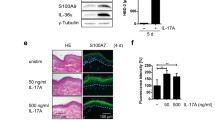
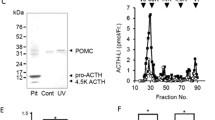
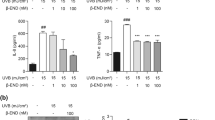
Abstract
Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is a large precursor protein of and β-endorphin. POMC expressed in keratinocytes regulates various pathophysiological responses, such as pruritus in atopic dermatitis. Interleukin (IL)-31 is a T helper 2 (Th2)-derived cytokine that functions as a pruritogen, stimulating the sensory neurons in the skin. However, the regulatory mechanism underlying IL-31-induced POMC expression in keratinocytes remains largely unknown. Herein, using a 5′-serial deletion and site-specific mutation constructs of the regulatory region of POMC, we demonstrated that a putative EGR1-binding sequence (EBS) motif in POMC is required for its upregulation by IL-31 in HaCaT keratinocytes. Notably, EGR-1 directly interacted with the EBS motif in POMC. The ectopic expression of EGR-1 stimulated the POMC promoter activity, whereas the knockdown of EGR-1 expression by RNA interference reduced IL-31-induced POMC expression. Furthermore, we observed that three major mitogen-activated protein kinases, ERK, JNK, and p38 kinase, mediated IL-31-induced EGR-1 expression. In summary, our results suggest that EGR-1 trans-activates POMC in response to IL-31 stimulation in HaCaT keratinocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- ANOVA:
-
One-way analysis of variance
- EGR1:
-
Early growth response 1
- EBS:
-
EGR-1-binding sequence
- EMSA:
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IL-31:
-
Interleukin 31
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MEK:
-
MAPK kinase
- MSH:
-
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
- POMC:
-
Pro-opiomelanocortin
- QR-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- TSLP:
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin
References
Barker JN, Mitra RS, Griffiths CE, Dixit VM, Nickoloff BJ (1991) Keratinocytes as initiators of inflammation. Lancet 337(8735):211–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(91)92168-2
Zeidler C, Pereira MP, Huet F, Misery L, Steinbrink K, Stander S (2019) Pruritus in autoimmune and inflammatory dermatoses. Front Immunol 10:1303. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01303
Mollanazar NK, Smith PK, Yosipovitch G (2016) Mediators of chronic pruritus in atopic dermatitis: getting the itch out? Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 51(3):263–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-015-8488-5
Xie B, Li XY (2019) Inflammatory mediators causing cutaneous chronic itch in some diseases via transient receptor potential channel subfamily V member 1 and subfamily A member 1. J Dermatol 46(3):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.14749
Candler T, Kuhnen P, Prentice AM, Silver M (2019) Epigenetic regulation of POMC; implications for nutritional programming, obesity and metabolic disease. Front Neuroendocrinol 54:100773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2019.100773
Maranduca MA, Branisteanu D, Serban DN, Branisteanu DC, Stoleriu G, Manolache N, Serban IL (2019) Synthesis and physiological implications of melanic pigments. Oncol Lett 17(5):4183–4187. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10071
Slominski A, Wortsman J, Luger T, Paus R, Solomon S (2000) Corticotropin releasing hormone and proopiomelanocortin involvement in the cutaneous response to stress. Physiol Rev 80(3):979–1020. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.2000.80.3.979
Wintzen M, Yaar M, Burbach JP, Gilchrest BA (1996) Proopiomelanocortin gene product regulation in keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 106(4):673–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/1523-1747.ep12345496
Rousseau K, Kauser S, Pritchard LE, Warhurst A, Oliver RL, Slominski A, Wei ET, Thody AJ, Tobin DJ, White A (2007) Proopiomelanocortin (POMC), the ACTH/melanocortin precursor, is secreted by human epidermal keratinocytes and melanocytes and stimulates melanogenesis. FASEB J 21(8):1844–1856. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-7398com
Schauer E, Trautinger F, Kock A, Schwarz A, Bhardwaj R, Simon M, Ansel JC, Schwarz T, Luger TA (1994) Proopiomelanocortin-derived peptides are synthesized and released by human keratinocytes. J Clin Invest 93(5):2258–2262. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI117224
Harno E, Gali Ramamoorthy T, Coll AP, White A (2018) POMC: the physiological power of hormone processing. Physiol Rev 98(4):2381–2430. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00024.2017
Tominaga M, Ogawa H, Takamori K (2007) Possible roles of epidermal opioid systems in pruritus of atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 127(9):2228–2235. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5700942
Wang W, Guo DY, Lin YJ, Tao YX (2019) Melanocortin regulation of inflammation. Front Endocrinol 10:683. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00683
Dillon SR, Sprecher C, Hammond A, Bilsborough J, Rosenfeld-Franklin M, Presnell SR, Haugen HS, Maurer M, Harder B, Johnston J, Bort S, Mudri S, Kuijper JL, Bukowski T, Shea P, Dong DL, Dasovich M, Grant FJ, Lockwood L, Levin SD, LeCiel C, Waggie K, Day H, Topouzis S, Kramer J, Kuestner R, Chen Z, Foster D, Parrish-Novak J, Gross JA (2004) Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces dermatitis in mice. Nat Immunol 5(7):752–760. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1084
Matsuda H, Watanabe N, Geba GP, Sperl J, Tsudzuki M, Hiroi J, Matsumoto M, Ushio H, Saito S, Askenase PW, Ra C (1997) Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion with IgE hyperproduction in NC/Nga miceInt Immunol 9(3):461–466. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/9.3.461
Takaoka A, Arai I, Sugimoto M, Yamaguchi A, Tanaka M, Nakaike S (2005) Expression of IL-31 gene transcripts in NC/Nga mice with atopic dermatitis. Eur J Pharmacol 516(2):180–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.04.040
Silverberg JI, Pinter A, Pulka G, Poulin Y, Bouaziz JD, Wollenberg A, Murrell DF, Alexis A, Lindsey L, Ahmad F, Piketty C, Clucas A (2020) Phase 2B randomized study of nemolizumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis and severe pruritus. J Allergy Clin Immunol 145(1):173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2019.08.013
Cevikbas F, Wang X, Akiyama T, Kempkes C, Savinko T, Antal A, Kukova G, Buhl T, Ikoma A, Buddenkotte J, Soumelis V, Feld M, Alenius H, Dillon SR, Carstens E, Homey B, Basbaum A, Steinhoff M (2014) A sensory neuron-expressed IL-31 receptor mediates T helper cell-dependent itch: involvement of TRPV1 and TRPA1. J Allergy Clin Immunol 133(2):448–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.10.048
Lee CH, Hong CH, Yu WT, Chuang HY, Huang SK, Chen GS, Yoshioka T, Sakata M, Liao WT, Ko YC, Yu HS (2012) Mechanistic correlations between two itch biomarkers, cytokine interleukin-31 and neuropeptide beta-endorphin, via STAT3/calcium axis in atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 167(4):794–803. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11047.x
Xu AW, Ste-Marie L, Kaelin CB, Barsh GS (2007) Inactivation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in proopiomelanocortin (Pomc) neurons causes decreased pomc expression, mild obesity, and defects in compensatory refeeding. Endocrinology 148(1):72–80. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2006-1119
Ernst MB, Wunderlich CM, Hess S, Paehler M, Mesaros A, Koralov SB, Kleinridders A, Husch A, Munzberg H, Hampel B, Alber J, Kloppenburg P, Bruning JC, Wunderlich FT (2009) Enhanced Stat3 activation in POMC neurons provokes negative feedback inhibition of leptin and insulin signaling in obesity. J Neurosci 29(37):11582–11593
Kim J, Jung E, Choi J, Min DY, Lee YH, Shin SY (2019) Leptin is a direct transcriptional target of EGR1 in human breast cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 46(1):317–324
Shin SY, Kim JH, Baker A, Lim Y, Lee YH (2010) Transcription factor Egr-1 is essential for maximal matrix metalloproteinase-9 transcription by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mol Cancer Res 8(4):507–519
Singh B, Jegga AG, Shanmukhappa KS, Edukulla R, Khurana Hershey GH, Medvedovic M, Dillon SR, Madala SK (2016) IL-31-driven skin remodeling involves epidermal cell proliferation and thickening that lead to impaired skin-barrier function. PLoS ONE 11(8):e0161877
Shin SY, Lee JM, Lim Y, Lee YH (2013) Transcriptional regulation of the growth-regulated oncogene alpha gene by early growth response protein-1 in response to tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1829(10):1066–1074
Son SW, Min BW, Lim Y, Lee YH, Shin SY (2008) Regulatory mechanism of TNFalpha autoregulation in HaCaT cells: the role of the transcription factor EGR-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374(4):777–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.07.117
Yan SF, Fujita T, Lu J, Okada K, Shan Zou Y, Mackman N, Pinsky DJ, Stern DM (2000) Egr-1, a master switch coordinating upregulation of divergent gene families underlying ischemic stress. Nat Med 6(12):1355–1361. https://doi.org/10.1038/82168
Shin SY, Kim HW, Jang HH, Hwang YJ, Choe JS, Kim JB, Lim Y, Lee YH (2017) gamma-Oryzanol suppresses COX-2 expression by inhibiting reactive oxygen species-mediated Erk1/2 and Egr-1 signaling in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 491(2):486–492
Cornelissen C, Luscher-Firzlaff J, Baron JM, Luscher B (2012) Signaling by IL-31 and functional consequences. Eur J Cell Biol 91(6–7):552–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.07.006
Che DN, Cho BO, Shin JY, Kang HJ, Kim JS, Oh H, Kim YS, Jang SI (2019) Apigenin inhibits IL-31 cytokine in human mast cell and mouse skin tissues. Molecules 24(7):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071290
Ip WK, Wong CK, Li ML, Li PW, Cheung PF, Lam CW (2007) Interleukin-31 induces cytokine and chemokine production from human bronchial epithelial cells through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathways: implications for the allergic response. Immunology 122(4):532–541. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02668.x
Dambacher J, Beigel F, Seiderer J, Haller D, Goke B, Auernhammer CJ, Brand S (2007) Interleukin 31 mediates MAP kinase and STAT1/3 activation in intestinal epithelial cells and its expression is upregulated in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 56(9):1257–1265. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2006.118679
Glinski W, Brodecka H, Glinska-Ferenz M, Kowalski D (1994) Increased concentration of beta-endorphin in sera of patients with psoriasis and other inflammatory dermatoses. Br J Dermatol 131(2):260–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1994.tb08502.x
Lee CH, Chuang HY, Shih CC, Jong SB, Chang CH, Yu HS (2006) Transepidermal water loss, serum IgE and beta-endorphin as important and independent biological markers for development of itch intensity in atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 154(6):1100–1107. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07191.x
Ryu WI, Lee H, Kim JH, Bae HC, Ryu HJ, Son SW (2015) IL-33 induces Egr-1-dependent TSLP expression via the MAPK pathways in human keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol 24(11):857–863. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.12788
Jeong SH, Kim HJ, Jang Y, Ryu WI, Lee H, Kim JH, Bae HC, Choi JE, Kye YC, Son SW (2014) Egr-1 is a key regulator of IL-17A-induced psoriasin upregulation in psoriasis. Exp Dermatol 23(12):890–895. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.12554
Hunt G, Todd C, Cresswell JE, Thody AJ (1994) Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone and its analogue Nle4DPhe7 alpha-MSH affect morphology, tyrosinase activity and melanogenesis in cultured human melanocytes. J Cell Sci 107(Pt 1):205–211
Kauser S, Schallreuter KU, Thody AJ, Gummer C, Tobin DJ (2003) Regulation of human epidermal melanocyte biology by beta-endorphin. J Invest Dermatol 120(6):1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12242.x
Ray DW, Gibson S, Crosby SR, Davies D, Davis JR, White A (1995) Elevated levels of adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) precursors in post-adrenalectomy Cushing’s disease and their regulation by glucocorticoids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80(8):2430–2436. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.80.8.7629238
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (Grant No. NRF-2018R1A2B2004653). This paper was supported by the KU Research Professor Program of Konkuk University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY constructed the promoter reports and performed the reporter assays. SSA performed the DNA-protein binding experiments and immunoblotting. YHL designed the experiments and analyzed the data. SYS conceived and supervised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval and informed consent were not required for this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeo, H., Ahn, S.S., Lee, Y.H. et al. Regulation of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) gene transcription by interleukin-31 via early growth response 1 (EGR-1) in HaCaT keratinocytes. Mol Biol Rep 47, 5953–5962 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05668-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05668-0