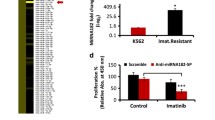
Abstract
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a malignant transformation with uncontrolled proliferation of lymphoid precursor cells within bone marrow including a dismal prognosis after relapse. Survival of a population of quiescent leukemia stem cells (LSCs, also termed leukemia-initiating cells (LICs)) after treatment is one of the relapse reasons in Ph+ ALL patient. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are known as highly conserved 19–24 nucleotides non-protein-coding small RNAs that regulate the expression of human genes. miRNAs are often involved in the tuning of hematopoiesis. Therefore, the deregulation of miRNA expression and function in hematopoietic cells can cause cancer and promote its progression. This is the first comprehensive analysis of miRNA expression differences between CD34+CD38− LSCs and CD34+CD38+ leukemic progenitors (LPs) from the same Ph+ B-ALL bone marrow samples using high-throughput sequencing technologies. We identified multiple differentially expressed miRNAs including hsa-miR-3143, hsa-miR-6503-3p, hsa-miR-744-3p, hsa-miR-1226-3p, hsa-miR-10a-5p, hsa-miR-4658 and hsa-miR-493-3p related to LSC and LP populations which have regulatory functions in stem-cell associated biological processes. The deregulation of these miRNAs could affect leukemogenesis, clonogenic and stemness capacities in these subpopulations of Ph+ B-ALL. Therefore, identification of these LSC associated miRNAs may improve the diagnosis and management of B-ALL. These findings may also lead to future strategies to eliminate the presence of resistant LSCs, either by induction of apoptosis or by sensitizing these cells to chemotherapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Purizaca J, Meza I, Pelayo R (2012) Early Lymphoid Development and Microenvironmental Cues in B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Arch Med Res 43:89–101
Pérez-Vera P, Reyes-León A, Fuentes-Pananá E (2011) Signaling Proteins and Transcription Factors in Normal and Malignant Early B Cell Development. Bone Marrow Res 2011:1–10
Liew E, Atenafu E, Schimmer A, Yee K, Schuh A, Minden M, Gupta V, Brandwein J (2012) Outcomes of adult patients with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia following frontline treatment with a pediatric regimen. Leuk Res 36:1517–1520
Bassan R, Hoelzer D (2011) Modern Therapy of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J Clin Oncol 29:532–543
Hoelzer D (2006) Advances in the management of Ph-positive ALL. Clin. Adv. Hematol Oncol 4:804–805
Kong Y, Wu Y, Song Y, Shi M, Cao X, Zhao H, Qin Y, Lai Y, Jiang H, Jiang Q, Huang XJ (2017) Ruxolitinib/nilotinib cotreatment inhibits leukemia-propagating cells in Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL. Journal of Translational Medicine 15:184
Eppert K, Takenaka K, Lechman ER, Waldron L, Nilsson B, van Galen P, Metzeler KH, Poeppl A, Ling V, Beyene J, Canty AJ, Danska JS, Bohlander SK, Buske C, Minden MD, Golub TR, Jurisica I, Ebert BL, Dick JE (2011) Stem cell gene expression programs influence clinical outcome in human leukemia. Nat Med 17:1086–1093
Gentles A (2010) Association of a Leukemic Stem Cell Gene Expression Signature With Clinical Outcomes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. JAMA 304:2706
Jiang Z, Deng M, Wei X, Ye W, Xiao Y, Lin S, Wang S, Li B, Liu X, Zhang G, Lai P, Weng J, Wu D, Chen H, Wei W, Ma Y, Li Y, Liu P, Du X, Pei D, Yao Y, Xu B, Li P (2016) Heterogeneity of CD34 and CD38 expression in acute B lymphoblastic leukemia cells is reversible and not hierarchically organized. J Hematol Oncol 9:94
Herrmann H, Sadovnik I, Cerny-Reiterer S, Rulicke T, Stefanzl G, Willmann M, Hoermann G, Bilban M, Blatt K, Herndlhofer S, Mayerhofer M, Streubel B, Sperr WR, Holyoake TL, Mannhalter C, Valent P (2014) Dipeptidylpeptidase IV (CD26) defines leukemic stem cells (LSC) in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 123:3951–3962
de Leeuw D, Denkers F, Olthof M, Rutten A, Pouwels W, Jan Schuurhuis G, Ossenkoppele G, Smit L (2014) Attenuation of microRNA-126 Expression That Drives CD34 + 38- Stem/Progenitor Cells in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Leads to Tumor Eradication. Can Res 74:2094–2105
Cobaleda C, Gutierrez-Cianca N, Perez-Losada J, Flores T, Garcia-Sanz R, Gonzalez M, Sanchez-Garcia I (2000) A primitive hematopoietic cell is the target for the leukemic transformation in human philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 95:2211
le Viseur C, Hotfilder M, Bomken S, Wilson K, Röttgers S, Schrauder A, Rosemann A, Irving J, Stam RW, Shultz LD, Harbott J, Jürgens H, Schrappe M, Pieters R, Vormoor J (2008) In Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Blasts at Different Stages of Immunophenotypic Maturation Have Stem Cell Properties. Cancer Cell 14:47–58
Jiang Z, Wu D, Lin S, Li P (2016) CD34 and CD38 are prognostic biomarkers for acute B lymphoblastic leukemia. Biomarker Research 4:23
Guo H, Ingolia N, Weissman J, Bartel D (2010) Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 466:835–840
Valiollahi E, Behravan J (2016) Leukemogenesis associated miRNAs regulate OSKM and Tp53 genes. Biomedical Research Special Issue: S376-S383
Martiáñez Canales T, de Leeuw D, Vermue E, Ossenkoppele G, Smit L (2017) Specific Depletion of Leukemic Stem Cells: Can MicroRNAs Make the Difference? Cancers 9:74
WangX,ZhuB,HuangZ,ChenL,HeZ,ZhangH(2014)MicroRNAs as biomarkers in leukemia.Stem Cell Investig 1:11.
Nemes K, Csóka M, Nagy N, Márk Á, Váradi Z, Dankó T, Kovács G, Kopper L, Sebestyén A (2014) Expression of Certain Leukemia/Lymphoma Related microRNAs and its Correlation with Prognosis in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pathology Oncology Research 21:597–604
Ju X, Li D, Shi Q, Hou H, Sun N, Shen B (2009) Differential microrna Expression In Childhood B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 26:1–10
Luna-Aguirre C, de la Luz Martinez-Fierro M, Mar-Aguilar F, Garza-Veloz I, Treviño-Alvarado V, Rojas-Martinez A, Jaime-Perez J, Malagon-Santiago G, Gutierrez-Aguirre C, Gonzalez-Llano O, Salazar-Riojas R, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Martinez-Rodriguez HG, Gomez-Almaguer D, Ortiz-Lopez R (2015) Circulating microRNA expression profile in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Biomarkers 15:299–310
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg S (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R25
Love M, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550
Chou CH, Shrestha S, Yang CD, Chang NW, Lin YL, Liao KW, Huang WC, Sun TH, Tu SJ, Lee WH, Chiew MY, Tai CS, Wei TY, Tsai TR, Huang HT, Wang CY, Wu HY, Ho SY, Chen PR, Chuang CH, Hsieh PJ, Wu YS, Chen WL, Li MJ, Wu YC, Huang XY, Ng FL, Buddhakosai W, Huang PC, Lan KC, Huang CY, Weng SL, Cheng YN, Liang C, Hsu WL, Huang HD (2017) miRTarBase update 2018: a resource for experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D296–D302
Wang J, Vasaikar S, Shi Z, Greer M, Zhang B (2017) WebGestalt 2017: a more comprehensive, powerful, flexible and interactive gene set enrichment analysis toolkit. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W130–W137
Bar M, Wyman SK, Fritz BR, Qi J, Garg KS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Bendoraite A, Mitchell PS, Nelson AM, Ruzzo WL, Ware C, Radich JP, Gentleman R, Ruohola-Baker H, Tewari M (2008) MicroRNA Discovery and Profiling in Human Embryonic Stem Cells by Deep Sequencing of Small RNA Libraries. Stem Cells 26:2496–2505
Glazov E, Cottee P, Barris W, Moore R, Dalrymple B, Tizard M (2008) A microRNA catalog of the developing chicken embryo identified by a deep sequencing approach. Genome Res 18:957–964
Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, Park SY, Namkoong B, Kim DH, Hur K, Yoo MW, Lee HJ, Yang HK, Kim VN (2009) Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 37:1672–1681
Creighton C, Hernandez-Herrera A, Jacobsen A, Levine D, Mankoo P, Schultz N, Du Y, Zhang Y, Larsson E, Sheridan R, Xiao W, Spellman PT, Getz G, Wheeler DA, Perou CM, Gibbs RA, Sander C, Hayes DN, Gunaratne PH (2012) Integrated Analyses of microRNAs Demonstrate Their Widespread Influence on Gene Expression in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 7:e34546
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A, D’Urso L, Collura D, Peschle C, De Maria R, Muto G (2009) The mir-15a/mir-16-1 Cluster Controls Prostate Cancer Progression Control by Targeting of Multiple Oncogenic Activities. The Journal of Urology 181:188
Hashimoto Y, Akiyama Yuasa Y (2013) Multiple-to-Multiple Relationships between MicroRNAs and Target Genes in Gastric Cancer. PLoS ONE 8:e62589
Liu S, Patel SH, Ginestier C, Ibarra I, Martin-Trevino R, Bai S, McDermott SP, Shang L, Ke J, Ou SJ, Heath A, Zhang KJ, Korkaya H, Clouthier SG, Charafe-Jauffret E, Birnbaum D, Hannon GJ, Wicha MS (2012) MicroRNA93 Regulates Proliferation and Differentiation of Normal and Malignant Breast Stem Cells. PLoS Genet 8:e1002751
Yu X (2011) miR-93 suppresses proliferation and colony formation of human colon cancer stem cells. World J Gastroenterol 17:4711
Wang J, Yang I (2016) Development of a deregulating MicroRNA panel for the detection of early relapse in postoperative colorectal cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 61:S180
Wu X, Feng X, Zhao X, Ma F, Liu N, Guo H, Li C, Du H, Zhang B (2016) Role of Beclin-1-Mediated Autophagy in the Survival of Pediatric Leukemia Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 39:1827–1836
Gal H, Pandi G, Kanner A, Ram Z, Lithwick-Yanai G, Amariglio N, Rechavi Givol D (2008) MIR-451 and Imatinib mesylate inhibit tumor growth of Glioblastoma stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376:86–90
Lechman E, Gentner B, Ng S, Schoof E, van Galen P, Kennedy J, Nucera S, Ciceri F, Kaufmann K, Takayama N, Dobson SM, Trotman-Grant A, Krivdova G, Elzinga J, Mitchell A, Nilsson B, Hermans KG, Eppert K, Marke R, Isserlin R, Voisin V, Bader GD, Zandstra PW, Golub TR, Ebert BL, Lu J, Minden M, Wang JC, Naldini L, Dick JE (2016) miR-126 Regulates Distinct Self-Renewal Outcomes in Normal and Malignant Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Cancer Cell 29:602–606
Downing J (2011) A New FOXO Pathway Required for Leukemogenesis. Cell 146:669–670
Burotto M, Chiou V, Lee J, Kohn E (2014) The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: A new perspective. Cancer 120:3446–3456
Martini M, De Santis M, Braccini L, Gulluni F, Hirsch E (2014) PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann Med 46:372–383
Zhou X, Li Zhou J (2017) Tumor necrosis factor α in the onset and progression of leukemia. Exp Hematol 45:17–26
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Research Vice Chancellor of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS), Mashhad, Iran for financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valiollahi, E., Ribera, J.M., Genescà, E. et al. Genome-wide identification of microRNA signatures associated with stem/progenitor cells in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol Biol Rep 46, 1295–1306 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04600-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04600-5