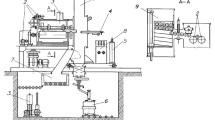
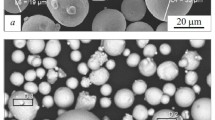
Results of a study of the production of spherical-shape powder from shavings of high-alloy high-temperature steel 13Kh11N2V2MF (ÉI961) are presented. It is shown that the rate of feeding of the powder into the flow of thermal plasma affects the process of spheroidization of the particles. The chemical composition of the powder is compared to that required by the GOST standard.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. K. Reck and T. E. Graedel, “Challenges in metal recycling,” Science, 337(6095), 690 – 695 (2012).
T. E. Graedel, J. Allwood, J.-P. Birat, et al., “What do we know about metal recycling rates?” J. Ind. Ecology, 15(3), 355 – 366 (2011).
E. G. Zolotnikov and V. V. Maksarov, “Recent processes of retreatment and briquetting of metallic shavings in automated productions,” Zapiski Gorn. Inst., 209, 34 – 41 (2014).
S. J. Seo, K. Asakura, and K. Shibata, “Evaluation of susceptibility to surface hot shortness in Cu-containing steels by tensile test,” ISIJ Int., 37(3), 232 – 239 (1997).
W. Z. Misiolek, M. Haase, N. Ben Khalifa, et al., “High quality extrudates from aluminum chips by new billet compaction and deformation routes,” CIRP Annals, 61(1), 239 – 242 (2012).
J. M. Linag, Z. Zhang, M. T. Jia, et al., “The microstructures and tensile mechanical properties of ultrafine grained and coarse grained Al – 7Si – 0.3Mg alloy rods fabricated form machining chips,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 729, 29 – 36 (2018).
Z. Sherafat, M. H. Paydar, and R. Ebrahimi, “Fabrication of Al7075/Al two phase material by recycling Al7075 alloy chips using powder metallurgy route,” J. Alloys Compd., 478(1 – 2), 395 – 399 (2009).
A. Mohr, A. Rottger, M. Windmann, and W. Theisen, “Recycling of metallic chips by electro-discharge sintering,” Materialwissenschaft undWerkstofftechnik, 45(6), 552 – 560 (2014).
F. Yang, S. Raynova, A. Singh, et al., “Producing high-quality titanium alloy by a cost-effective route combining fast heating and hot pressing,” JOM, 70(5), 632 – 637 (2018).
A. I. Rudskoy, A. M. Zolotov, and S. V. Ganin, “Simulation of the process of equal-channel angular pressing of billets from powder compositions based on aluminum and rare-earth metals in capsules,” Tsvet. Met., No. 4, 30 – 35 (2014).
E. W. Lui, S. Palanisamy, M. S. Dargusch, and K. Xia, “Effects of chip conditions on the solid state recycling of Ti – 6Al – 4V machining chips,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 238, 297 – 304 (2016).
J. Umada, T. Mimoto, H. Imai, and K. Kondoh, “Powder forming process from machined titanium chips via heat treatment in hydrogen atmosphere,” Mater. Trans., 58(12), 1 – 6 (2017).
X. Goso and A. Kale “Production of titanium metal powder by HDH process,” in: Light Metals Conf. (2010), pp. 292 – 305.
Z. Z. Fang, R. Chandran, and M. Koopman, New Method of Low Cost Production of Titanium Alloys to Reducing Energy Consumption of Mechanical Systems, Technical Report, United States (2016), 219 p.
N. S. Gamba, I. A. Carbajal-Ramos, M. A. Ulla, et al., “Zirconium alloys produced by recycling zircaloy tunings,” J. Alloys Compd., 578, 553 – 558 (2013).
W. E. Frazier, “Metal additive manufacturing: Areview,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 23(6), 1917 – 1928 (2014).
T. Wohlers, Wohlers Report 2014: Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing State of the Industry. Annual Worldwide Progress Report, Wohlers Associates Inc. (2014), 275 p.
A. Uriondo, M. Esperon-Miguez, and S. Perinpanayagam, “The present and future of additive manufacturing in the aerospace sector: Areview of important aspects, in: Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G,” J. Aerospace Eng., 229(11), 2132 – 2147 (2015).
M. I. Boulos, “The inductively coupled R.F. (radio frequency) plasma,” Pure and Appl. Chem., 57(9), 1321 – 1352 (1985).
S. Samal, “Thermal plasma technology: The prospective future in material processing,” J. Cleaner Prod., 142, 3131 – 3150 (2017).
A. I. Rudskoy, K. N. Volkov, S. Yu. Kondrat’ev, and Yu. A. Sokolov, Physical Processes and Technologies of Fabrication of Metallic Powders from Melt [in Russian], Izd. Polytekh. Univ. (2018), 610 p.
Y.-L. Li and T. Ishigaki, “Spheroidization of titanium carbide powders by induction thermal plasma processes,” J. Am. Ceramic Soc., 84(9), 1929 – 1936 (2001).
N. G. Razumov, A. A. Popovich, and Q. S. Wang, “Thermal plasma spheroidization by mechanical alloying,” Metall. Mater. Int., 24(2), 363 – 370 (2018).
S. Kumar and V. Selvarajan, “Spheroidization of metal and ceramic powders in thermal plasma jet,” Comp. Mater. Sci., 36, 451 – 456 (2006).
S. Sun, Z. Ma, Y. Liu, et al., “Induction plasma spheroidization of ZrB2– SiC powders for plasma-spray coating,” J. Europ. Ceram. Soc., 38(9), 3073 – 3082 (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 11, pp. 23 – 28, November, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razumov, N.G., Popovich, A.A., Grigor’ev, A.V. et al. Morphology of High-Strength Heat-Resistant Steel Powder for Machines for Additive Production from Shavings. Met Sci Heat Treat 60, 710–714 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-019-00344-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-019-00344-y