Abstract
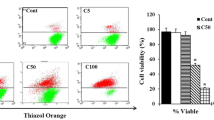
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the diverse potential biological activity of partially purified crude extract (PPCEBS) of marine Bacillus subtilis NMK17 associated with marine sponge Clathria frondifera. Symbionts were isolated from a marine sponge, only the potential strain which exhibited apoptosis was sequenced using 16S rRNA and extract of the active strain was subjected to purification using HPLC. The potential pro-apoptotic role of PPCEBS was investigated in MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line for cytotoxicity by MTT assay, which showed dose-dependent cytotoxicity on 24 h of exposure. The apoptotic findings demonstrated that PPCEBS significantly induces apoptosis, which was characterised by apoptotic morphological changes. Further, an increased expression of the Caspase 3 and Bax whereas decreased Bcl-2 was confirmed by immunofluorescence and western blotting analysis in MCF-7 cell line, which revealed that PPCEBS has potent apoptosis-inducing property. Added to the desirable apoptotic activity, PPCEBS exhibited excellent antibacterial and antioxidant activities too. The pharmacological effect of the marine sponge-associated bacteria from Gulf of Mannar India needs further attention in discovering new bioactive compounds. Our results suggested that the compounds present in the PPCEBS in marine bacterial B. subtilis NMK17 could be candidates for developing an apoptosis-specific drug with minimal toxicity. This study indicated that marine sponge-associated bacteria could be a good source to find the cytotoxic metabolites which would induce apoptosis and cause cancer cell death. Also, this study explores that marine natural products as a potential source of pharmaceuticals.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Franceschi S, Wild CP (2013) Meeting the global demands of epidemiologic transition—the indispensable role of cancer prevention. Mol Oncol 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2012.10.010
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136:E359–E386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Kaliberov SA, Buchsbaum DJ (2012) Cancer treatment with gene therapy and radiation therapy. Adv Cancer Res 115:221–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-398342-8.00007-0
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2013) Natural products: a continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:3670–3695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.02.008
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Keyzers RA, Munro MH, Prinsep MR (2015) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 32:116–211. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NP00144C
Shantikumar SSL, Baruah I, Bora TC (2006) Actinomycetes of Loktak habitat: isolation and screening for antimicrobial activities. Biotechnology 5:217–221. https://doi.org/10.3923/biotech.2006.217.221
Bernardes N, Seruca R, Chakrabarty AM, Fialho AM (2010) Microbial-based therapy of cancer: current progress and future prospects. Bioeng Bugs 1:178–190. https://doi.org/10.4161/bbug.1.3.10903
Nagle DG, Zhou YD, Mora FD, Mohammed KA, Kim YP (2004) Mechanism targeted discovery of antitumor marine natural products. Curr Med Chem 11:1725–1756. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867043364991
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Keyzers RA, Munro MHG, Prinsep MR (2017) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 34:235–294. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6np00124f
Skariyachan S, Roa GA, Patil MR, Saikia B, Bharadwaj Kn V, Rao Gs J (2014) Antimicrobial potential of metabolites extracted from bacterial symbionts associated with marine sponges in coastal area of Gulf of Mannar Biosphere, India. Lett Appl Microbiol 58:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12178
Mohan G, Thipparamalai Thangappanpillai AK, Ramasamy B (2016) Antimicrobial activities of secondary metabolites and phylogenetic study of sponge endosymbiotic bacteria, Bacillus sp. at Agatti Island, Lakshadweep Archipelago. Biotechnol Rep (Amst) 11:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2016.06.001
Aoki S, Cao L, Matsui K, Rachmat R, Akiyama S-i, Kobayashi M (2004) Kendarimide A, a novel peptide reversing P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in tumor cells, from a marine sponge of Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 60:7053–7059. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TET.2003.07.020
Shigemori H, Bae MA, Yazawa K, Sasaki T, Kobayashi J (1992) Alteramide A, a new tetracyclic alkaloid from a bacterium Alteromonas sp. associated with the marine sponge Halichondria okadai. J Org Chem 57:4317–4320. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00041a053
Mondol MA, Shin HJ, Islam MT (2013) Diversity of secondary metabolites from marine Bacillus species: chemistry and biological activity. Mar Drugs 11:2846–2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11082846
Dhinakaran ID, Lipton AP (2012) Antifungal and cytotoxic activities of some marine sponges collected from the south east coast of India. J Appl Pharm Sci 2:52–55
Hooper JNA (2000) ‘Sponguide’ guide to sponge collection and identification version. Queensland museum, South Brisbane
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, pp 115–175
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Samarakoon K, Senevirathne M, Lee WW, Kim YT, Kim JI, Oh MC, Jeon YJ (2012) Antibacterial effect of citrus press-cakes dried by high speed and far-infrared radiation drying methods. Nutr Res Pract 6:187–194. https://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2012.6.3.187
Sowmya Shree G, Yogendra Prasad K, Arpitha HS, Deepika UR, Nawneet Kumar K, Mondal P, Ganesan P (2017) Beta-carotene at physiologically attainable concentration induces apoptosis and down-regulates cell survival and antioxidant markers in human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells. Mol Cell Biochem 436:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3071-4
Muthiyan R, Nambikkairaj B, Mahanta N, Immanuel T, Mandal RS, Kumaran K, De AK (2017) Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of marine sponge hyrtios erectus extract on breast carcinoma cell line (MCF-7). Pharmacogn Mag 13:S41–S47. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.203983
Shimada K, Fujikawa K, Yahara K, Nakamura T (1992) Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the autoxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J Agric Food Chem 40:945–948. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00018a005
Bansal P, Paul P, Nayak PG, Pannakal ST, Zou J-h, Laatsch H, Priyadarsini KI, Unnikrishnan MK (2011) Phenolic compounds isolated from Pilea microphylla prevent radiation-induced cellular DNA damage. Acta Pharm Sinica B 1:226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2011.10.006
Eloff JN (1998) A sensitive and quick microplate method to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration of plant extracts for bacteria. Planta Med 64:711–713
Alshatwi AA, Subash-Babu P, Antonisamy P (2016) Violacein induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells through up regulation of BAX, p53 and down regulation of MDM2. Exp Toxicol Pathol 68:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2015.10.002
Leite M, Quinta-Costa M, Leite PS, Guimaraes JE (1999) Critical evaluation of techniques to detect and measure cell death–study in a model of UV radiation of the leukaemic cell line HL60. Anal Cell Pathol 19:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1155/1999/ 176515
Cantz T, Key G, Bleidissel M, Gentile L, Han DW, Brenne A, Scholer HR (2008) Absence of OCT4 expression in somatic tumor cell lines. Stem Cells 26:692–697. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2007-0657
Madankumar A, Tamilarasi S, Premkumar T, Gopikrishnan M, Nagabhishek N, Devaki T (2017) Geraniol attenuates 4NQO-induced tongue carcinogenesis through downregulating the activation of NF-kB in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 434:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3030-0
Fink SL, Cookson BT (2005) Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun 73:1907–1916. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.73.4.1907-1916.2005
Afsar T, Trembley JH, Salomon CE, Razak S, Khan MR, Ahmed K (2016) Growth inhibition and apoptosis in cancer cells induced by polyphenolic compounds of Acacia hydaspica: involvement of multiple signal transduction pathways. Sci Rep 6:23077. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23077
Chae S, Kim JS, Kang KA, Bu HD, Lee Y, Hyun JW, Kang SS (2004) Antioxidant activity of jionoside D from Clerodendron trichotomum. Biol Pharm Bull 27:1504–1508. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.27.1504
Arun J, Selvakumar S, Sathishkumar R, Moovendhan M, Ananthan G, Maruthiah T, Palavesam A (2017) In vitro antioxidant activities of an exopolysaccharide from a salt pan bacterium Halolactibacillus miurensis. Carbohydr Polym 155:400–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.085
Abdhul K, Ganesh M, Shanmughapriya S, Kanagavel M, Anbarasu K, Natarajaseenivasan K (2014) Antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharide from probiotic strain Enterococcus faecium (BDU7) from Ngari. Int J Biol Macromol 70:450–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.07.026
Bultel-Ponce VV, Berge JP, Debitus C, Nicolas JL, Guyot M (1999) Metabolites from the sponge-associated bacterium Pseudomonas Species. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 1:384–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011792
Armstrong E, Yan L, Boyd KG, Wright PC, Burgess JG (2001) The symbiotic role of marine microbes on living surfaces. Hydrobiologia 461:37–40. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012756913566
Li JW, Vederas JC (2009) Drug discovery and natural products: end of an era or an endless frontier? Science 325:161–165. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1168243
Nies DH (1999) Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:730–750
Azumi M, Ogawa KI, Fujita T, Takeshita M, Yoshida R, Furumai T, Igarashi Y (2008) Bacilosarcins A and B, novel bioactive isocoumarins with unusual heterocyclic cores from the marine-derived bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Tetrahedron 64:6420–6425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2008.04.076
Li D, Carr G, Zhang Y, Williams DE, AmLani A, Bottriell H, Mui AL, Andersen RJ (2011) Turnagainolides A and B, cyclic depsipeptides produced in culture by a Bacillus sp.: isolation, structure elucidation, and synthesis. J Nat Prod 74:1093–1099. https://doi.org/10.1021/np200033y
Trischman JA, Jensen PR, Fenical W (1994) Halobacillin: a cytotoxic cyclic acylpeptide of the iturin class produced by a marine Bacillus. Tetrahedron Lett 35:5571–5574. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(00)77249-2
Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, Albertini AM, Alloni G, Azevedo V, Bertero MG et al (1997) The complete genome sequence of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Nature 390:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1038/36786
Gao CH, Tian XP, Qi SH, Luo XM, Wang P, Zhang S (2010) Antibacterial and antilarval compounds from marine gorgonian-associated bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SCSIO 00856. J Antibiot 63:191. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2010.7
Barsby T, Kelly MT, Gagne SM, Andersen RJ (2001) Bogorol A produced in culture by a marine Bacillus sp. reveals a novel template for cationic peptide antibiotics. Org Lett 3:437–440. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol006942q
Gerard J, Haden P, Kelly MT, Andersen RJ (1996) Loloatin B, A cyclic decapeptide antibiotic produced in culture by a tropical marine bacterium. Tetrahedron Lett 37:7201–7204. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-4039(96)01624-3
Zhang HL, Hua HM, Pei YH, Yao XS (2004) Three new cytotoxic cyclic acylpeptides from marine Bacillus sp. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 52:1029–1030. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.52.1029
Cane DE, Walsh CT (1999) The parallel and convergent universes of polyketide synthases and nonribosomal peptide synthetases. Chem Bio l6:R319–R325
Lin J, Yan XJ, Zheng L, Ma HH, Chen HM (2005) Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction of some selected marine bacteria metabolites. J Appl Microbiol 99:1373–1382. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02741.x
Wang H, Haridas V, Gutterman JU, Xu ZX (2010) Natural triterpenoid avicins selectively induce tumor cell death. Commun Integr Biol 3:205–208
Jeong JK, Gurunathan S, Kang MH, Han JW, Das J, Choi YJ, Kwon DN, Cho SG, Park C, Seo HG, Song H, Kim JH (2016) Hypoxia-mediated autophagic flux inhibits silver nanoparticle-triggered apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Sci Rep 6:21688. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21688
Akram M, Iqbal M, Daniyal M, Khan AU (2017) Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer. Biol Res 50:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-017-0140-9
Nobili S, Lippi D, Witort E, Donnini M, Bausi L, Mini E, Capaccioli S (2009) Natural compounds for cancer treatment and prevention. Pharmacol Res 59:365–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2009.01.017
Hata AN, Engelman JA, Faber AC (2015) The BCL2 family: key mediators of the apoptotic response to targeted anticancer therapeutics. Cancer Discov 5:475–487. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0011
Nami Y, Abdullah N, Haghshenas B, Radiah D, Rosli R, Yari Khosroushahi A (2014) A newly isolated probiotic Enterococcus faecalis strain from vagina microbiota enhances apoptosis of human cancer cells. J Appl Microbiol 117:498–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12531.
Naseri MH, Mahdavi M, Davoodi J, Tackallou SH, Goudarzvand M, Neishabouri SH (2015) Up regulation of Bax and down regulation of Bcl2 during 3-NC mediated apoptosis in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int 15:55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-015-0204-2
Parrish AB, Freel CD, Kornbluth S (2013) Cellular mechanisms controlling caspase activation and function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008672
Kim CG, Castro-Aceituno V, Abbai R, Lee HA, Simu SY, Han Y, Hurh J, Kim YJ, Yang DC (2018) Caspase-3/MAPK pathways as main regulators of the apoptotic effect of the phyto-mediated synthesized silver nanoparticle from dried stem of Eleutherococcus senticosus in human cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother 99:128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.050.
Choi EJ, Park JS, Kim YJ, Jung JH, Lee JK, Kwon HC, Yang HO (2011) Apoptosis-inducing effect of diketopiperazine disulfides produced by Aspergillus sp. KMD 901 isolated from marine sediment on HCT116 colon cancer cell lines. J Appl Microbiol 110:304–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04885.x
Ajji PK, Binder MJ, Walder K, Puri M (2017) Balsamin induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells via DNA fragmentation and cell cycle arrest. Mol Cell Biochem 432, 189–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3009-x
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author is grateful to the grant sanctioned by Department of science and technology, Govt of India under Start-up research grant (young scientist) DST-SERB (SB/YS/LS-101/2014). The authors wish to thank Dr Siva Leela, Scientist-C, Zoological survey of India, Chennai for her support for the identification of marine sponge species. The author also thank Dr.R.Rajesh Kannan for the usage HPLC facility and Mr.Arul maximus rebel for the technical help to obtain SEM images at Sathyabama Institute of science and technology, Chennai. India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirpu Natesh, N., Arumugam, M. & Karanam, G. Apoptotic role of marine sponge symbiont Bacillus subtilis NMK17 through the activation of caspase-3 in human breast cancer cell line. Mol Biol Rep 45, 2641–2651 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4434-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4434-y