Abstract
Background
Replication of the influenza A viruses occurs in the cells through the viral RdRP consisting of PB1, PB2, and PA. Several cellular proteins are involved in these processes. This study aims to reveal the interaction between human SNX2 protein and the PA protein and the effects of the SNX2 on the virus replication.
Results
To identify potential host interacting proteins to the PA, yeast two-hybrid assay was carried out with HEK293 cell cDNA library and the PA as a bait. We focused on SNX2 protein, which interacts with the PA in the yeast cells. By using the co-immunoprecipitation assays, it has been demonstrated that the amino-terminal part of the PA was important for binding to the SNX2. Immunolocalization of the proteins in HeLa cells supported this interaction. Knockdown of the SNX2 with siRNA in the cells resulted in a significant increase in both viral transcripts and virus growth. However, the increase of SNX2 in transfected cells didn’t cause a significant change in the viral RdRP activity in minireplicon assay. This may suggest that the negative effect of SNX2 on the virus replication could be saturated with its authentic intra-cellular amount.
Conclusions
This study revealed that the SNX2 and PA protein interact with each other in both yeast and HEK293 cells, and the SNX2 has a negative regulatory function on the virus replication. However, more knowledge is required to elucidate the action mechanism of the SNX2 on the influenza A virus replication at the molecular level.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Influenza A viruses are classified in the Orthomyxoviridae family having a negative sense RNA genome. These viruses infect a wide range of avian and mammalian species including human, swine, and domestic poultry, and mostly the wild waterfowl are the reservoir of the viruses [1]. The segmented genome structure of the influenza viruses and their ability to infect different hosts resulted in reassortment and the emergence of new virus types during co-infections [2]. The reassortment of the viral genome is one of the most significant factors in the emergence of pandemic influenza A viruses that easily spread in the absence of pre-existing immunity in humans [3]. The viral genome consists of eight single-stranded RNA molecules. At least 10 virus-specific proteins are encoded through this segmented genome. The viral RNA segments 1, 3, 4 and 5 encode a single polypeptide; the PB2, PA, HA, and NP, respectively. The M1 (matrix) and the M2 (ion channel) proteins are expressed on viral segment 7 by RNA splicing [4]. Similarly, the interferon-antagonist NS1 protein, and the NS2/NEP, which have a role in the viral RNP export from the host cell nucleus, were expressed on segment 8 [5]. Recently, many non-structural proteins have been discovered in influenza A virus infected cells. They are generated with the splicing, frame shift or truncation of the coding region of the structural proteins. These non-structural proteins are PB1 frame 2 (PB1-F2), PB1-N40 [6], PA-X [7], PA-N155, PA-N182 [8], M42 [9] and NS3 [10].
All viral proteins including the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) enzyme composed of PB2, PB1, and PA subunits interact with the host cell membranes or some cellular protein factors at different stages of viral replication [11]. Several host proteins, including nuclear pore complex proteins [12], G proteins [13], cytoskeletal elements [14], caspases [15], heat shock proteins [16] and some protein kinases [17, 18] interact with the viral replication processes. Additionally, the proteins of the vacuolar protein sorting pathway have been shown to interact with the matrix proteins of several viruses including Tsg101, other ESCRT components, and proteins containing WW domains (such as Nedd4 family proteins) [19, 20]. In infected cells, many cellular proteins participate in the transport and assembly of the vRNPs that make up the genome of influenza A viruses and viral budding stages. It has been suggested that the components of cytoskeleton, particularly microfilaments, are involved in the maturation of influenza virus, including bud formation. Actin and actin-binding protein ezrin-radixin moesin (ERM) have also been found in influenza virus particles [21]. The existence of actin and the proteins associated with it in virions suggests certain functions of the actin filament in assembly of the viruses.
Although there are very few SNX proteins reported to be associated with influenza A viruses [22], it has been reported that several proteins belonging to the sorting nexin (SNX) protein family have interacted with some other virus replications. The SNX proteins, including the SNX2, are a large family of proteins in the cell cytoplasm that have the potential to interact with membranes through their PX (phox-homology) domains or protein-protein interactions in the membrane through protein complexes [23]. Some of the proteins in this family have been shown to contribute to protein traffic. These proteins are evolutionarily well conserved from yeast to mammals, and consist of a protein family involved in cargo recognition and sorting during retrograde transport from the endosome to the Golgi complex [24, 25].
It has been reported that SNX17, a member of the Sorting Nexin family, interacts with the human papillomavirus [26] and the human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus (HTLV-1) [27]. The SNX3 and SNX5 proteins of the SNX family interact with the proteins of the vaccinia virus (VACV) and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) [28, 29].
In this study, the interaction between the human SNX2 protein and the influenza A/duck/Pennsylvania-H5N2 (DkPen) PA protein was demonstrated by the yeast two-hybrid assay. The relationship of human SNX2 protein with viral PA protein in human cells and its effects on the virus replication were investigated. It was demonstrated that the amino-terminal part of the PA protein (PAΔC) was particularly important for binding to the SNX2 protein. The human SNX2 protein was found to negatively affect avian influenza A/DkPen virus replication. These results suggested that the SNX2 protein may have a role in avian influenza A/DkPen virus pathogenesis.
Materials and methods
Cells and viruses
Human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) and HeLa cells were employed in experiment related to transient transfection and/or in cases viral infections. They were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (Gibco, USA), 100 µg/ml streptomycin, 100 IU/ml penicillin, 2 mM glutamine, and 1.5 mg/ml Na2HCO3 at 37 °C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. Avian influenza virus A/duck/Pennsylvania/10,218/84/H5N2 (DkPen) were propagated in specific pathogen-free chicken embryos. The quantity of viruses was defined by employing a standard plaque formation assay [30].
RNA extraction and preparation of the first-strand cDNA
In order to PCR amplification of SNX2 cDNA and/or quantitation of transcripts with a real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), total RNA was extracted from the cells with the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Germany). The cDNAs were synthesized from the total RNA using a reverse transcriptase (ReverTra Ace, Toyobo Co. Ltd., Japan) and oligo dT as a primer for 60 min at 45 °C.
Construction of plasmid vectors
For the construction of Sorting Nexin 2 (SNX2) expression plasmids, the full length of the SNX2 gene consisting of 1560 bp was amplified by PCR with HEK293 cDNA and the phosphorylated specific primers, 5′-ATCATGGCGGCCGAGAGGGAA-3′ and 5′-ATCTAGGCAATGGCTTTGGCTTC-3′. PCR was performed with a high fidelity DNA polymerase (KOD plus, Toyobo Co., Ltd., Japan). The PCR product was purified with an agarose gel extraction kit (QiaexII, Qiagen, Germany). In order to create the pCHA-SNX2 plasmid encoding the HA-tagged SNX2 protein (H.SNX2), the SNX2 cDNA was cloned into a pCHA [31] plasmid digested with EcoRV (New England Biolabs, UK) and dephosphorylated with shrimp alkaline phosphatase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). The plasmids encoding deleted SNX2 proteins were constructed with the inverse PCR method by using the pCHA-SNX2 plasmid as a template. For SNX2ΔN (exons 1–3 deleted), 5′-GATATCACGCGTGGTGACC-3′ and 5′-ATGATTGAAGAAGAAGCAAATGG-3′ were used; for SNX2ΔM (exons 4–8 deleted), 5′-CTCTTCCCTGGATCTATCAAAG-3′ and 5′-CTGCCTAGAGCAGTTAATACAC-3′ were used; for SNX2ΔC (exons 9–15 deleted), 5′-TAGATATCTTAAGTGACTGAATTC-3′ and 5′-CTCTGAACTTTCCAAGAACTG-3′ phosphorylated primer pairs were used. The PCR products were purified and self-ligated.
For construction of the bait plasmid coding influenza A/DkPen PA protein (pGBD-PA), the DNA fragment was amplified with PCR by using virus-infected cell cDNA as a template and the phosphorylated specific primers, 5′-CGGAGGATCTGGAATGGAAGACTTTGTGCGACAATG-3′ and 5′-CTAGTTCTTTGTCTTTGGGATCTTC-3′. The PCR amplified gene was ligated with the pGBD-C1 [32] plasmid DNA digested with EcoRI and blunted with Klenow enzyme. For the construction of the pACT2-SNX2 yeast two-hybrid plasmid, the PCR amplified full-size SNX2 cDNA was ligated with pACT2 (Clontech, # 638,822) plasmid linearized with BglII and treated with Klenow enzyme. The nucleotide sequences of all plasmids were verified by DNA sequencing.
The plasmids used for transient expression of the viral RNA polymerase subunits in mammalian cells have been described previously [33, 34].
Yeast two-hybrid screening
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain PJ69-4 A was grown in 5 ml YPAD media at 30 °C in a shaking incubator at a speed of 200 rpm overnight. The fresh culture was transformed with pGBD-PA bait plasmid coding GAL4.BD-PA fusion protein using the lithium acetate/polyethylene glycol (LiAc/PEG) method [35]. The transformants were chosen based on a synthetic defined (SD) medium (without Trp). One of the bait colonies was grown in YPAD media and re-transformed with a cDNA library of HEK293 cells (Clontech # 638,826) and screened on the basis of the yeast two-hybrid method. The positive transformants were grown on the SD agar medium (without Ade, His, Leu, and Trp) and consequently checked again using the β-galactosidase assay. The plasmids carrying the cDNAs were isolated from the transformants with a yeast plasmid DNA extraction kit (Bio Basic, Canada) following the guidelines of the manufacturer. The plasmids were transformed into E. coli DH5α and amplified. Their cDNA inserts were sequenced and identified using the BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) analysis.
Transforming pACT2-SNX2 into yeast cells and examining SNX2 and PA interaction
pACT2-SNX2 or pACT2 plasmid (control) were transformed into the S. cerevisiae strain PJ69-4 A carrying the bait plasmid (pGBD-PA) with LiAc/PEG method. Double transformants were selected on SD agar medium (without Trp and Leu). A limited number of colonies were grown on a SD agar medium (without His, Leu, Ade, and Trp); growth profiles were determined and checked for β-galactosidase activities.
β-galactosidase assay
The yeast cells were cultured in 5 ml SD medium (without Trp-Leu or Leu) at 30 °C. The saturated cultures (500 µl) were centrifuged and the cells were re-suspended in 300 µl Z-buffer (0.1 M sodium phosphate, pH 7.0, 10 mM KCl, 1 mM MgSO4 and 0.27% β mercaptoethanol). The cells in suspensions were destroyed with the freeze-thaw in liquid nitrogen. Then, 60 µl o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (ONPG) (4 mg/ml) was added into the samples, and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. Three hundred µl Na2CO3 (0.5 M) was added to stop the reactions. The samples were centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 5 min and the absorbance of the supernatants at 420 nm (OD420) was measured.
Plasmid DNA transfection
Polyethylenimine (PEI) was used for plasmid DNA transfection into the HEK293 or HeLa cells [36]. Plasmid DNA and PEI were diluted in OPTI-MEM (Gibco, USA) to a concentration of 20 ng/µl and 40 ng/µl, respectively, and mixed in equal volumes to form complexes. After incubation at room temperature for 5–10 min, the complexes were added to the culture media. The cultures were incubated under the standard culture conditions for 20–48 h and used in the experiments.
Immunoblotting
The synthesis of the SNX2 and viral proteins in the cells transfected and/or virus-infected were examined with western blotting. The cells grown in 12-well plates were lysed in lysis buffer A (50 mM Tris- HCl pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, and 0.1% NP-40) or SDS-PAGE sample buffer. The proteins were separated on 10% polyacrylamide gel and blotted to a PVDF membrane. After transfer, the membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat dry milk and exposed to the specific primary antibodies (monoclonal mouse anti-HA [Santa Cruz # sc-7392]; monoclonal mouse anti-actin [Mybiosource # MBS9400413] or anti-PA polyclonal rabbit antisera overnight at 4 °C and then to the horseradish peroxidase-conjugated second antibody (anti-mouse IgG-HRP [Invitrogen # 31,420] and/or anti-rabbit IgG-HRP [Invitrogen # 31,423]) against species-specific immunoglobulins for 45 min. The protein bands were visualized using an ECL substrate (GE Healthcare, Italy).
Co-immunoprecipitation assay
The interaction between PA and SNX2 proteins in the HEK293 cells was investigated with co-immunoprecipitation assay. The cells were seeded at a density of 5 × 105 cells/well in 6 well plate and grown at 37 °C in a CO2 incubator for 20–24 h. The SNX2 plasmids were co-transfected with the plasmids expressing the viral PA proteins into the HEK293 cells using PEI and incubated for 48 h. After the incubation periods, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and subjected to chemical cross-linking (1 h, 4 °C) by addition of DSP (dithiobis [succinimidyl propionate]) at 1 mM final concentration. The cross-linking reaction was stopped by the addition of glycine at 100 mM final concentration, and then the cells were lysed in lysis buffer A. The cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 5 min and the supernatants (250 µl) were incubated with a 5 µL monoclonal mouse anti-HA antibody (sc-7392) at 4 °C for 2 h. Protein A-Sepharose (GE Healthcare, Sweden) was added to the samples and incubated overnight with mixing at 4 °C. The beads were washed three times with buffer A. The proteins bound the beads were recovered by heating the samples at 95 °C for 5 min in a SDS-PAGE sample buffer and then analyzed by western blotting.
Immunofluorescence assay
The HeLa cells were grown on coverslips and transfected with pCAGGS-PA, pCHA-SNX2, pCHA-SNX2/pCAGGS-PA, pCHA-SNX2/pCAGGS-nPA, or pCHA-SNX2/pCAGGS-cPA plasmids. After 36–40 h transfection, the cells were washed with PBS and fixed with PBS containing 3% paraformaldehyde for 15 min. The cells were permeabilized with 0.1% NP-40, washed twice with PBS, and then incubated in 1% nonfat dry milk for 30 min. The cells were then treated for 60 min with primary antibodies (mouse anti-HA and/or rabbit anti-PA) diluted in 1% nonfat dry milk and washed three times with PBS. The coverslips were incubated in 1% nonfat dry milk for 20 min once again and then cells were stained with Alexa-488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG and/or Alexa-568-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (at 1:300 dilutions) for 60 min. The nuclei of the cells were stained with DAPI. The coverslips were washed with PBS and mounted on glass plates and the cells were observed by using a laser confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss LSM 700).
In situ proximity ligation assay (PLA)
The HeLa cells were seeded on coverslips and cultured until they reach 50–60% confluence, then co-transfected with SNX2 and viral PA coding plasmids. After 36–40 h of transfection, the cells were exposed to the primary antibodies (monoclonal mouse anti-HA and polyclonal rabbit anti-PA) as previously mentioned. The assay was performed using a Duolink PLA kit (Sigma-Aldrich # DUO92104) by following the guidelines of the manufacturer. Briefly, the cells grown on coverslips were washed in wash buffer A (10 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl and 0.5% Tween-20) and incubated with a mixture of plus (mouse) and minus (rabbit) PLA probes for one and a half hours. The cell monolayers were then washed three times in wash buffer A for 10 min and subjected to ligation. After ligation, the closed circles were amplified using a rolling-circle amplification with the DNA polymerase and complementary fluorescently labeled oligonucleotides for 3 h at 37 °C. The monolayers were washed three times in wash buffer B (200 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl) for 10 min and rinsed once with 0.01x wash buffer B. After washing the samples were mounted on glass plates and the cells were observed by the laser confocal microscope.
siRNA transfection, and quantitation of viral RNAs and viral proteins
The small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting exon 2 of the SNX2 gene (Cat. / Assay ID: Cat#1,299,001/HSS110066) was purchased from Life Technologies. The HeLa cells were seeded in six cm petri dishes (5 × 105 cells) and incubated at standard culture conditions for 20–24 h. The cells were transfected with 30 pmol SNX2 gene-specific siRNA (Life Technologies, Cat#1,299,001/HSS110066) or a negative control siRNA (Invitrogen, Cat#12,935-200) with lipofectamine RNAiMAX (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) following the guidelines of the manufacturer and incubated for 48 h. The cells were then sub-cultured into 12-well plates (2 × 105 cells/well) for 24 h. Total RNA was isolated from some monolayers and used for quantitation of the transcripts. Some of the monolayers were infected with influenza A/DkPen viruses at a one moi. After half an hour of adsorption, the the non-adsorbed viral inoculum was removed and the cells were incubated in the maintenance medium (DMEM containing 0.2% BSA fraction V and 4 mg/ml TPCK-trypsin) for 6 or 12 h. After incubation, the cells were lysed in SDS-PAGE sample buffer and viral proteins in lysates were analyzed with western blotting. At 8-h post infection, the total RNA was isolated from some of the infected cultures for quantitation of the viral RNAs. Quantitation of SNX2 transcript and viral mRNAs/cRNA (segment 8) was performed with qPCR. The qPCR reactions were carried out using FastStart Universal SYBR Green Master Mix (Roche, Germany). The qPCR temperature cycling conditions were as follows; initial denaturation at 95 °C for 10 min, 45 cycles of denaturation for 5 s at 95 °C, annealing at 55 °C for 10 s and elongation at 72 °C for 20 s. The quantities of SNX2 transcript and viral RNAs were normalized by the amount of actin beta (ACTB). The primers used in the real-time PCR are given in supplementary Table 1.
Virus growth in the SNX2 knockdown cells
After 48 h transfection with siRNAs as previously described, the HeLa cells were sub-cultured into 12-well plates (2 × 105 cells/well) and incubated for 24 h. The monolayers were inoculated with 200 µl of virus suspension (5 × 103 pfu) in 1% BSA for 30 min for adsorption. The virus inoculum was removed and the cells were washed with PBS and the cells were incubated in the maintenance medium. The released viruses into the medium were titrated at various time intervals with plaque formation assay [30].
Influenza A virus RNA polymerase activity assay
Influenza A virus RdRP activity in the HEK293 cells transiently expressing SNX2 proteins was investigated with the influenza virus minireplicon [13, 34]. The cells were grown in 24-well plates (5 × 104 cells/well) for 20–24 h at standard culture conditions and transfected with certain amounts of a minireplicon plasmid set (pCAGGS-PB2, pCAGGS-PB1, pCAGGS-PA, pCAGGS-NP, and pHH21-vNS-luc) and increasing amounts of the SNX2 plasmids. A control Renilla luciferase plasmid (pRL-SV40) was used for normalization. After 48 h, the cells were lysed in 100 µl lysis buffer (passive lysis buffer; Promega#E194A). Both firefly and Renilla luciferase activities in the lysates were determined using a commercial kit (Promega # E1501 and E2820). The enzyme activity was measured as luminesces in a luminometer (GloMax20/20 Luminometer, Promega Corp., Madison, WI, USA).
Titration of influenza A virus PA inhibitory effects on reporter SEAP expression with SNX2 proteins
The influenza A virus PA subunit of RdRP has strong inhibitory effects on PolII polymerase activity [33, 37]. To determine the rescue effects of the SNX2 proteins on viral PA protein, the pSEAP (Clontech) reporter plasmid was used. The HEK293 cells grown in a 24-well plate (1 × 105 cells/well) were transfected with a certain amount of pSEAP and pCAGGS-PA(D) [33] and increasing amounts of the SNX2 plasmids. The cells were incubated at standard culture conditions for 24 h, and secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) activity in the medium was determined with a commercial kit (Roche Diagnostics GmbH#31,420) following the guidelines of the manufacturer. The enzyme activity was measured as luminesces in the luminometer.
Results
Identification of interaction between human SNX2 and influenza A virus PA proteins using Y2H analysis
The yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) method is a well-established technique for detecting protein-protein interactions. In this study, using the influenza A/DkPen virus PA protein as a bait, possible PA interactor proteins encoded on the HEK293 cDNA library were screened with the Y2H method. The human SNX2 protein was identified as one of the candidate proteins that interact with viral PA protein. When the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA isolated from the positive colony was analyzed, it was determined that the peptide interacting with the PA consisted of the carboxyl-terminal region of the SNX2 protein composed of 276 amino acid residues (Supplementary Fig. S1A). In order to study the interaction of the full-length SNX2 protein with the PA protein in more detail, the complete cDNA of SNX2 gene was cloned into the pACT2 plasmid and the possible interaction of this protein with PA bait in yeast cells was re-assayed. The growth profiles of the yeast cells transformed with both plasmids coding viral PA bait and human SNX2 protein on SD agar medium (without Ade, His, Leu and Trp) are given in Fig. S1B. It was defined that double transformant yeast cells expressing the GAL4 binding domain (pGBD-C1) and AD-SNX2 fusion protein (pACT2-SNX2) showed very limited growth on the SD agar medium. The yeast cells grown in a small-scale SD medium (without Trp and Leu) were further analyzed for β-galactosidase enzyme activity (Supplementary Fig. S1C). The results were found in correlation with the growth profile of the colonies on the SD agar medium.
SNX2 proteins show interactions with influenza A virus PA proteins in human cells
To investigate the interaction of the human SNX2 protein with the viral PA protein and its effect on the viral replication in mammalian cells, the plasmid vectors coding the full-length SNX2 and SNX2 proteins with a deletion in regions corresponding to specific exons were constructed. The domain structure of the SNX2 protein and the schematic representations of the proteins encoded by plasmid vectors are given in Fig. 1A and B. The full-length SNX2 (variant 1) and the SNX2 proteins having deletions in some exons synthesized in HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the plasmids were analyzed by SDS-PAGE/western blotting. The proteins were found to be efficiently synthesized in transfected HEK293 cells (data not shown). The interaction between human SNX2 and viral PA protein was investigated by both co-immunoprecipitation assays and analysis of the intracellular localization of the proteins using immunofluorescence staining. The SNX2 proteins with an HA tag synthesized with viral PA proteins in HEK293 cells were precipitated with monoclonal mouse anti-HA antibodies, and SNX2 and PA proteins in the precipitates were determined by western blotting (Fig. 1C).
A The domain structure of human SNX2 protein. B The schematic representation of the SNX2 proteins encoded by the pCHA plasmids. Deletions in the SNX2 gene were carried out according to the exon/intron structure of the gene; Exons 1–3, exons 4–8, and exons 9–15 were deleted in the SNX2ΔN, SNX2ΔM, and SNX2ΔC genes, respectively. C Co-immunoprecipitation of influenza A/DkPen PA proteins with human SNX2 synthesized in transiently transfected HEK293T cells. The cells were transfected with the plasmids coding the proteins shown in the figures. Immunoprecipitation was performed with an anti-HA antibody, and the precipitate was subjected to SDS-PAGE. The proteins were detected by western blotting using either monoclonal anti-HA antibody or rabbit anti-PA. HRP conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG or anti-rabbit IgG was used as the secondary antibody for labeling the proteins
The results revealed that viral full-length PA protein and PA proteins with deletions (PAΔC and PAΔN) were co-precipitated with the SNX2 at different levels. It was observed that the SNX2 proteins with a deletion in amino-terminal (SNX2ΔN) and inner domains (SNX2ΔM) did not co-precipitate with the viral PA protein at all. In contrast, the SNX2 protein with a deletion in carboxyl-terminal domains (SNX2ΔC) was efficiently precipitated with the PA protein. In addition, the SNX2 protein showed a strong interaction with PAΔC while no co-precipitation with PAΔN was detected. These results suggested that the amino-terminal moiety of the influenza A/DkPen PA protein and some motifs located in the intermediate domains of the SNX2 protein are important for the interaction.
To support the IP results, we also examined the subcellular localization of the viral PA and human SNX2 proteins in HeLa cells. The cells were transfected alone or together with plasmids encoding SNX2 and PA proteins. Thirty-six hours after transfection, SNX2 and PA proteins were labeled with mouse monoclonal anti-HA and/or rabbit polyclonal anti-PA antibodies. Then, the proteins stained with the secondary antibodies conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 and/or Alexa Fluor 568 were examined with a laser confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM 700, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) (Fig. 2A and B). The results showed that SNX2 protein encoded from the plasmid DNA in HeLa cells gave the co-localization profiles with both viral PA and PAΔC proteins. The subcellular localization of SNX2 and PA proteins were found to confirm the co-immunoprecipitation tests.
Subcellular detection of the PA and the SNX2 proteins in HeLa cells with immunostaining (A and B) and the PLA (C). A HeLa cells were transfected with the plasmid encoding PA or SNX2 protein. B The cells were co-transfected with the plasmids encoding PA and SNX2 proteins. At 36 h post-transfection, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, and labeled with mouse monoclonal anti-HA (for SNX2) and/or rabbit polyclonal anti-PA. As the secondary antibodies, monoclonal anti-mouse IgG conjugated Alexa Fluor 488 (for SNX2) and/or monoclonal anti-rabbit IgG conjugated Alexa Fluor 568 (for PA) were used. C HeLa cells co-transfected with plasmids were treated with mouse monoclonal anti-HA (for SNX2) and rabbit polyclonal anti-PA. Then, the PLA was carried out with Duolink proximity ligation assay reagents according to the manufacturer’s instructions and analyzed with the laser scanning microscope. The nuclei were counterstained by DAPI. Stained cells were examined under the laser scanning microscope
The relationship between human SNX2 and influenza A virus PA protein encoded on plasmid DNAs in HeLa cells was also examined by the proximity ligation assay (PLA), which is a fairly new technique. After the proximity ligation reaction had taken place, fluorescent red dots were examined under the laser scanning microscope (Fig. 2C). The results revealed that SNX2 and PA proteins co-synthesized in HeLa cells were localized closer to each other than 40 nm (fluorescence dot formation), which is showed the interaction of the proteins.
Knockdown of the SNX2 gene positively affects the influenza A virus replication in the cells
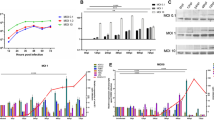
RNA interference (RNAi) was used to knockdown SNX2 in HeLa cells, and the influenza A/DkPen viral replication was subsequently assessed in these cells. In the cells transfected with SNX2 siRNAs, it was observed that this gene-specific transcript level decreased by an average of 95% just before the viral infection (Fig. 3A). In contrast, the influenza A virus replication was positively regulated in the SNX2 gene-knockdown cells. It was found that the levels of viral cRNA and mRNA increased by 85% average in the SNX2 gene knockdown cells at the 8th h of viral infection compared to the control cells (Fig. 3B). In correlation with the changes of viral transcripts, a significant increase was observed in the amount of PA subunit of the RdRP enzyme (Fig. 3C). We tested the growth of influenza A virus in the SNX2 gene knockdown cells. The viruses replicated more efficiently in these cells. In the 24th h, it was observed that the virus titer was around 10 times higher in the SNX2 knockdown cells in comparison to the control cultures (Fig. 3D and Supplementary Fig. S2). These results revealed that the SNX2 protein had a negative effect on the influenza A/DkPen virus replication.
Influenza A/DkPen virus replication in the SNX2 gene knockdown cells. A The quantity of endogenous SNX2 transcript in the knockdown HeLa cells. B The quantities of the viral mRNAs and cRNA transcribed from segment 8 viral RNA in the virus-infected knockdown cells. The quantities of SNX2 mRNA (just before infection) and viral RNAs transcribed from viral segment 8 (at 8 h p.i.) in the knockdown cells were determined with qPCR. C Western blot analysis of viral PA protein in the virus infected knockdown cells. The proteins were labeled with rabbit polyclonal anti-PA or mouse monoclonal anti-actin, and HRP conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG or goat anti-mouse IgG and visualized with an ECL Western blotting detection kit (GE Healthcare). D Growth kinetics of the influenza A virus in the SNX2 knockdown cells
The effect of over-expression of SNX2 proteins on the influenza A/DkPen virus RdRP enzyme was also investigated using the influenza minireplicon system [13]. The results showed that there was no significant change in viral RdRP enzyme activities in the cells transfected with increasing amounts of SNX2 plasmids (Supplementary Fig. S3).
We assessed the SNX2 gene expression pattern in the cells infected with influenza A/DkPen viruses. The transcript level of the SNX2 gene was normalized with the ACTB gene. The results showed that the expression of the SNX2 gene in the virus-infected cells was on average 50% down-regulated relative to uninfected cells (Supplementary Fig. S4).
The increase of SNX2 proteins has rescue effects on the inhibitory activities of viral PA protein on host gene expression. Influenza A virus RdRP enzyme PA subunit is known to inhibit host cell gene expression [38]. In our previous study, it was shown that the avian type influenza A/DkPen virus PA protein, in particular, more aggressively inhibits the transcription of host genes than that of human type influenza A/WSN virus protein [33]. Based on these results, we evaluated whether SNX2 proteins neutralize the inhibitory effect of influenza A/DkPen PA protein on PolII transcription. It was determined that full-length SNX2, SNX2ΔC and SNX2ΔM proteins decreased the inhibitory effects of the viral PA protein depending on the quantity of the SNX2 plasmids (Fig. 4). In contrast, SNX2ΔN protein did not show a rescue effect on PA inhibition. These results were found important in supporting the interactions of SNX2 and PA proteins.
Rescue effect of SNX2 proteins on influenza A/DkPen PA inhibitory activity to host gene expression. The HEK293 cells were grown in a 24-well plate (5 × 104 cells/well) for 24 h in standard culture conditions and transfected with constant amounts of pCAGGS-PA(D) (1 ng/well) and pSEAP (20 ng/well) plasmids and indicated amounts of the SNX2 plasmids in the figure. After 24 h of transfection, the reporter SEAP activities in culture media was detected with a commercial kit
Discussion
The sorting nexin (SNX) family is a diverse group of cellular proteins characterized by the presence of a phospholipid-binding motif termed the phox homology (PX) domain [23]. These proteins are highly conserved and bind to phosphotidylinositol-3-phosphate in membranes through the PX region. SNX proteins interact with various cytoplasmic groups and membrane proteins and involve in many cellular pathways such as intracellular protein trafficking, regeneration of transmembrane proteins, transport of endosomes, and endocytosis [39, 40]. Mammalian genomes encode 33 SNX proteins sharing the phox homology domain. SNX1, SNX2, SNX5, SNX6, and SNX32 constitute the membrane deformation subcomplex of the retromer. Its most important function concerns the selection of cargo proteins for retrograde transport from early endosomes to the Golgi complex. Recently, it has been revealed that some of the viruses utilize retromer-mediated trafficking in order to replicate [41]. However, no study was found that revealed a relationship between influenza A viruses and SNX proteins.
In this study, we demonstrated that the human SNX2 protein interacts with the influenza A/DkPen virus PA protein by the Y2H assay (Supplementary Figure S1). Human SNX2 protein was also found to be associated with the viral PA protein in transiently transfected HEK293 cells with IP and IF analysis. The IP analyzes indicated that specifically the amino-terminal region of the viral PA protein and some motifs close to the amino-terminal of the SNX2 protein are important in this interaction (Fig. 1). IF and PLA results correlated with IP data (Fig. 2). The results of the study to determine the relationship between PA and SNX2 in yeast and mammalian cells suggested that these two proteins interact in the cells and the SNX2 protein may interfere with the influenza A virus replication. Therefore, we investigated the effects of changes in the amount of SNX2 protein on viral replication in the cells. We found that influenza A/DkPen virus replication is upregulated both at the level of transcript and viral protein in SNX2 knockdown cells. The viruses grown more rapidly in SNX2 gene knockdown cells comparison to the control cells (Fig. 3D and Supplementary Fig. S2).
The upregulation of viral transcripts in knockdown cells suggests that the SNX 2 protein has a negative regulatory effect on influenza A/DkPen virus replication. In a previous study, it was reported that the L1 protein, which is the major component of the human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16) capsid, has a strong interaction with sorting nexin 17 (SNX17) and is crucial for HPV-16 virus infection [42]. Similarly, the SNX2 protein a retromer component, has interaction with HRSV structural proteins M and N and plays an important role in the traffic of HRSV structural proteins toward assembly sites [43]. It was also shown that gene knockdown of specific retromer components inhibits specific steps in the intracellular life cycle of the vaccinia virus [28], hepatitis C virus [44], and human papillomavirus [26]. Our results contradict the replication stimulating effects of SNX family proteins on some of the viruses.
The SNX2 gene transcription was negatively effected with the virus infection. The gene transcript level of infected HeLa cells decreased about 50% in the 8th h of the infection when compared with the uninfected cells (Supplementary Figure S4). It is known that the expression profiles of many genes in the cells infected with the influenza A virus is either negatively (down-regulation) or positively (up-regulation) regulated [33]. However, there is no data about the importance of the SNX2 gene down-regulation for the influenza A/DkPen virus replication.
We examined influenza A/DkPen virus RdRP enzyme activity in the HEK293 cells transiently transfected with increasing amounts of SNX2 plasmids by using the minireplicon assay. The increase of SNX2 proteins in the cells did not cause a significant change in viral RdRP enzyme activity (Supplementary Figure S3). Influenza A virus RdRP enzyme is a heterotrimeric complex composed of PB2, PB1, and PA proteins [45]. The fact that the increase in SNX2 protein did not inhibit the viral RdRP enzyme in the minireplicon model suggested that the negative effect of this protein on viral replication occurs by a different mechanism associated with the PA protein.
Influenza A virus PA protein is known to inhibit host gene expression at the transcription and/or translation stage [38]. In our previous study, this inhibition was found to be much higher in the avian type virus-specific PA protein than in the human influenza A/WSN virus [33]. One of the reasons avian influenza A/DkPen viruses replicate much more slowly in mammalian cells may be the relationship of the viral PA protein with the SNX2 and some other cellular proteins. In this study, it was observed that the inhibitory effects of the viral PA protein on host Pol II dependent gene expression was partially rescued by the SNX2 protein (Fig. 4). The increase in the SNX2ΔN protein did not affect the inhibition of the PA protein. These results support the association of the SNX2 protein with the viral PA protein, especially with some motifs close to the amino-terminal region. On the other hand, the interaction of the SNX2 with the viral PA protein in both yeast cells and the HEK293 cells suggests that these proteins directly interacts each other.
In conclusion, we demonstrated with the Y2H method that human SNX2 protein, a member of the sorting nexins family, has an interaction with avian influenza A/DkPen virus PA protein. It was shown that these two proteins also interact with each other in the HEK293 cells, and the SNX2 protein has a negative regulatory function on virus replication. However, the increase in SNX2 proteins did not cause a significant change in the viral RdRP activity. This may suggest that the negative effect of the SNX2 protein on the influenza A/DkPen virus replication could be saturated with its authentic intra-cellular amount or independent of the viral RdRP enzyme.
Therefore, more knowledge is required to elucidate the action mechanism of the SNX2 protein on influenza A/DkPen virus replication at the molecular level.
Data availability
The datasets used during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Parrish CR, Murcia PR, Holmes EC (2015) Influenza virus reservoirs and intermediate hosts: dogs, horses, and new possibilities for influenza virus exposure of humans. J Virol 89:2990–4. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.03146-14
Taubenberger JK, Kash JC (2010) Influenza virus evolution, host adaptation, and pandemic formation. Cell Host Microbe 7:440–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2010.05.009
Garten RJ, Davis CT, Russell CA et al (2009) Antigenic and genetic characteristics of swine-origin 2009 A(H1N1) influenza viruses circulating in humans. Science 325:197–201. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1176225
Lamb RA, Lai CJ, Choppin PW (1981) Sequences of mRNAs derived from genome RNA segment 7 of influenza virus: colinear and interrupted mRNAs code for overlapping proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:4170–4. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.78.7.4170
Lamb RA, Choppin PW, Chanock RM, Lai CJ (1980) Mapping of the two overlapping genes for polypeptides NS1 and NS2 on RNA segment 8 of influenza virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1857–1861. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.77.4.1857
Chen W, Calvo PA, Malide D, Gibbs J, Schubert U, Bacik I, Basta S, O’Neill R, Schickli J, Palese P, Henklein P, Bennink JR, Yewdell JW (2001) A novel influenza A virus mitochondrial protein that induces cell death. Nat Med 7:1306–1312. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1201-1306
Jagger BW, Wise HM, Kash JC, Walters KA, Wills NM, Xiao YL, Dunfee RL, Schwartzman LM, Ozinsky A, Bell GL, Dalton RM, Lo A, Efstathiou S, Atkins JF, Firth AE, Taubenberger JK, Digard P (2012) An overlapping protein-coding region in influenza A virus segment 3 modulates the host response. Science 337:199–204. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222213
Muramoto Y, Noda T, Kawakami E, Akkina R, Kawaoka Y (2013) Identification of novel influenza A virus proteins translated from PA mRNA. J Virol 87:2455–62. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02656-12
Wise HM, Hutchinson EC, Jagger BW, Stuart AD, Kang ZH, Robb N, Schwartzman LM, Kash JC, Fodor E, Firth AE, Gog JR, Taubenberger JK, Digard P (2012) Identification of a novel splice variant form of the influenza A virus M2 ion channel with an antigenically distinct ectodomain. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002998. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002998
Selman M, Dankar SK, Forbes NE, Jia JJ, Brown EG (2012) Adaptive mutation in influenza A virus non-structural gene is linked to host switching and induces a novel protein by alternative splicing. Emerg Microbes Infect 1:e42. https://doi.org/10.1038/emi.2012.38
Zhao M, Wang L, Li S (2017) Influenza A virus-host protein interactions control viral pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081673
Senbas Akyazi B, Pirincal A, Kawaguchi A, Nagata K, Turan K (2020) Interaction of influenza A virus NS2/NEP protein with the amino-terminal part of Nup214. Turk J Biol 44:82–92. https://doi.org/10.3906/biy-1909-49
Turan K, Mibayashi M, Sugiyama K, Saito S, Numajiri A, Nagata K (2004) Nuclear MxA proteins form a complex with influenza virus NP and inhibit the transcription of the engineered influenza virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:643–652. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh192
Avalos RT, Yu Z, Nayak DP (1997) Association of influenza virus NP and M1 proteins with cellular cytoskeletal elements in influenza virus-infected cells. J Virol 71:2947–2958. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.71.4.2947-2958.1997
Zhirnov OP, Ksenofontov AL, Kuzmina SG, Klenk HD (2002) Interaction of influenza A virus M1 matrix protein with caspases. Biochemistry (Mosc) 67:534–9. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1015542110798
Cao M, Wei C, Zhao L, Wang J, Jia Q, Wang X, Jin Q, Deng T (2014) DnaJA1/Hsp40 is co-opted by influenza A virus to enhance its viral RNA polymerase activity. J Virol 88:14078–14089. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02475-14
Tan SL, Katze MG (1998) Biochemical and genetic evidence for complex formation between the influenza A virus NS1 protein and the interferon-induced PKR protein kinase. J Interferon Cytokine Res 18:757–766. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.1998.18.757
Zhang J, Li G, Ye X (2010) Cyclin T1/CDK9 interacts with influenza A virus polymerase and facilitates its association with cellular RNA polymerase II. J Virol 84:12619–27. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01696-10
Garrus JE, von Schwedler UK, Pornillos OW, Morham SG, Zavitz KH, Wang HE, Wettstein DA, Stray KM, Cote M, Rich RL, Myszka DG, Sundquist WI (2001) Tsg101 and the vacuolar protein sorting pathway are essential for HIV-1 budding. Cell 107:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00506-2
Rauch S, Martin-Serrano J (2011) Multiple interactions between the ESCRT machinery and arrestin-related proteins: implications for PPXY-dependent budding. J Virol 85:3546–3556. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02045-10
Sagara J, Tsukita S, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Kawai A (1995) Cellular actin-binding ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) family proteins are incorporated into the rabies virion and closely associated with viral envelope proteins in the cell. Virology 206:485–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0042-6822(95)80064-6
Bhowmick S, Chakravarty C, Sellathamby S, Lal SK (2017) The influenza A virus matrix protein 2 undergoes retrograde transport from the endoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm and bypasses cytoplasmic proteasomal degradation. Arch Virol 162:919–929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-3153-8
Worby CA, Dixon JE (2002) Sorting out the cellular functions of sorting nexins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:919–931. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm974
Carlton JG, Bujny MV, Peter BJ, Oorschot VM, Rutherford A, Arkell RS, Klumperman J, McMahon HT, Cullen PJ (2005) Sorting nexin-2 is associated with tubular elements of the early endosome, but is not essential for retromer-mediated endosome-to-TGN transport. J Cell Sci 118:4527–4539. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02568
Cullen PJ, Korswagen HC (2011) Sorting nexins provide diversity for retromer-dependent trafficking events. Nat Cell Biol 14:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2374
Bergant M, Banks L (2013) SNX17 facilitates infection with diverse papillomavirus types. J Virol 87:1270–3. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01991-12
Al-Saleem J, Dirksen WP, Martinez MP, Shkriabai N, Kvaratskhelia M, Ratner L, Green PL (2019) HTLV-1 Tax-1 interacts with SNX27 to regulate cellular localization of the HTLV-1 receptor molecule, GLUT1. PLoS ONE 14:e0214059. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0214059
Hsiao JC, Chu LW, Lo YT, Lee SP, Chen TJ, Huang CY, Ping YH, Chang W (2015) Intracellular transport of vaccinia virus in HeLa cells requires WASH-VPEF/FAM21-retromer complexes and recycling molecules Rab11 and Rab22. J Virol 89:8365–8382. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00209-15
Phillips SL, Cygnar D, Thomas A, Bresnahan WA (2012) Interaction between the human cytomegalovirus tegument proteins UL94 and UL99 is essential for virus replication. J Virol 86:9995–10005. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01078-12
Turan K, Nagata K, Kuru A (1996) Antiviral effect of Sanicula europaea L. leaves extract on influenza virus-infected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 225:22–26. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1996.1125
Nagata K, Saito S, Okuwaki M, Kawase H, Furuya A, Kusano A, Hanai N, Okuda A, Kikuchi A (1998) Cellular localization and expression of template-activating factor I in different cell types. Exp Cell Res 240:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1997.3930
James P, Halladay J, Craig EA (1996) Genomic libraries and a host strain designed for highly efficient two-hybrid selection in yeast. Genetics 144:1425–1436
CaGlayan E, Turan K (2021) Expression profiles of interferon-related genes in cells infected with influenza A viruses or transiently transfected with plasmids encoding viral RNA polymerase. Turk J Biol 45:88–103. https://doi.org/10.3906/biy-2005-73
Pham PTV, Turan K, Nagata K, Kawaguchi A (2018) Biochemical characterization of avian influenza viral polymerase containing PA or PB2 subunit from human influenza A virus. Microbes Infect 20:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2018.04.003
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH (2007) High-efficiency yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat Protoc 2:31–34. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.13
Longo PA, Kavran JM, Kim MS, Leahy DJ (2013) Transient mammalian cell transfection with polyethylenimine (PEI). Methods Enzymol 529:227–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-418687-3.00018-5
Oishi K, Yamayoshi S, Kawaoka Y (2015) Mapping of a region of the PA-X protein of influenza A virus that is important for its shutoff activity. J Virol 89:8661–5. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01132-15
De Vlugt C, Sikora D, Pelchat M (2018) Insight into influenza: A virus cap-snatching. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10110641
Johannes L, Popoff V (2008) Tracing the retrograde route in protein trafficking. Cell 135:1175–1187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.009
Kanzawa M, Hara S, Semba S, Yokozaki H, Hirokawa M, Itoh T (2014) Sorting Nexin 2 (SNX2): a potential marker of active thyrocytes in normal and hyperfunctioning thyroid disorders. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 22:302–307. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAI.0b013e31828badd3
Elwell C, Engel J (2018) Emerging role of retromer in modulating pathogen growth. Trends Microbiol 26:769–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2018.04.001
Bergant Marusic M, Ozbun MA, Campos SK, Myers MP, Banks L (2012) Human papillomavirus L2 facilitates viral escape from late endosomes via sorting nexin 17. Traffic 13:455–467. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01320.x
Cle M, Desmetz C, Barthelemy J, Martin MF, Constant O, Maarifi G, Foulongne V, Bollore K, Glasson Y, De Bock F, Blaquiere M, Dehouck L, Pirot N, Tuaillon E, Nisole S, Najioullah F, Van de Perre P, Cabie A, Marchi N, Gosselet F, Simonin Y, Salinas S (2020) Zika virus infection promotes local inflammation, cell adhesion molecule upregulation, and leukocyte recruitment at the blood-brain barrier. mBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01183-20
Yin P, Hong Z, Yang X, Chung RT, Zhang L (2016) A role for retromer in hepatitis C virus replication. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2027-7
Kawaguchi A, Naito T, Nagata K (2005) Involvement of influenza virus PA subunit in assembly of functional RNA polymerase complexes. J Virol 79:732–744. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.79.2.732-744.2005
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Marmara University Research Foundation (Grant No: SAG-C-YLP-120619-0224) and by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (Grant No: SBAG-112S518).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KT and KN conceived and designed the study. TK, EC, ER and KT performed the experiments. KT wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the research in ensuring that the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work is appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
In this study, neither human subjects nor animals were used.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koçmar, T., Çağlayan, E., Rayaman, E. et al. Human sorting nexin 2 protein interacts with Influenza A virus PA protein and has a negative regulatory effect on the virus replication. Mol Biol Rep 49, 497–510 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06906-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06906-9