telephone applications. IEEE Inter Conf Acous, Spec Sig Proc 4:IV-1089
Makihara Y, Okumura M, Iwama H, Yagi Y (2011). In: Gait-based age estimation using a whole-generation gait database IEEE IJCB 1–6
Meinl A, Tangl S, Pernicka E, Fenes C, Watzek G (2007) On the applicability of secondary dentin formation to radiological age estimation in young adults. J Foren Sci 52:438–441
Nabila M, Mohammed AI, Yousra BJ (2017) Gait-based human age classification using a silhouette model. IET Biometrics 7(2):116–124
Paolis AD, Bikson JT, Nelson de Ru JA, Packe M, Cardoso L (2017) Analytical and numerical modeling of the hearing system: Advances towards the assessment of hearing damage. Hear Res 349:111–128
Paewinsky E, Pfeiffer H, Brinkmann B (2005) Quantification of secondary dentine formation from orthopantomogramme–a contribution to forensic age estimation methods in adults. Inter J Leg Medi 119:27–30
Parson W (2018) Age estimation with DNA: from forensic DNA fingerprinting to forensic epi genomics: a mini-review. Gerontology 64(4):326–332
Ramlee R, Muda AK, Syed ASS (2013) PCA and LDA as dimension reduction for individuality of handwriting in writer verification. In: 13th Inter Conf Intel Sys Des Appl: 104-108
Ramu T, Suthendran K, Arivoli T (2013) Machine learning based soft biometrics for enhanced keystroke recognition system, Multi Tools Appl,1–17
Rossing T (2007) Springer Handbook of Acoustics 1st ed Springer: 747-748
Rothe R, Timofte R, Van Gool L (2018) Deep expectation of real and apparent age from a single image without facial landmarks. International Journal of Computer Vision 126(2-4):144–157
Sakata A, Takemura N, Yagi Y (2019) Gait-based age estimation using multi-stage convolutional neural network. IPSJ Trans Comp Vis Appl 11(1):4
Scheffer T (1999) Error estimation and model selection. Ph.D.Thesis, Technischen Universität Berlin, School of Com Sci
Seber GA, Lee AJ (2012) Linear regression analysis Vol. 329 John Wiley & Sons
Semwal VB, Neha G, Nandi GC (2019) Human gait state prediction using cellular automata and classification using ELM. In: Machine Intelligence and Signal Analysis , Springer, Singapore, 135–145
Semwal VB, Mondal K (2017) Robust and accurate feature selection for humanoid push recovery and classification: deep learning approach . Neural Computing and Applications 28(3):565–574
Semwal VB, Singha J, Sharma PK, Chauhan A, Behera B (2017) An optimized feature selection technique based on incremental feature analysis for biometric gait data classification. Multi tools appl 76(22):24457–24475
Shafran I, Riley M, Mohri M (2003) Voice signatures. IEEE ASRU 03:31–36
Shen W, Guo Y, Wang Y, Zhao K, Wang B, Yuille AL (2018) Deep regression forests for age estimation. In: Inproceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2304–2313
Statnikov A, Tsamardinos I, Dosbayev Y, Aliferis CF (2005) GEMS: A system for automated cancer diagnosis and biomarker discovery from microarray gene expression data. Int J Med Inform 74:491–503
Stockwell CW, Ades HW, Engström H (2017) XCVII Patterns of hair cell damage after intense auditory stimulation. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 78:1144–1168
Stuart R, Howel lP (2011) Signals and Systems for Speech and Hearing. 2nd ed, BRILL: 163
Tingting Y, Junqian W, Lintai W (2019) CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology. Three-stage network for age estimation 4(2):122–126
Tsimperidis G, Katos V, Rostami S (2017) Age detection through keystroke dynamics from user authentication failures. IJDCF 9(1):1–16
Uzun Y, Bicakci K, Uzunay Y (2015) Could We Distinguish Child Users from Adults Using Keystroke Dynamics? arXiv:1511.05672
Wen J, Xu Y, Li Z, Ma Z, Xu Y (2018) Inter-class sparsity based discriminative least square regression. Neural Networks 102:36–47
Williams G (2001) A review of the most commonly used dental age estimation techniques. J Forensic Odontostomatol 19(1):9–17
Zhu H, Zhang Y, Li G, Zhang J, Shan H (2020) Ordinal distribution regression for gait-based age estimation. Science China Information Sciences 63(2):120102
Zwicker E (1961) Subdivision of the audible frequency range into critical bands frequenzgruppen. J Acoust Soc Am 33:248
Zubakov D, Liu F, Kokmeijer I, Choi Y, van Meurs JB, van IJcken WF, Lewin J (2016) Human age estimation from blood using mRNA, DNA methylation, DNA rearrangement, and telomere length. Forensic Science International: Genetics 24:33–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilyas, M., Othmani, A. & Nait-ali, A. Auditory perception based system for age classification and estimation using dynamic frequency sound. Multimed Tools Appl 79, 21603–21626 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08843-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08843-4