Abstract
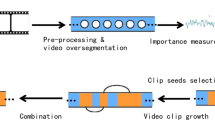
Video Summarization is to generate an important or interesting short video from a long video. It is important to reduce the time required to analyze the same archived video by removing unnecessary video data. This work proposes a novel method to generate dynamic video summarization by fusing the global importance and local importance based on multiple features and image quality. First, videos are split into several suitable video clips. Second, video frames are extracted from each video clip, and the center parts of frames are also extracted. Third, for each frame and the center part, the global importance and the local importance are calculated by using a set of features and image quality. Finally, the global importance and the local importance are fused to select an optimal subset for generating video summarization. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate that the proposed method enables to generate high-quality video summarization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avila S, Lopes A, Luz A, Ara A, Jo A (2011) Vsumm: a mechanism designed to produce static video summaries and a novel evaluation method. Pattern Recogn Lett 32(1):56–68
Bahmanyar R, Oca A, Datcu M (2015) The semantic gap: an exploration of user and computer perspectives in earth observation images. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(10):2046– 2050
Chen X, Zhang Y, Xu H, Yan J, Qin Z (2017) Personalized key frame recommendation. In: International ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, pp 315–324
Cheong LF, Huo H (2001) Shot change detection using scene-based constraint. Multimed Tools Appl 14(2):175–186
Crete F, Nicolas M (2007) The blur effect: perception and estimation with a new no-reference perceptual blur metric. In: Proceedings of SPIE - the international society for optical engineering, vol 12, pp 64920I–64920I–11
Dan BG, Curless B, Salesin D, Seitz SM (2006) Schematic storyboarding for video visualization and editing. ACM Trans Graph 25(3):862–871
Datta R, Joshi D, Li J, Wang JZ (2006) Studying aesthetics in photographic images using a computational approach. In: European conference on computer vision, vol 3953, pp 288–301
Dugad R, Ratakonda K, Ahuja N (1998) Robust video shot change detection. In: IEEE Second workshop on multimedia signal processing, pp 376–381
Ejaz N, Mehmood I, Baik SW (2013) Efficient visual attention based framework for extracting key frames from videos. Signal Process Image Commun 28(1):34–44
Gong Y, Liu X (2000) Video summarization using singular value decomposition. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 157–168
Gygli M, Grabner H, Riemenschneider H, Gool LV (2014) Creating summaries from user videos. European Conference on Computer Vision 8695:505–520
Hou XD, Harel J, Koch C (2012) Image signature: highlighting sparse salient regions. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(1):194
Hu TL, Li ZC, Xing M, Su W, Tang JH (2017) Unsupervised video summaries using multiple features and image quality. In: IEEE third international conference on multimedia big data, pp 117–120
Li ZC, Liu J, Yang Y, Zhou XF, Lu HQ (2014) Clustering-guide sparse structural learning for unsupervised feature selection. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26 (9):2138–2150
Li ZC, Tang JH (2017) Weakly supervised deep matrix factorization for social image understanding. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(1):276–288
Liu Y, Zhou F, Liu W, Torre FDL, Liu Y (2010) Unsupervised summarization of rushes videos. In: International conference on multimedea, pp 751–754
Mahmoud KM, Ghanem NM, Ismail MA (2013) Unsupervised video summarization via dynamic modeling-based hierarchical clustering. In: International conference on machine learning and applications, pp 303–308
Mascelli JV (1998) The five C’s of cinematography: motion picture filming techniques. Silman-James Press, CA
Min W, Bao BK, Xu CS (2014) Multimodal spatio-temporal theme modeling for landmark analysis. IEEE MultiMedia 21(3):20–29
Pritch Y, Rav-Acha A, Gutman A, Peleg S (2007) Webcam synopsis: peeking around the world. In: IEEE International conference on computer vision, pp 1–8
Potapov D, Douze M, Harchaoui Z, Schmid C (2014) Category-specific video summarization. In: European conference on computer vision, vol 8694, pp 540–555
Ravacha A, Pritch Y, Peleg S (2006) Making a long video short: dynamic video synopsis. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 435–441
Rui Y, Gupta A, Acero A (2000) Automatically extracting highlights for tv baseball programs. In: Eighth ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 105–115
Shih CC, Tyan HR, Liao HYM (2001) Shot change detection based on the reynolds transport theorem. In: IEEE Pacific rim conference on multimedia: advances in multimedia information processing, pp 819–824
Sun M, Farhadi A, Seitz S (2014) Ranking domain-specific highlights by analyzing edited videos. European Conference on Computer Vision 8689:787–802
Tamura H, Mori S, Yamawaki T (1978) Textural features corresponding to visual perception. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 8(6):460–473
Wolf W (1996) Key frame selection by motion analysis. In: Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, pp 1228–1231
Zhang HJ, Wu J, Zhong D, Smoliar SW (1997) An integrated system for content-based video retrieval and browsing. Pattern Recogn 30(4):643–658
Zhang L, Xia Y, Mao K, Ma H (2015) An effective video summarization framework toward handheld devices. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(2):1309–1316
Zhao B, Xing EP (2014) Quasi real-time summarization for consumer videos. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2513–2520
Zhu S, Yan J, Liu Y (2009) Improving semantic scene categorization by exploiting audio-visual features. In: International conference on image and graphics, pp 435–440
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the 973 Program (Project No. 2014CB34 7600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61522203 and 61772275) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant BK20140058 and BK20170033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, T., Li, Z. Video summarization via exploring the global and local importance. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 22083–22098 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5479-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5479-y