Abstract
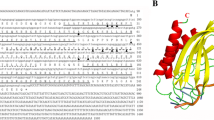
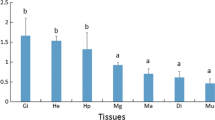
To better explore the application potential of heat shock protein Hsp70s in diverse areas including biomonitoring, a further investigation of the details of the regulatory mechanism governing Hsp70 transcription is required. A transcriptional factor ChGATA-4 that displayed affinity to the ChHsp70 promoter of Crassostrea hongkongensis was isolated and identified by DNA affinity purification as well as mass spectrometry analysis. The ChGATA-4 cDNA is 2162 bp in length and the open reading frame encodes a polypeptide containing 482 amino acids with a conserved zinc finger domain. The over-expression of ChGATA-4 significantly inhibited the expression of ChHsp70 promoter in heterologous HEK293T cells. However, the depletion of ChGATA-4 mRNA by RNAi technique resulted in significant increase of ChHsp70 transcription in oyster hemocytes. The RT-PCR results demonstrated that the transcription of both ChHsp70 and ChGATA-4 were induced by heat, Cd, or NP (Nonyl phenol) stress. This suggested a potential correlation between ChHsp70 and ChGATA-4 in the stress-mediated genetic regulatory cascade. This study demonstrated that ChGATA-4 acts in a negative manner in controlling ChHsp70 transcription in C. hongkongensis and promotes to further understand the mechanisms leading Hsp70 transcription.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saibil H (2013) Chaperone machines for protein folding, unfolding and disaggregation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14(10):630–642. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3658
Whitley D, Goldberg SP, Jordan WD (1999) Heat shock proteins: a review of the molecular chaperones. J Vasc Surg 29(4):748–751
Piano A, Franzellitti S, Tinti F, Fabbri E (2005) Sequencing and expression pattern of inducible heat shock gene products in the European flat oyster, Ostrea edulis. Gene 361:119–126. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2005.06.034
Zorzi E, Bonvini P (2011) Inducible hsp70 in the regulation of cancer cell survival: analysis of chaperone induction, expression and activity. Cancers (Basel) 3(4):3921–3956. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers3043921
Young JC (2014) The role of the cytosolic HSP70 chaperone system in diseases caused by misfolding and aberrant trafficking of ion channels. Dis Model Mech 7(3):319–329. doi:https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.014001
Mayer MP, Bukau B (2005) Hsp70 chaperones: cellular functions and molecular mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci 62(6):670–684. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4464-6
Morimoto RI (1993) Cells in stress: transcriptional activation of heat shock genes. Science 259:1409–1409
Chuang KH, Ho SH, Song YL (2007) Cloning and expression analysis of heat shock cognate 70 gene promoter in tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Gene 405(1–2):10–18. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2007.08.016
Pirkkala L, Nykanen P, Sistonen L (2001) Roles of the heat shock transcription factors in regulation of the heat shock response and beyond. FASEB J 15(7):1118–1131
Mason PB, Lis JT (1997) Cooperative and competitive protein interactions at the hsp70 promoter. J Biol Chem 272(52):33227–33233
Imbriano C, Bolognese F, Gurtner A, Piaggio G, Mantovani R (2001) HSP-CBF is an NF-Y-dependent coactivator of the heat shock promoters CCAAT-boxes. J Biol Chem 276(28):26332–26339
Bevilacqua A, Fiorenza MT, Mangia F (1997) Developmental activation of an episomic hsp70 gene promoter in two-cell mouse embryos by transcription factor Sp1. Nucl Acids Res 25(7):1333–1338
Shopland LS, Hirayoshi K, Fernandes M, Lis JT (1995) HSF access to heat shock elements in vivo depends critically on promoter architecture defined by GAGA factor, TFIID, and RNA polymerase II binding sites. Genes Dev 9(22):2756–2769
Miao Z, Xu D, Cui M, Zhang Q (2016) High mobility group protein DSP1 negatively regulates HSP70 transcription in Crassostrea hongkongensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 474(4):634–639. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.163
Xu D, Yang Q, Cui M, Zhang Q (2017) The novel transcriptional factor HP1BP3 negatively regulates Hsp70 transcription in Crassostrea hongkongensis. Sci Rep 7(1):1401. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01573-y
Xu D, Wang D, Cui M, Zhang Q (2018) The purine-rich element-binding protein ChPur-alpha negatively regulates Hsc70 transcription in Crassostrea hongkongensis. Cell Stress Chaperones 23(1):91–100. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0826-5
Zhang L, Xu D, Cui M, Tang L, Hou T, Zhang Q (2018) The guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha subunit protein ChGnaq positively regulates Hsc70 transcription in Crassostrea hongkongensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 499(2):215–220. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.130
Liu H, Xu D, Cui M, Hou T, Zhang Q (2018) The transcriptional factor YB-1 positively regulates Hsc70 transcription in Crassostrea hongkongensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495(4):2404–2409. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.110
Liu Y, Li L, Huang B, Wang W, Zhang G (2019) RNAi based transcriptome suggests genes potentially regulated by HSF1 in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas under thermal stress. BMC Genom 20(1):639. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6003-8
Zhang Z, Zhang Q (2012) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of heat shock protein 70 gene from the oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis responding to thermal stress and exposure of Cu(2+) and malachite green. Gene 497(2):172–180. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.01.058
Whitelaw E, Tsai S-F, Hogben P, Orkin S (1990) Regulated expression of globin chains and the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 during erythropoiesis in the developing mouse. Mol Cell Biol 10(12):6596–6606
Zhang Y, Li F, Xiao X, Deng W, Yin C, Zhang T, Murthy KS, Hu W (2017) Regulator of G protein signaling 4 is a novel target of GATA-6 transcription factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483(3):923–929
Molkentin JD (2000) The zinc finger-containing transcription factors GATA-4,-5, and-6: ubiquitously expressed regulators of tissue-specific gene expression. J Biol Chem 275(50):38949–38952
Li HX, Zhou YF, Jiang B, Zhao X, Jiang TB, Li X, Yang XJ, Jiang WP (2014) GATA-4 induces changes in electrophysiological properties of rat mesenchymal stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840(6):2060–2069. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.02.020
Peterkin T, Gibson A, Loose M (2005) Patient R The roles of GATA-4,-5 and-6 in vertebrate heart development. In: Seminars in cell & developmental biology. Elsevier, New York, pp 83–94
Xia Y, McMillin JB, Lewis A, Moore M, Zhu WG, Williams RS, Kellems RE (2000) Electrical stimulation of neonatal cardiac myocytes activates the NFAT3 and GATA4 pathways and up-regulates the adenylosuccinate synthetase 1 gene. J Biol Chem 275(3):1855–1863
Silverman E, Yivgi-Ohana N, Sher N, Bell M, Eimerl S, Orly J (2006) Transcriptional activation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) gene: GATA-4 and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta confer synergistic responsiveness in hormone-treated rat granulosa and HEK293 cell models. Mol Cell Endocrinol 252(1–2):92–101. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2006.03.008
Yamagata T, Nishida J, Sakai R, Tanaka T, Honda H, Hirano N, Mano H, Yazaki Y, Hirai H (1995) Of the GATA-binding proteins, only GATA-4 selectively regulates the human interleukin-5 gene promoter in interleukin-5-producing cells which express multiple GATA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol 15(7):3830–3839
Molkentin JD, Kalvakolanu DV, Markham BE (1994) Transcription factor GATA-4 regulates cardiac muscle-specific expression of the alpha-myosin heavy-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol 14(7):4947–4957
Yue F, Zhou Z, Wang L, Wang M, Song L (2014) A conserved zinc finger transcription factor GATA involving in the hemocyte production of scallop Chlamys farreri. Fish Shellfish Immunol 39(2):125–135. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.05.010
Tao YF, Fang F, Hu SY, Lu J, Cao L, Zhao WL, Xiao PF, Li ZH, Wang NN, Xu LX, Du XJ, Sun LC, Li YH, Li YP, Xu YY, Ni J, Wang J, Feng X, Pan J (2015) Hypermethylation of the GATA binding protein 4 (GATA4) promoter in Chinese pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Cancer 15:756. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1760-5
Ip HS, Wilson DB, Heikinheimo M, Tang Z, Ting C-N, Simon MC, Leiden JM, Parmacek MS (1994) The GATA-4 transcription factor transactivates the cardiac muscle-specific troponin C promoter-enhancer in nonmuscle cells. Mol Cell Biol 14(11):7517–7526
Stocco C (2004) In vivo and in vitro inhibition of cyp19 gene expression by prostaglandin F2α in murine luteal cells: implication of GATA-4. Endocrinology 145(11):4957–4966
Peng L, Huang Y, Jin F, Jiang S-W, Payne AH (2004) Transcription enhancer factor-5 and a GATA-like protein determine placental-specific expression of the type I human 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene, HSD3B1. Mol Endocrinol 18(8):2049–2060
Shih M-CM, Chiu Y-N, Hu M-C, Guo C, Chung B-c (2011) Regulation of steroid production: analysis of Cyp11a1 promoter. Mol Cell Endocrinol 336(1–2):80–84
Sher N, Yivgi-Ohana N, Orly J (2007) Transcriptional regulation of the cholesterol side chain cleavage cytochrome P450 gene (CYP11A1) revisited: binding of GATA, cyclic adenosine 3′, 5′-monophosphate response element-binding protein and activating protein (AP)-1 proteins to a distal novel cluster of cis-regulatory elements potentiates AP-2 and steroidogenic factor-1-dependent gene expression in the rodent placenta and ovary. Mol Endocrinol 21(4):948–962
Tremblay JJ, Viger RS (1999) Transcription factor GATA-4 enhances Mullerian inhibiting substance gene transcription through a direct interaction with the nuclear receptor SF-1. Mol Endocrinol 13(8):1388–1401
Charron F, Paradis P, Bronchain O, Nemer G, Nemer M (1999) Cooperative interaction between GATA-4 and GATA-6 regulates myocardial gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 19(6):4355–4365
Heicklen-Klein A, Evans T (2004) T-box binding sites are required for activity of a cardiac GATA-4 enhancer. Dev Biol 267(2):490–504. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.09.042
Mukhopadhyay I, Nazir A, Saxena DK, Chowdhuri DK (2003) Heat shock response: hsp70 in environmental monitoring. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 17(5):249–254. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.10086
Broderick TL, Jankowski M, Wang D, Danalache BA, Parrott CR, Gutkowska J (2012) Downregulation in GATA4 and downstream structural and contractile genes in the db/db mouse heart. ISRN Endocrinol 2012:736860. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/736860
Aries A, Whitcomb J, Shao W, Komati H, Saleh M, Nemer M (2014) Caspase-1 cleavage of transcription factor GATA4 and regulation of cardiac cell fate. Cell Death Dis 5(12):e1566
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41476100), the Key Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. S2013020012720), and Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (2019B020217001), as well as the Shellfish and Large Algae Industry Innovation Team Project of Guangdong Province (2019KJ146).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Informed consent
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all authors.
Research involving in human and animal rights
No human participants and/or animals involved.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, T., Xu, D., Cui, M. et al. The transcriptional factor GATA-4 negatively regulates Hsp70 transcription in Crassostrea hongkongensis. Mol Biol Rep 47, 7107–7114 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05778-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05778-9