Abstract
Objective
To compare the mRNA expression of placental iron transporters (TfR-1 and FPN), markers of placental vascularization (VEGF and sFLT1) and marker of structural integrity (LMN-A) in term women with and without iron deficiency anemia.
Materials and methods
A total of 30 pregnant women were enrolled; 15 cases of iron deficiency anemia (Hb 7-10.9 gm/dL) and 15 gestational age matched healthy controls (Hb ≥ 11 gm/dL). Peripheral venous blood was collected for assessment of hemoglobin levels and serum iron profile. Placental tissue was used for assessing the mRNA expression of TfR-1, FPN, VEGF, sFLT-1 and LMN-A via real time PCR.
Results
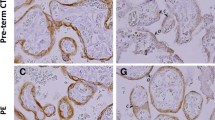
Placental expression of TfR-1, VEGF and LMN-A was increased in pregnant women with anemia compared to healthy pregnant controls. Placental expression of sFLT-1 was decreased in pregnant women with anemia compared to healthy pregnant controls. There was no change in the placental expression of FPN.
Conclusion
The increased expression of TfR-1, VEGF and LMN-A in cases of iron deficiency anemia are most likely to be compensatory in nature to help maintain adequate fetal iron delivery.
What does this study adds to the clinical work
: Compensatory changes in the placenta aimed at buffering transport of iron to the fetus are seen in pregnant women with anemia compared to healthy pregnant controls.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to administrative reasons but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Cao C, Fleming MD (2016) The placenta: the forgotten essential organ of iron transport. Nutr Rev 74(7):421–431
Sangkhae V, Nemeth E (2019) Placental iron transport: the mechanism and regulatory circuits. Free Radic Biol Med 133:254–261
Fisher AL, Nemeth E (2017) Iron homeostasis during pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 106(Suppl 6):1567S–1574S. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.117.155812
Benson CS, Shah A, Frise MC, Frise CJ (2021) Iron deficiency anaemia in pregnancy: a contemporary review. Obstet Med 14(2):67–76. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753495X20932426
WHO (2001) Iron deficiency anemia: assessment, prevention and control. WHO/NHD/01.3, Geneva. World Health Organization, Switzerland
Means RT (2020) Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia: implications and impact in pregnancy, Fetal Development, and early childhood parameters. Nutrients 11(122):447
Georgieff MK (2020) Iron deficiency in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 223(4):516–524
Vanderpuye OA, Kelley LK, Smith CH (1986) Transferrin receptors in the basal plasma membrane of the human placental syncytiotrophoblast. Placenta 7(5):391–403
Nmezi B, Xu J, Fu R, Armiger TJ, Rodriguez-Bey G, Powell JS et al (2019) Concentric organization of A- and B-type lamins predicts their distinct roles in the spatial organization and stability of the nuclear lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(10):4307–4315. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1810070116
Corrales-Agudelo V, Bueno-Sanchez JC, Pena-Arboleda B, Cardona-Ospina A, Lopez-Rojas E (2018) Transferrin Receptor 1 and Ferroportin expression in the Full-Term Human Placenta and its Association with maternal and neonatal Iron status: a pilot study. J Clin Nutr Metab 3:1
Li YQ, Yan H, Bai B (2008) Change in iron transporter expression in human term placenta with different maternal iron status. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 140(1):48–54
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Liao QK (1992) Effect of placental transferrin receptors on iron nutritional state of normal full-term gravidas and their newborns. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. ;72(10):619 – 21, 640
Venkata Surekha M, Singh S, Sarada K, Sailaja G, Balakrishna N, Srinivas M et al (2019) Study on the effect of severity of maternal Iron Deficiency Anemia on regulators of Angiogenesis in Placenta. Fetal Pediatr Pathol 38(5):361–375
Cao C, O’ Brien KO (2013) Pregnancy and iron homeostasis: an update. Nutr Rev 71:35–51
McArdle HJ, Gambling L, Kennedy C (2014) Iron deficiency during pregnancy: the consequences for placental function and fetal outcome. Proc Nutr Soc 73:9–15
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the patients who participated in the study.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA: Concept, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, clinical studies, data acquisition, data analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing. MM Concept, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, clinical studies, data acquisition, data analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript editing and manuscript review. EAA: Concept, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, clinical studies, data acquisition, data analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing. MK: Concept, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, clinical studies, data acquisition, data analysis and manuscript review. BG: Concept, design, definition of intellectual content, clinical studies, clinical studies, data acquisition, data analysis and manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by Institutional Ethics Committee- Human Research (IECHR/2022/54/9-R1).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Author declaration
The manuscript has been read and approved by all the authors, the requirements for authorship as stated earlier in this document have been met, each author believes that the manuscript represents honest work.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, M., Mehndiratta, M., Almeida, E.A. et al. Gene expression of iron transporters, markers of vascularization and structural integrity in placenta of mothers with and without anemia. Mol Biol Rep 51, 652 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09609-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09609-z