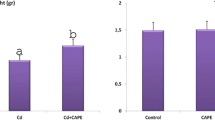
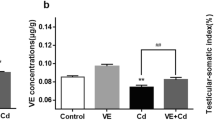
Abstract
Background
Cadmium (Cd) is a strong toxic agent and causes serious damage to testicular tissues. Chrysin (CHR) is a natural flavonoid with many effective properties, especially antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties. The current study describes new evidence for the ameliorative effects of CHR on oxidative stress, apoptosis, autophagy and inflammation pathways in Cd-induced testicular tissue toxicity.
Methods
Thirty-five male Wistar rats were divided into five groups, control, Cd, CHR, Cd + CHR25, and Cd + CHR50. Cd was administered alone at a dose of 25 mg/kg body weight or in combination with CHR 25 mg/kg and CHR 50 mg/kg for 7 days. Cd and CHR were administered orally. Biochemical, molecular, and histological methods were used to investigate inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and oxidant pathways in testicular tissue.
Results
Cd increased lipid peroxidation, JAK-2/STAT-3 levels, inflammation-related NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, COX-2, and iNOS levels, AKT-2, FOXO1, Bax, Apaf-1 and Caspase-3 levels, autophagic Beclin-1, LC3A and LC3B. The Cd also caused a decrease in the activities of antioxidant enzymes and GSH levels, antiapoptotic Bcl-2 levels. CHR, on the other hand, had the opposite effect of all these Cd-induced changes.
Conclusions
Overall, the data of this study indicate that testicular damage associated with Cd toxicity could be ameliorated by CHR administration.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Otamere HO, Adisa WA (2023) Oxidative stress in testis of rats exposed to cadmium. Afr J Biomedical Res 26(1):97–101
Şimşek H, Akaras N, Gür C, Küçükler S, Kandemir FM (2023) Beneficial effects of chrysin on cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: modulating the levels of Nrf2/HO-1, RAGE/NLRP3, and Caspase-3/Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathways. Gene 875:147502
Marini HR, Micali A, Squadrito G, Puzzolo D, Freni J, Antonuccio P, Minutoli L (2022) Nutraceuticals: a new challenge against cadmium-induced testicular injury. Nutrients 14(3):663
Onuoha SC, Ezim OE, Chisom NE, Chukwuebuka CB, Abarikwu SO (2023) Combined protective effects of quercetin, rutin, and gallic acid against cadmium-induced testicular damages in young-adult rats. Andrologia. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/9787664
Liu H, Wang R, OuYang H, Wang Y, Wu J, Li M…, Ji Y (2023) Cadmium induced mouse spermatogonia apoptosis via mitochondrial calcium overload mediated by IP3R-MCU signal pathway. Toxicology 486:153448
Zhang C, Huang Y, Talukder M, Ge J, Lv MW, Bi SS, Li JL (2020) Selenium sources differ in their potential to alleviate the cadmium-induced testicular dysfunction. Environ Pollut 267:115610
Bhardwaj JK, Panchal H, Saraf P (2021) Cadmium as a testicular toxicant: a review. J Appl Toxicol 41(1):105–117
Mouro VG, Martins AL, Silva J, Menezes TP, Gomes ML, Oliveira JA, Matta SL (2019) Subacute testicular toxicity to cadmium exposure intraperitoneally and orally. Oxidat Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3429635
Xiong L, Zhou B, Young JL, Wintergerst K, Cai L (2022) Exposure to low-dose cadmium induces testicular ferroptosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 234:113373
El-Tabaa EFM, Rabah H, Basha E, Eid A, Tahoon D, Elkholy R, Khattab H (2023) Silent information regulator 1 mediates quercetin protective effect on cadmium-induced testicular damage in adult male rats. Bull Egypt Soc Physiol Sci 43:47–63
Kassab RB, Lokman MS, Daabo HM, Gaber DA, Habotta OA, Hafez MM, Fouda MS (2020) Ferulic acid influences Nrf2 activation to restore testicular tissue from cadmium-induced oxidative challenge, inflammation, and apoptosis in rats. J Food Biochem 44(12):e13505
Varışlı B, Caglayan C, Kandemir FM, Gür C, Ayna A, Genç A, Taysı S (2023) Chrysin mitigates diclofenac-induced hepatotoxicity by modulating oxidative stress, apoptosis, autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats. Mol Biol Rep 50(1):433–442
Tekeli MY, Eraslan G, Bayram L, Aslan C, Çalımlı S (2023) The protective effects of baicalin and chrysin against emamectin benzoate-induced toxicity in Wistar albino rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:53997
El-Marasy SA, AbouSamra MM, Moustafa PE, Mabrok HB, Ahmed-Farid OA, Galal AF, Farouk H (2023) Chrysin loaded nanovesicles ameliorated diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Role of NGF/AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Chemico-Biol Interact 375:1104
Tew WY, Tan CS, Yan CS, Loh HW, Wen X, Wei X, Yam MF (2023) Evaluation of vasodilatory effect and antihypertensive effect of chrysin through in vitro and sub-chronic in vivo study. Biomed Pharmacother 157:114020
Salama A, Elgohary R, Kassem AA, Asfour MH (2023) Chrysin–phospholipid complex-based solid dispersion for improved anti-aging and neuroprotective effects in mice. Pharm Dev Technol 28:109
Kucukler S, Benzer F, Yildirim S, Gur C, Kandemir FM, Bengu AS, Dortbudak MB (2021) Protective effects of chrysin against oxidative stress and inflammation induced by lead acetate in rat kidneys: a biochemical and histopathological approach. Biol Trace Element Res 199(4):1501–1514
Kandemir FM, Caglayan C, Darendelioğlu E, Küçükler S, İzol E, Kandemir Ö (2021) Modulatory effects of carvacrol against cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity by molecular targeting regulation. Life Sci 277:119610
Ileriturk M, Benzer F, Aksu EH, Yildirim S, Kandemir FM, Dogan T, Genc A (2021) Chrysin protects against testicular toxicity caused by lead acetate in rats with its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic properties. J Food Biochem 45(2):e13593
Placer ZA, Cushman LL, Johnson BC (1966) Estimation of product of lipid peroxidation (malonyl dialdehyde) in biochemical systems. Anal Biochem 16(2):359–364
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Lawrence RA, Burk RF (1976) Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 71(4):952–958
Sun YI, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34(3):497–500
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic press, pp 673–684
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Kandemir FM, Ileriturk M, Gur C (2022) Rutin protects rat liver and kidney from sodium valproate-induce damage by attenuating oxidative stress, ER stress, inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy. Mol Biol Rep 49:6063
Yesildag K, Gur C, Ileriturk M, Kandemir FM (2022) Evaluation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative DNA damage and metalloproteinases in the lungs of rats treated with cadmium and carvacrol. Mol Biol Rep 49:1–11
Aksu EH, Özkaraca M, Kandemir FM, Ömür AD, Eldutar E, Küçükler S, Çomaklı S (2016) Mitigation of paracetamol-induced reproductive damage by chrysin in male rats via reducing oxidative stress. Andrologia 48(10):1145–1154
Küçükler S, Çomaklı S, Özdemir S, Çağlayan C, Kandemir FM (2021) Hesperidin protects against the chlorpyrifos-induced chronic hepato‐renal toxicity in rats associated with oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and up‐regulation of PARP‐1/VEGF. Environ Toxicol 36(8):1600–1617
Gur C, Kandemir O, Kandemir FM (2022) Investigation of the effects of hesperidin administration on abamectin-induced testicular toxicity in rats through oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and JAK2/STAT3 pathways. Environ Toxicol 37(3):401–412
Yıldız MO, Çelik H, Caglayan C, Kandemir FM, Gür C, Bayav İ, Kandemir Ö (2022) Neuromodulatory effects of hesperidin against sodium fluoride-induced neurotoxicity in rats: Involvement of neuroinflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis and autophagy. Neurotoxicology 90:197–204
Akcılar R, Akcılar A, Koçak C, Koçak FE, Bayat Z, Şimşek H, Savran B (2015) Effects of Ukrain on intestinal apoptosis caused by ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(12):22158
Mantawy EM, El-Bakly WM, Esmat A, Badr AM, El-Demerdash E (2014) Chrysin alleviates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol 728:107–118
Semis HS, Kandemir FM, Kaynar O, Dogan T, Arikan SM (2021) The protective effects of hesperidin against paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats. Life Sci 287:120104
Ekinci-Akdemir FN, Bingöl Ç, Yıldırım S, Kandemir FM, Küçükler S, Sağlam YS (2020) The investigation of the effect of fraxin on hepatotoxicity induced by cisplatin in rats. Iran J basic Med Sci 23(11):1382–1387. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2020.38773.9200
Kocak C, Kocak FE, Akcilar R, Isiklar OO, Kocak H, Bayat Z, Altuntas I (2016) Molecular and biochemical evidence on the protective effects of embelin and carnosic acid in isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial injury in rats. Life Sci 147:15–23
Akdemir FNE, Yıldırım S, Kandemir FM (2022) The possible beneficial impacts of evodiamine on hepatotoxicity induced by cisplatin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(59):89522–89529
Şimşek H, Demiryürek Ş, Demir T, Atabay HD, Çeribasi AO, Bayraktar R, Kaplan DS, Öztuzcu S, Cengiz B (2016) Assessment of expressions of Bcl-XL, b-FGF, Bmp-2, Caspase-3, PDGFR-α, Smad1 and TGF-β1 genes in a rat model of lung ischemia/reperfusion. Iran J basic Med Sci 19(2):209–214
Caglayan C, Kandemir FM, Darendelioğlu E, Yıldırım S, Kucukler S, Dortbudak MB (2019) Rutin ameliorates mercuric chloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats via interfering with oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 56:60–68
Akaras N, Gur C, Kucukler S, Kandemir FM (2023) Zingerone reduces sodium arsenite-induced nephrotoxicity by regulating oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and histopathological changes. Chemico-Biol Interact 374:110410
Yardim A, Kandemir FM, Ozdemir S, Kucukler S, Comakli S, Gur C, Celik H (2020) Quercetin provides protection against the peripheral nerve damage caused by vincristine in rats by suppressing caspase 3, NF-κB, ATF-6 pathways and activating Nrf2, akt pathways. Neurotoxicology 81:137–146
Kandemir FM, Yıldırım S, Kucukler S, Caglayan C, Darendelioğlu E, Dortbudak MB (2020) Protective effects of morin against acrylamide-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity: a multi-biomarker approach. Food Chem Toxicol 138:111190
Brand Y, Levano S, Radojevic V, Naldi AM, Setz C, Ryan AF, Bodmer D (2015) All Akt isoforms (Akt1, Akt2, Akt3) are involved in normal hearing, but only Akt2 and Akt3 are involved in auditory hair cell survival in the mammalian inner ear. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0121599
Green BD, Jabbour AM, Sandow JJ, Riffkin CD, Masouras D, Daunt CP, Ekert PG (2013) Akt1 is the principal Akt isoform regulating apoptosis in limiting cytokine concentrations. Cell Death Differ 20(10):1341–1349
Kızıl HE, Caglayan C, Darendelioğlu E, Ayna A, Gür C, Kandemir FM, Küçükler S (2023) Morin ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity via targeting Nrf2/HO-1 and Bax/Bcl2/Caspase-3 signaling pathways. Mol Biol Rep 50:3479
Varışlı B, Darendelioğlu E, Caglayan C, Kandemir FM, Ayna A, Genç A, Kandemir Ö (2022) Hesperidin attenuates oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and cardiac dysfunction in sodium fluoride-Induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol 22(8):727–735
Kucukler S, Caglayan C, Darendelioğlu E, Kandemir FM (2020) Morin attenuates acrylamide-induced testicular toxicity in rats by regulating the NF-κB, Bax/Bcl-2 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Life Sci 261:118301
Nassar M, Samaha H, Ghabriel M, Yehia M, Taha H, Salem S, El-Naggar S (2017) LC3A silencing hinders aggresome vimentin cage clearance in primary choroid plexus carcinoma. Sci Rep 7(1):8022
Li JL, Gao R, Li S, Wang JT, Tang ZX, Xu SW (2010) Testicular toxicity induced by dietary cadmium in cocks and ameliorative effect by selenium. Biometals 23:695–705
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by SÇT, SK, CG, SA, and FMK. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SÇT and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Sibel Çiğdem Tuncer, Sefa Küçükler, Cihan Gür, Serpil Aygörmez, Fatih Mehmet Kandemir declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Ethics committee approval was received for this study from the ethics committee of Necmettin Erbakan University KONUDAM Experimental Medicine Research and Study Center’s (No: 2022/65, Date: 30.12.2022). This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
The authors gave their explicit consent to publish the manuscript. Sibel Çiğdem Tuncer is free to contact any of the people involved in the research to seek further clarification and information.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tuncer, S.Ç., Küçükler, S., Gür, C. et al. Effects of chrysin in cadmium-induced testicular toxicity in the rat; role of multi-pathway regulation. Mol Biol Rep 50, 8305–8318 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08715-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08715-8