Abstract
Background
Bacterial pathogens are the causative agents of some of the most serious disease problems in cultured fish causing mortalities and severe economic losses. This study was conducted to determine the occurrence and characterization of Proteus mirabilis from infected farmed African catfish in Ogun State, Nigeria.
Methodology
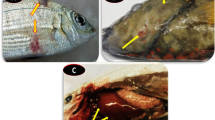
The bacteria were isolated from diseased farmed African catfish (Clarias gariepinus, n=128) with clinical signs of skin haemorrhages, ulceration, and ascites purposively sampled from farms within three senatorial districts namely Ogun East (OE; n=76), Ogun Central (OC; n=30) and Ogun West (OW; n=22) in Ogun State. The isolates were identified based on morphological characteristics, biochemical tests, and 16S rRNA gene characterisation. The 16S rRNA gene sequences were analysed using BLAST, submitted to the NCBI database, and an accession number was generated.
Results
The occurrence of Proteus mirabilis in infected Clarias gariepinus was 13.16%, 25%, and 31.25% in OE, OC, and OW, respectively. A significantly higher incidence was recorded in OW compared to other areas. All the Proteus mirabilis isolates were motile, gram-negative, short rod, non-lactose fermenter bacteria that showed positive catalase reactions, negative oxidase, and positive for methyl-red. The Proteus mirabilis isolates (OP 594726.1) were closely related to isolates from Pakistan, Italy, and India
Conclusions
We conclude that Proteus mirabilis colonises farmed Clarias gariepinus in Ogun State, Nigeria and the identified strain showed an evolutionary relationship with known pathogenic NCBI reference strains from other countries.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Reference
Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (2018) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. FAO, Rome
Granada L, Sousa N, Lopes S, Lemos MFL (2016) Is integrated multitrophic aquaculture the solution to the sectors’ major challenges?—a review. Rev Aquac 208:283–300
Lund EK (2013) Health benefits of seafood; is it just the fatty acids? Food Chem 140:413–420
Gufe C, Canaan Hodobo T, Mbonjani B, Majonga O, Marumure J, Musari S, Machakwa J (2019) Antimicrobial profiling of bacteria isolated from fish sold at an informal market in Mufakose. Int J Microbiol Zimbabwe. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8759636
Qasim DA (2020) Screening the Proteus mirabilis by isolation from tuna fish and compared the occurrence with local fish. Biochem Cell Arch 20(1):481–486
Remilekun AO, Akinola OG, Olubusola OO (2021) Causal factors of mass mortality of hatchery-reared Clarias gariepinus fry during exogenous feeding. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 9(1):235–239
Noor Uddin GM, Larsen MH, Guardabassi L, Dalsgaard A (2013) Bacterial flora and antimicrobial resistance in raw frozen cultured seafood imported to Denmark. J Food Protec 76:490–499
Thongkao K, Sudjaroen Y (2017) Human pathogenic bacteria isolation from Tilapia fishes (Oreochromis niloticus), a possible reservoir for zoonotic transmission. Ann Trop Med Public Health. https://doi.org/10.4103/ATMPH.ATMPH_511_17
Usman MD, Wakawa AM, Musa A, Ahmad KH, Isiaku A (2021) Occurrence of multi-drug resistant enterobacteriaceae in cultured Clarias gariepinus (African catfish) in Kano metropolis, Nigeria. Sokoto J Vet Sci 19(2):106–111
Usikalu MR, Maleka PP, Malik M, Oyeyemi KD (2015) Assessment of geogenic natural radionuclides contents of soil samples collected from Ogun State, Southwestern Nigeria. Int J Radiat Res 13(4):355–361
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergy’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Anifowose OR, Akinniyi OO, Banwo OG, Oladosu GA (2023) Occurrence and characterization of Enterococcus faecalis from infected farmed African catfish in Ogun State. Int J Oceanogr Aquac 7(3):252
Mukhtar AA, Abd Alfadil NA, Mohamed MS, Altayb HN, Elzak SG, Hassan MS (2018) Identification of Proteus mirabilis on banknotes using 16s rRNA gene in Khartoum State. Sud J Med Sc 13(3):175–186
Lee PY, Costumbrado J, Hsu C et al (2012) Agarose gel electrophoresis for the separation of DNA fragments. J Vis Exp 62:1–5
Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y, Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S, Madden TL (2008) NCBI BLAST a better web interface. Nucleic Acids res 36(suppl2):W5–W9
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinform 23(21):2947–2948
Wamala SP, Mugimba KK, Mutoloki S, Evensen Ø, Mdegela R, Byarugaba DK, Sørum H (2018) Occurrence and antibiotic susceptibility of fish bacteria isolated from Oreochromis niloticus (Nile tilapia) and Clarias gariepinus (African catfish) in Uganda. Fish Aquat Sci 21(1):1–10
Al-Bassam WW, Al-Kazaz AK (2013) The isolation and characterization of Proteus mirabilis from different clinical samples. J Biotechnol 7(2):24–30
Schmidt TM, Delong EF, Pace NR (1991) Analysis of a marine picoplankton community by 16S rRNA gene cloning and sequencing. J Bacteriol 173(14):4371–4378
Das A (2021) Molecular identification and pathogenecity study of the Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from fishes of West Bengal (Doctoral dissertation, Vidyasagar University, Midnapore.
Gopi M, Kumar TT, Prakash S (2016) Opportunistic pathogen Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from Maldive’s clown fish amphiprion nigripes with hemorrhages at Agatti Island, Lakshadweep archipelago. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 4:464–467
Bera AK, Das BK, Mohanty D, Chakraborty N, Dey S, Malick RC, Sarkar UK (2022) Multiple etiological factors led septicemic disease with mass mortality of fishes in freshwater reservoir of Odisha, India. Aquaculture 548:737696
Fournier PE, Raoult D (2011) Prospects for the future using genomics and proteomics in clinical microbiology. Annu Rev Microbiol 65:169–188
Clarridge JE (2004) Impact of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis for identification of bacteria on clinical microbiology and infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev 17(4):840–862
Acknowledgements
We want to acknowledge Miss Nike Dada for her assistance during Bioinformatics.
Funding
This study was completely funded by the personal funds of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OR and GA Conceptualized the study, OR, GA, and OO generated data and carried out fieldwork, OR analyzed data and made the manuscript draft, GA and OO edited the manuscript, OR, GA, and OO approved the final manuscript.OR and GA Conceptualized the study, OR, GA, and OO generated data and carried out fieldwork, OR analyzed data and made the manuscript draft, GA and OO edited the manuscript, OR, GA, and OO approved the final manuscript.OR and GA Conceptualized the study, OR, GA, and OO generated data and carried out fieldwork, OR analyzed data and made the manuscript draft, GA and OO edited the manuscript, OR, GA, and OO approved the final manuscript.OR and GA Conceptualized the study, OR, GA, and OO generated data and carried out fieldwork, OR analyzed data and made the manuscript draft, GA and OO edited the manuscript, OR, GA, and OO approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was received from the University of Ibadan, Animal Care and Use Research Ethics Committee (UI-ACUREC) with the assigned number UI-ACUREC/056–0622/9.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Anifowose, O.R., Oladosu, G.A. & Omotosho, O.O. Occurrence and characterization of Proteus mirabilis from infected farmed African catfish in Ogun State, Nigeria. Mol Biol Rep 51, 446 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08973-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08973-6