Abstract
Background
Hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury (I/R) is an important factor affecting the prognosis of patients undergoing liver surgery. This study aimed to explore the value of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in hepatic I/R and its mechanism in a rat model.
Materials and methods
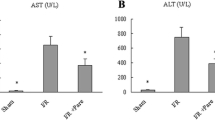
Forty eight adult male Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats were divided into six groups randomly: (1–2) treated with normal saline (NS) without ischemia or reperfusion; (3–4) treated with NS + 30 min ischemia; (5–6) treated with IVIG + 30 min ischemia. Rats of group 1/3/5 were euthanized at 12 h after operation (sham + NS + 12 h, I/R + NS + 12 h, I/R + IVIG + 12 h group) while group 2/4/6 were euthanized at 24 h (sham + NS + 24 h, I/R + NS + 24 h, I/R + IVIG + 24 h group). Interleukin 10 (IL-10), interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) were quantified as well as serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Hepatic pathological changes were observed while nuclear factor kappa B p65 (NF-κB p65), Inhibitory Subunit of NF Kappa B Alpha (IKB-alpha) and cleaved caspase-3 were detected.
Conclusion
ALT, AST, IL-6, TNF-alpha, NF-κB p65 and cleaved caspase-3 were increased by I/R whereas IL-10 and IKB-alpha were decreased. However, IVIG pretreatment reduced ALT, AST, IL-6, TNF-alpha, NF-κB p65 and cleaved caspase-3, but increased IL-10 and IKB-alpha. IVIG treatment attenuates the infiltration of inflammatory cell and cell apoptosis which were observed in I/R groups. IVIG may alleviate hepatic I/R in rats by inhibiting the classical NF-κB signaling pathway, reducing IL-6, TNF-alpha, promoting IL-10, and inhibiting cell apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
Glutamic pyruvic transaminase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin G
- NS:
-
Normal saline
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- TNF-alpha:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- NF-κB:
-
P65 nuclear factor kappa B p65
- IKB-alpha:
-
Inhibitory Subunit of NF Kappa B Alpha
- IL-10:
-
Interleukin 10
- IVIG:
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin
- I/R:
-
Ischemia + reperfusion
- MFI:
-
The mean fluorescence intensity
References
Dar WA, Sullivan E, Bynon JS, Eltzschig H, Ju C (2019) Ischaemia reperfusion injury in liver transplantation: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Liver Int 39(5):788–801. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.14091
Theodoraki K, Karmaniolou I, Tympa A, Tasoulis MK, Nastos C, Vassiliou L et al (2016) Beyond preconditionin: postconditioning as an alternative technique in the prevention of liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:8235921. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8235921
Ohhof PB, van Golen RF, Meijer B, van Beek RF, Bennink RJ, Verheij J et al (1863) (2017) Warm ischemia time- dependent variation in liver damage, inflammation, and function in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2:375–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.10.022
Glanemann M, Langrehr JM, Stange BJ, Neumann U, Settmacher U, Steinmüller T et al (2003) Clinical implications of hepatic preservation injury after adult liver transplantation. Am J Transplant 3(8):1003–1009. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-6143.2003.00167.x
de Souza VR, Carreno MP, Kaveri SV, Ledur A, Sadeghi H, Cavaillon JM et al (1995) Selective induction of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-8 in human monocytes by normal polyspecific IgG (intravenous immunoglobulin). Eur J Immunol 25(5):1267–1273. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.1830250521
Galeotti C, Hegde P, Das M, Stephen-Victor E, Canale F, Muñoz M et al (2016) Heme oxygenase-1 is dispensable for the anti-inflammatory activity of intravenous immuno- globulin. Sci Rep 6:19592. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19592
Liu XM, Huang T, Chen X, Yan M, Yu F, Gu H et al (2016) Immunoglobulin G promotes skin graft acceptance in an immunologically potent rat model. Oncotarget 7(26):39408–39420. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9823
Lin YZ, Lu ZY, Liang XH, Li K, Peng B, Gong J et al (2016) Effect of breviscapine against hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury. J Surg Res 203(2):268–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.02.013
Charan J, Kantharia ND (2013) How to calculate sample size in animal studies? J Pharmacol Pharmacother 4(4):303–306. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-500X.119726
Guan LY, Fu PY, Li PD, Li ZN, Liu HY, Xin MG et al (2014) Mechanisms of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and protective effects of nitric oxide. World J Gastrointest Surg 6(7):122–128. https://doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v6.i7.122
Abu-Amara M, Yang SY, Tapuria N, Fuller B, Davidson B, Seifalian A (2010) Liver ischemia/reperfusion injury: processes in inflammatory networks: a review. Liver Transpl 16(9):1016–1032. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.22117
Jaeschke H (1991) Reactive oxygen and ischemia/reperfusion injury of the liver. Chem Biol Interact 79(2):115–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2797(91)90077-k
Colletti LM, Remick DG, Burtch GD, Kunkel SL, Strieter RM, Campbell DA Jr (1990) Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the pathophy- siologic alterations after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. J Clin Invest 85(6):1936–1943. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI114656
Wanner GA, Ertel W, Muller P, Hofer Y, Leiderer R, Menger MD et al (1996) Liver ischemia and reperfusion induces a systemic inflammatory response through Kupffer cell activation. Shock 5(1):34–40. https://doi.org/10.1097/00024382-199601000-00008
Colletti LM, Cortis A, Lukacs N, Kunkel SL, Green M, Strieter RM (1998) Tumor necrosis factor up-regulates intercellular adhesion molecule 1, which is important in the neutrophil-dependent lung and liver injury associated with hepatic ischemia and reperfusion in the rat. Shock 10(3):182–191. https://doi.org/10.1097/00024382-199809000-00006
Schmidt KN, Traenckner EB, Meier B, Baeuerle PA (1995) Induction of oxidative stress by okadaic acid is required for activation of transcription factor NF-kappa. J Biol Chem 270(45):27136–27142. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.45.27136
Chen Z, Hagler J, Palombella VJ, Melandri F, Scherer D, Ballard D et al (1995) Signal-induced site-specific phosphorylation targets I kappa B alpha to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev 9(13):1586–1597. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.9.13.1586
Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB (1998) NF-kappa B and rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 16:225–260. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.16.1.225
Li JD, Peng Y, Peng X, Li QL, Li Q (2010) Suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB activity in Kupffer cells protects rat liver graft from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplant Proc 42(5):1582–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.12.077
Luedde T, Assmus U, Wustefeld T, Meyer zu Vilsendorf A, Roskams T, Schmidt-Supprian M et al (2005) Deletion of IKK2 in hepatocytes does not sensitize these cells to TNF-induced apoptosis but protects from ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 115(4):849–859. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI23493
Bonfoco E, Krainc D, Ankarcrona M, Nicotera P, Lipton SA (1995) Apoptosis and necrosis: two distinct events induced, respectively, by mild and intense insults with N-methyl-d-aspartate or nitric oxide/superoxide in cortical cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(16):7162–7166. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.16.7162
Eguchi Y, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y (1997) Intracellular ATP levels determine cell death fate by apoptosis or necrosis. Cancer Res 57(10):1835–1840
Leist M, Single B, Castoldi AF, Kuhnle S, Nicotera P (1997) Intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) concentration: a switch in the decision between apoptosis and necrosis. Cancer Res 57(10):1835–1840
Gujral JS, Bucci TJ, Farhood A, Jaeschke H (2001) Mechanism of cell death during warm hepatic ischemia-reperfusion in rats: apoptosis or necrosis? Hepatology 33(2):397–405. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2001.22002
Yang M, Antoine DJ, Weemhoff JL, Jenkins RE, Farhood A, Park BK et al (2014) Biomarkers distinguish apoptotic and necrotic cell death during hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Liver Transpl 20(11):1372–1382. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.23958
Kang SJ, Sanchez I, Jing N, Yuan JY (2003) Dissociation between Neuro- degeneration and caspase-11-mediated activation of caspase-1 and caspase-3 in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci 23(13):5455–5460. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05455.2003
Avni D, Ernst O, Philosoph A, Zor T (2010) Role of CREB in modulation of TNF-alpha and IL-10 expression in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Mol Immunol 47(7–8):1396–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2010.02.015
Ji H, Shen XD, Zhang Y, Gao F, Huang CY, Chang WW et al (2012) Activation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase a signaling prevents liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Liver Transpl 18(6):659–670. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.23399
Zhang F, Lu M, Wang H, Ren T (2013) Aspirin attenuates angiotensin II-induced inflammation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the inhibition of ERK1/2 and NF-κB activation. Biomed Rep 1(6):930–934. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2013.160
Jung M, Sola A, Hughes J, Kluth DC, Vinuesa E, Viñas JL, Pérez-Ladaga A, Hotter G (2012) Infusion of IL-10-expressing cells protects against renal ischemia through induction of lipocalin-2. Kidney Int 81(10):969–982. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2011.446
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Medical Science and Technology Research Foundation of Guangdong province (Grant No. A2015513), and Shantou Medical and Health Science and Technology Project (Grant No. 190620235268989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZC and RL designed and performed experiments, analyzed data and wrote the article. HZ and FX helped performing experiments. HZ and XL helped with preparation of the article. XL oversaw the design of the study, coordinated analyses, and revised the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
Animal experiments during our study were performed according to the guidelines for animal use provided by the Animal Experimental Center. Our experimental scheme was approved by the Animal Experimental Ethics Committee of Shantou University Medical College. And all applicable institutional and governmental regulations concerning the ethical use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Lin, R., Zhuo, H. et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin is effective in alleviating hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury: a rat model study. Mol Biol Rep 49, 341–349 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06879-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06879-9