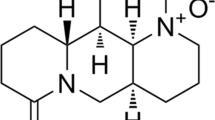
Abstract
Background
Intestinal barrier dysfunction is a serious complication associated with acute pancreatitis (AP). Angiotensin (Ang)-(1–7) plays a protective role in the intestinal barrier, but the underlying mechanism remains clear. This study investigated the impact of Ang-(1–7) on AP-induced intestinal dysfunction and its involvement in the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
Methods and results
We studied caerulein- and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced AP in mice and an epithelial cell line (IEC-6) from the small intestinal crypt of rats. Ang-(1–7) was administered orally or via the tail vein. IEC-6 cells were divided into five groups: control; LPS; LPS + Ang-(1–7); LPS + Ang-(1–7) + ML385 (an Nrf2 inhibitor); and LPS + ML385. Pancreatic and intestinal histopathology scores were analyzed using the Schmidt and Chiu scores. The expression of intestinal barrier-associated proteins and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway constituents was assessed by RT-PCR and western blotting. The peroxide and antioxidant activities in the IEC-6 cells were measured. Compared to those in AP mice, Ang-(1–7) diminished the intestinal levels of proinflammatory factors (interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor α) and serum levels of intestine permeability (d-lactate). Ang-(1–7) increased the expression of barrier-associated proteins (aquaporin-1, claudin-1, and occludin) compared to those in the AP and LPS group. Moreover, Ang-(1–7) promoted the Keap/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which resulted in significantly reduced malondialdehyde and increased superoxide dismutase levels.. However, ML385 abolished the effects of Ang-(1–7) on barrier-associated proteins and reversed the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
Conclusions
Ang-(1–7) reduces AP-induced intestinal inflammation and oxidative injuries by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are not openly available and are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Petrov MS, Yadav D (2019) Global epidemiology and holistic prevention of pancreatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16(3):175–184. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-018-0087-5
Boxhoorn L, Voermans RP, Bouwense SA et al (2020) Acute pancreatitis. Lancet 396(10252):726–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31310-6
Wei B, Wu Q, Yang X, Lai C, Su Z (2022) Liang Z (2022) Effect of TRAF6 in acute pancreatitis-induced intestinal barrier injury via TLR4/NF-κB signal pathway. Tissue Cell. 76:101792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tice.2022.101792
Agarwala R, Rana SS, Sharma R et al (2020) Gastrointestinal failure is a predictor of poor outcome in patients with acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 65(8):2419–2426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05952-5
Scaldaferri F, Pizzoferrato M, Gerardi V et al (2012) The gut barrier: new acquisitions and therapeutic approaches. J Clin Gastroenterol 46(Suppl):S12–S17. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e31826ae849
Liu J, Huang L, Luo M et al (2019) Bacterial translocation in acute pancreatitis. Crit Rev Microbiol 45(5–6):539–547. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2019.1621795
Karnik SS, Singh KD, Tirupula K, Unal H (2017) Significance of angiotensin 1–7 coupling with MAS1 receptor and other GPCRs to the renin-angiotensin system: IUPHAR review 22. Br J Pharmacol 174(9):737–753. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13742
Ma YP, Yang Y, Jiang SM et al (2020) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers favorably affect renal angiotensin II and MAS receptor expression in patients with diabetic nephropathy. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 21(2):1470320320919607. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470320320919607
Li S, Zhao W, Tao Y, Liu C (2020) Fugan Wan alleviates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting ACE/Ang II/AT-1R signaling pathway and enhancing ACE2/Ang 1–7/Mas signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis rat models. Am J Transl Res 12(2):592–601
Souza LKM, Nogueira KM, Araújo TSL et al (2021) Anti-diarrheal therapeutic potential of diminazene aceturate stimulation of the ACE II/Ang-(1–7)/Mas receptor axis in mice: a trial study. Biochem Pharmacol 186:114500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114500
Khajah MA, Fateel MM, Ananthalakshmi KV, Luqmani YA (2017) Anti-inflammatory action of angiotensin 1–7 in experimental colitis may be mediated through modulation of serum cytokines/chemokines and immune cell functions. Dev Comp Immunol 74:200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2017.05.005
Wang J, Liu R, Qi H et al (2015) The ACE2-angiotensin-(1–7)-Mas axis protects against pancreatic cell damage in cell culture. Pancreas 44(2):266–272. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000000247
Yu X, Cui L, Hou F et al (2018) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-angiotensin (1–7)-Mas axis prevents pancreatic acinar cell inflammatory response via inhibition of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor-κB pathway. Int J Mol Med 41(1):409–420. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.3252
Wang X, Liu M, Hu W et al (2020) Angiotensin-(1–7) treatment restores pancreatic microcirculation profiles: a new story in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 49(7):960–966. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000001609
Zhou X, Wang W, Wang C et al (2019) DPP4 inhibitor attenuates severe acute pancreatitis-associated intestinal inflammation via Nrf2 signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:6181754. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6181754
Qiu S, Li P, Zhao H, Li X (2020) Maresin 1 alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis by regulating Nrf2 and TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 78:106018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106018
Romero A, San Hipólito-Luengo Á, Villalobos LA et al (2019) The angiotensin-(1–7)/Mas receptor axis protects from endothelial cell senescence via klotho and Nrf2 activation. Aging Cell 18(3):e12913. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12913
Kamel EO, Gad-Elrab WM, Ahmed MA, Mohammedsaleh ZM, Hassanein EHM, Ali FEM (2022) Candesartan protects against cadmium-induced hepatorenal syndrome by affecting Nrf2, NF-κB, Bax/Bcl-2/Cyt-C, and Ang II/Ang 1–7 signals. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03286-4.10.1007/s12011-022-03286-4
Schmidt J, Lewandrowsi K, Warshaw AL et al (1992) Morphometric characteristics and homogeneity of a new model of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Int J Pancreatol 12(1):41–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02927069
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R et al (1970) Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. I. A morphological, hemodynamic, and metabolic reappraisal. Arch Surg 101(4):478–483. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1970.01340280030009
Barbieri JS, Riggio JM, Jaffe R (2016) Amylase testing for abdominal pain and suspected acute pancreatitis. J Hosp Med 11(5):366–368. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2544
Wu LM, Sankaran SJ, Plank LD, Windsor JA, Petrov MS (2014) Meta analysis of gut barrier dysfunction in patients with acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg 101(13):1644–1656. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.9665
Khajah MA, Fateel MM, Ananthalakshmi KV et al (2016) Anti-inflammatory action of angiotensin 1–7 in experimental colitis. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0150861. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150861
Jiang Y, Song J, Xu Y et al (2021) Piezo1 regulates intestinal epithelial function by affecting the tight junction protein claudin-1 via the ROCK pathway. Life Sci 275:119254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119254
Yang X, Wan J, Li N et al (2022) MiR155 disrupts the intestinal barrier by inducing intestinal inflammation and altering the intestinal microecology in severe acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 67(6):2209–2219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-07022-1
Li X, Wang X, Xie J, Liang B, Wu J (2019) Suppression of Angiotensin-(1–7) on the disruption of blood-brain barrier in rat of brain glioma. Pathol Oncol Res 25(1):429–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-018-0471-z
Mi X, Cao Y, Li Y et al (2021) The Non-peptide Angiotensin-(1–7) mimic AVE 0991 attenuates delayed neurocognitive recovery after laparotomy by reducing neuroinflammation and restoring blood-brain barrier integrity in aged rats. Front Aging Neurosci 13:624387. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.624387
Kang X, Lu XG, Zhan LB et al (2017) Dai-Huang-Fu-Zi-Tang alleviates pulmonary and intestinal injury with severe acute pancreatitis via regulating aquaporins in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 17(1):288. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-017-1789-x
Joyner J, Neves LA, Stovall K, Ferrario CM, Brosnihan KB (2008) Angiotensin-(1–7) serves as an aquaretic by increasing water intake and diuresis in association with downregulation of aquaporin-1 during pregnancy in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294(3):R1073–R1080. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00572.2007
Reimegård J, Tarbier M, Danielsson M et al (2021) A combined approach for single-cell mRNA and intracellular protein expression analysis. Commun Biol 4(1):624. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02142-w
Fabregat G, García-de-la-Asunción J, Sarriá B, et al (2014) Increased expression of AQP 1 and AQP 5 in rat lungs ventilated with low tidal volume is time dependent. PLoS ONE 9(12):e114247. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114247
Ahn C, Yang H, Lee D, An BS, Jeung EB (2015) Placental claudin expression and its regulation by endogenous sex steroid hormones. Steroids 100:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2015.05.001
Aghazadeh-Habashi A, Khajehpour S (2021) Improved pharmacokinetics and bone tissue accumulation of Angiotensin-(1–7) peptide through bisphosphonate conjugation. Amino Acids 53(5):653–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02972-2
Ma X, Pang Z, Zhou J et al (2018) Acetylation and amination protect angiotensin 1–7 from physiological hydrolyzation and therefore increases its antitumor effects on lung cancer. Mol Pharm 15(6):2338–2347. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00181
Wang Z, Huang W, Ren F et al (2021) Characteristics of Ang-(1–7)/Mas-mediated amelioration of joint inflammation and cardiac complications in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Front Immunol 12:655614. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.655614
Silva de Moura S, de Assis Dias Martins-Júnior F, Cruz de Oliveira E, et al (2023) Effects of oral HPβCD-angiotensin-(1–7) supplementation on recreational mountain bike athletes: a crossover study. Phys Sportsmed https://doi.org/10.1080/00913847.2023.2175587
Totou NL, de Moura SS, Martins Júnior FAD et al (2021) Oral administration of angiotensin-(1–7) decreases muscle damage and prevents the fibrosis in rats after eccentric exercise. Exp Physiol 106(8):1710–1719. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP089308
Vona R, Pallotta L, Cappelletti M, Severi C, Matarrese P (2021) The impact of oxidative stress in human pathology: focus on gastrointestinal disorders. Antioxidants 10(2):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10020201
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RRG conducted the study and was a main contributor in the drafting the manuscript. RRG, TYC, and XRW were in charge of AP modeling. RRG and TYC performed the molecular biology experiments and analyzed the data. RXL and CHY designed the experiments, contributed to key materials, and modified the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript modification and editing, reviewed, and authorized the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal experimental procedures complied with the regulations of the Capital Medical University Animal Experiment Committee ethics review board (Approval No: AEEI-2022-125).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, R., Cui, T., Guo, Y. et al. Angiotensin-(1–7) ameliorates intestinal barrier dysfunction by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in acute pancreatitis. Mol Biol Rep 50, 5991–6003 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08544-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08544-9