Abstract
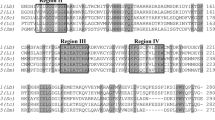
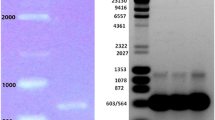
Leishmaniasis, a neglected tropical disease, is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Of the three main clinical forms, cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) is the most common and 40 million people are at risk in the endemic areas. Currently, the available drugs to fight leishmaniasis have high toxicity and poor efficiency. Then, it is very important to search for effective and safe drugs that would target essential enzymes from the parasite, such as lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (CYP51, EC 1.14.13.70) from Leishmania braziliensis. Because most drug design efforts have been directed for Leishmania non-braziliensis species, there is no structural or kinetic data regarding L. braziliensis CYP51. Herein, we present for the first time molecular biology efforts and purification protocol to obtain the enzyme LbCYP51. These results lay the ground for future investigation of drugs against this target.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodrigues JC, Godinho JL, de Souza W (2014) Biology of human pathogenic trypanosomatids: epidemiology, lifecycle and ultrastructure. Subcell Biochem 74:1–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7305-9_1
Jain K, Jain NK (2015) Vaccines for visceral leishmaniasis: a review. J Immunol Methods 422:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2015.03.017
Hotez PJ, Molyneux DH, Fenwick A, Ottesen E, Ehrlich Sachs S, Sachs JD (2006) Incorporating a rapid-impact package for neglected tropical diseases with programs for HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria. PLoS Med 3(5):e102. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0030102
Croft SL, Coombs GH (2003) Leishmaniasis–current chemotherapy and recent advances in the search for novel drugs. Trends Parasitol 19(11):502–508
Alvar J, Velez ID, Bern C, Herrero M, Desjeux P, Cano J, Jannin J, den Boer M, Team WHOLC. (2012) Leishmaniasis worldwide and global estimates of its incidence. PLoS ONE 7(5):e35671. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035671
Sundar S, Chakravarty J (2013) Leishmaniasis: an update of current pharmacotherapy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 14(1):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.2013.755515
Burrows JN, Elliott RL, Kaneko T, Mowbray CE, Waterson D (2014) The role of modern drug discovery in the fight against neglected and tropical diseases. MedChemComm 5(6):688–700. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4MD00011K
Lima EB, Porto C, Motta JOCD, Sampaio RNR (2007) Tratamento da Leishmaniose Tegumentar Americana. An Brasileiros de Dermatol 82:111–124
Kedzierski L, Zhu Y, Handman E (2006) Leishmania vaccines: progress and problems. Parasitology 133:S87-112. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182006001831
Sundar S, Singh A, Singh OP (2014) Strategies to overcome antileishmanial drugs unresponsiveness. J Trop Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/646932
Romero AH, Medina R, Alcala A, Garcia-Marchan Y, Nunez-Duran J, Leanez J, Mijoba A, Ciangherotti C, Serrano-Martin X, Lopez SE (2017) Design, synthesis, structure-activity relationship and mechanism of action studies of a series of 4-chloro-1-phthalazinyl hydrazones as a potent agent against Leishmania braziliensis. Eur J Med Chem 127:606–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.01.022
Alzahrani KJH, Ali JAM, Eze AA, Looi WL, Tagoe DNA, Creek DJ, Barrett MP, de Koning HP (2017) Functional and genetic evidence that nucleoside transport is highly conserved in Leishmania species: implications for pyrimidine-based chemotherapy. Int J Parasitol 7(2):206–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpddr.2017.04.003
Aoun K, Bouratbine A (2014) Cutaneous leishmaniasis in North Africa: a review. Parasite 21:14. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2014014
Lepesheva GI, Virus C, Waterman MR (2003) Conservation in the CYP51 family. Role of the B’ helix/BC loop and helices F and G in enzymatic function. Biochemistry 42(30):9091–9101. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi034663f
Aoyama Y, Yoshida Y, Sonoda Y, Sato Y (1989) Deformylation of 32-oxo-24,25-dihydrolanosterol by the purified cytochrome P-45014DM (lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylase) from yeast evidence confirming the intermediate step of lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylation. J Biol Chem 264(31):18502–18505
Fischer RT, Stam SH, Johnson PR, Ko SS, Magolda RL, Gaylor JL, Trzaskos JM (1989) Mechanistic studies of lanosterol 14 alpha-methyl demethylase: substrate requirements for the component reactions catalyzed by a single cytochrome P-450 isozyme. J Lipid Res 30(10):1621–1632
Shyadehi AZ, Lamb DC, Kelly SL, Kelly DE, Schunck WH, Wright JN, Corina D, Akhtar M (1996) The mechanism of the acyl-carbon bond cleavage reaction catalyzed by recombinant sterol 14 alpha-demethylase of Candida albicans (other names are: lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylase, P-45014DM, and CYP51). J Biol Chem 271(21):12445–12450
Hargrove TY, Wawrzak Z, Liu J, Nes WD, Waterman MR, Lepesheva GI (2011) Substrate preferences and catalytic parameters determined by structural characteristics of sterol 14alpha-demethylase (CYP51) from Leishmania infantum. J Biol Chem 286(30):26838–26848. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.237099
Lepesheva GI, Park HW, Hargrove TY, Vanhollebeke B, Wawrzak Z, Harp JM, Sundaramoorthy M, Nes WD, Pays E, Chaudhuri M, Villalta F, Waterman MR (2010) Crystal structures of Trypanosoma brucei sterol 14alpha-demethylase and implications for selective treatment of human infections. J Biol Chem 285(3):1773–1780. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.067470
Lepesheva GI, Hargrove TY, Kleshchenko Y, Nes WD, Villalta F, Waterman MR (2008) CYP51: a major drug target in the cytochrome P450 superfamily. Lipids 43(12):1117–1125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-008-3225-y
Lepesheva GI, Waterman MR (2011) Sterol 14alpha-demethylase (CYP51) as a therapeutic target for human trypanosomiasis and leishmaniasis. Curr Top Med Chem 11(16):2060–2071
Froger A, Hall JE (2007) Transformation of plasmid DNA into E. coli using the heat shock method. J Vis Exp (6):253. https://doi.org/10.3791/253
Pace CN, Vajdos F, Fee L, Grimsley G, Gray T (1995) How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci 4(11):2411–2423. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.5560041120
Lepesheva GI, Nes WD, Zhou W, Hill GC, Waterman MR (2004) CYP51 from Trypanosoma brucei is obtusifoliol-specific. Biochemistry 43(33):10789–10799. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi048967t
Lepesheva GI, Strushkevich NV, Usanov SA (1999) Conformational dynamics and molecular interaction reactions of recombinant cytochrome p450scc (CYP11A1) detected by fluorescence energy transfer. Biochim et Biophys Acta 1434(1):31–43
Bellamine A, Mangla AT, Nes WD, Waterman MR (1999) Characterization and catalytic properties of the sterol 14alpha-demethylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(16):8937–8942
Vincze T, Posfai J, Roberts RJ (2003) NEBcutter: a program to cleave DNA with restriction enzymes. Nucl Acids Res 31(13):3688–3691
Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G (1999) Machine learning approaches for the prediction of signal peptides and other protein sorting signals. Protein Eng 12(1):3–9
Sonnhammer EL, von Heijne G, Krogh A (1998) A hidden Markov model for predicting transmembrane helices in protein sequences. Proceedings / International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology; ISMB International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology, vol 6, pp 175–182
Chen CK, Leung SS, Guilbert C, Jacobson MP, McKerrow JH, Podust LM (2010) Structural characterization of CYP51 from Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei bound to the antifungal drugs posaconazole and fluconazole. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4(4):e651. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000651
Sorensen HP, Mortensen KK (2005) Advanced genetic strategies for recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 115(2):113–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.08.004
Rosano GL, Ceccarelli EA (2014) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Front Microbiol 5:172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00172
Lepesheva GI, Waterman MR (2007) Sterol 14alpha-demethylase cytochrome P450 (CYP51), a P450 in all biological kingdoms. Biochim et Biophys Acta 1770(3):467–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2006.07.018
Urbina JA, Lazardi K, Aguirre T, Piras MM, Piras R (1988) Antiproliferative synergism of the allylamine SF 86–327 and ketoconazole on epimastigotes and amastigotes of Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) cruzi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 32(8):1237–1242
Urbina JA, Lira R, Visbal G, Bartroli J (2000) In vitro antiproliferative effects and mechanism of action of the new triazole derivative UR-9825 against the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) cruzi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44(9):2498–2502
Zhao L, Liu D, Zhang Q, Zhang S, Wan J, Xiao W (2007) Expression and homology modeling of sterol 14alpha-demethylase from Penicillium digitatum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 277(1):37–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00929.x
Ichinose H, Wariishi H (2013) High-level heterologous expression of fungal cytochrome P450s in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 438(2):289–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.057
Looman AC, Bodlaender J, Comstock LJ, Eaton D, Jhurani P, de Boer HA, van Knippenberg PH (1987) Influence of the codon following the AUG initiation codon on the expression of a modified lacZ gene in Escherichia coli. EMBO J 6(8):2489–2492
Barnes HJ (1996) Maximizing expression of eukaryotic cytochrome P450s in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol 272:3–14
Bivona L, Zou Z, Stutzman N, Sun PD (2010) Influence of the second amino acid on recombinant protein expression. Protein Expr Purif 74(2):248–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2010.06.005
Lepesheva GI, Zaitseva NG, Nes WD, Zhou W, Arase M, Liu J, Hill GC, Waterman MR (2006) CYP51 from Trypanosoma cruzi: a phyla-specific residue in the B’ helix defines substrate preferences of sterol 14alpha-demethylase. J Biol Chem 281(6):3577–3585. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M510317200
Müller-Hill B, Crapo L, Gilbert W (1968) Mutants that make more lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 59(4):1259–1264
Schenkman JB, Jansson I (2006) Spectral analyses of cytochromes P450. Methods Mol Biol 320:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-998-2:11
Lepesheva GI, Hargrove TY, Anderson S, Kleshchenko Y, Furtak V, Wawrzak Z, Villalta F, Waterman MR (2010) Structural insights into inhibition of sterol 14alpha-demethylase in the human pathogen Trypanosoma cruzi. J Biol Chem 285(33):25582–25590. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.133215
Funding
Funding was provided by fapesb (Grant No. PNE009/2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freitas, H.F., Leal Pires, A.B. & Castilho, M.S. Cloning, expression, purification and spectrophotometric analysis of lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase from Leishmania braziliensis (LbCYP51). Mol Biol Rep 45, 175–183 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4150-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4150-7